An ultrasonic Based Path Finder Robot with Metal Detection Capability Rahul Agrawal
advertisement
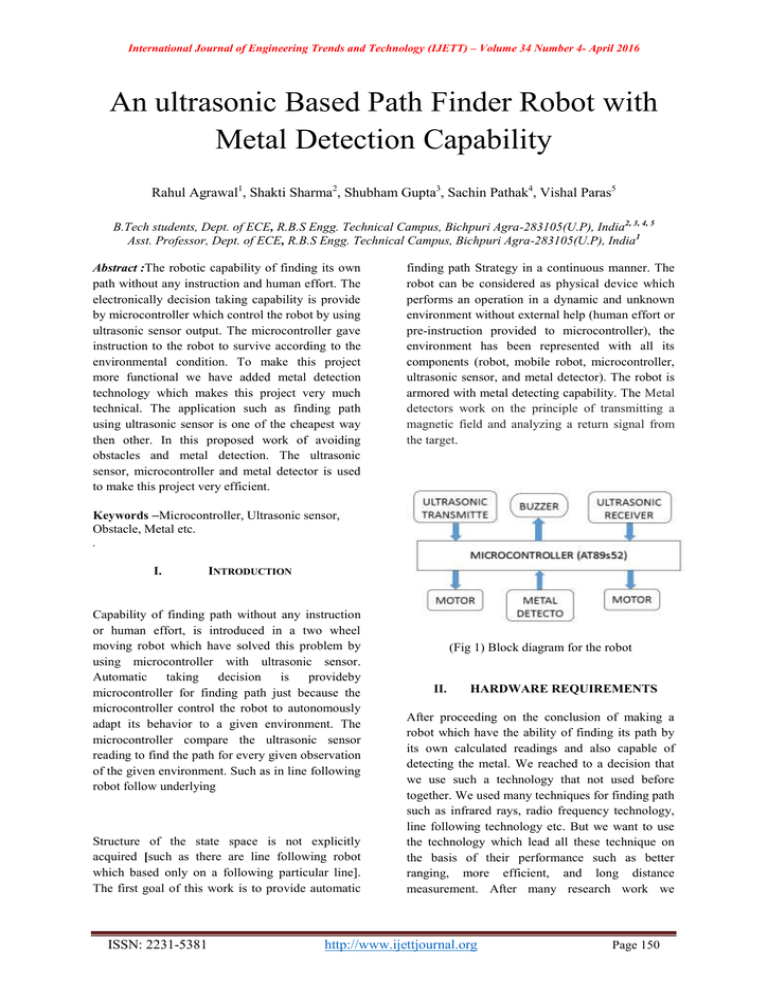
International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT) – Volume 34 Number 4- April 2016 An ultrasonic Based Path Finder Robot with Metal Detection Capability Rahul Agrawal1, Shakti Sharma2, Shubham Gupta3, Sachin Pathak4, Vishal Paras5 B.Tech students, Dept. of ECE, R.B.S Engg. Technical Campus, Bichpuri Agra-283105(U.P), India2, 3, 4, 5 Asst. Professor, Dept. of ECE, R.B.S Engg. Technical Campus, Bichpuri Agra-283105(U.P), India1 Abstract :The robotic capability of finding its own path without any instruction and human effort. The electronically decision taking capability is provide by microcontroller which control the robot by using ultrasonic sensor output. The microcontroller gave instruction to the robot to survive according to the environmental condition. To make this project more functional we have added metal detection technology which makes this project very much technical. The application such as finding path using ultrasonic sensor is one of the cheapest way then other. In this proposed work of avoiding obstacles and metal detection. The ultrasonic sensor, microcontroller and metal detector is used to make this project very efficient. finding path Strategy in a continuous manner. The robot can be considered as physical device which performs an operation in a dynamic and unknown environment without external help (human effort or pre-instruction provided to microcontroller), the environment has been represented with all its components (robot, mobile robot, microcontroller, ultrasonic sensor, and metal detector). The robot is armored with metal detecting capability. The Metal detectors work on the principle of transmitting a magnetic field and analyzing a return signal from the target. Keywords –Microcontroller, Ultrasonic sensor, Obstacle, Metal etc. . I. INTRODUCTION Capability of finding path without any instruction or human effort, is introduced in a two wheel moving robot which have solved this problem by using microcontroller with ultrasonic sensor. Automatic taking decision is provideby microcontroller for finding path just because the microcontroller control the robot to autonomously adapt its behavior to a given environment. The microcontroller compare the ultrasonic sensor reading to find the path for every given observation of the given environment. Such as in line following robot follow underlying Structure of the state space is not explicitly acquired [such as there are line following robot which based only on a following particular line]. The first goal of this work is to provide automatic ISSN: 2231-5381 (Fig 1) Block diagram for the robot II. HARDWARE REQUIREMENTS After proceeding on the conclusion of making a robot which have the ability of finding its path by its own calculated readings and also capable of detecting the metal. We reached to a decision that we use such a technology that not used before together. We used many techniques for finding path such as infrared rays, radio frequency technology, line following technology etc. But we want to use the technology which lead all these technique on the basis of their performance such as better ranging, more efficient, and long distance measurement. After many research work we http://www.ijettjournal.org Page 150 International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT) – Volume 34 Number 4- April 2016 decided to go through the ultrasonic sensor for finding path. But there is a problem that ultrasonic sensor is only a sensor use to sense the obstacle. There is need to controlling the ultrasonic sensor. So to solve this problem we used microcontroller. In market there are number of microcontroller (8051, Arduino etc.). Another sophisticated is added to the moving robot feature that is detection of metal. The metal detection technology make the moving the robot so much technological that is a single robot which can also called as equipped with technology. 1. 2. WORKING PRINCIPLE FOR ROBOT For the robot movement we use ultrasonic sensor as path finder. The ultrasonic transmitter transmit the ultrasonic waves with frequency of 40 KHZ. This frequency is generated by the microcontroller. The range of transmitted wave is between 2 cm to 4 meter. The ultrasonic sensor HC-SR04 operated at 15mA current and DC 5 volt. For movement of the robot let see different cases: START UP WITH POWER SUPPLY SOURCE In this project we use power supply of 9V. The provided power supply not have constant voltage so to maintain or make power supply constant we use capacitor to make the supply exactly 9V. As we know the microcontroller does not work on 9V supply it work on 5V supply so we uses regulator (7805) which make 9V power supply to 5V supply on which microcontroller work.In this project microcontroller AT89s52 is used. The AT89C51 is a low-power, high-performance CMOS 8-bit microcomputer with 4K bytes of Flash Programmable and Erasable Read Only Memory (PEROM). The device is manufactured using Atmel’s high density nonvolatile memory technology. The on-chip Flash allows the program memory to be reprogrammed in-system or by a conventional nonvolatile memory programmer. By combining a versatile 8-bit CPU with Flash on a monolithic chip, the Atmel AT89C51 is a powerful microcomputer which provides a highly flexible and cost effective solution to many embedded control applications. The AT89C51 provides the following standard features: 4K bytes of Flash, 128 bytes of RAM, 32 I/O lines, two 16-bit timer/counters, five vector two-level interrupt architecture, a full duplex serial port, and on-chip oscillator and clock circuitry.In addition, the AT89C51 is designed with static logic for operation down to zero frequency and supports two software selectable power saving modes. The Idle Mode stops the CPU while allowing the RAM, timer/counters, serial port and interrupt system to continue functioning. The Power down Mode saves the RAM contents but freezes the oscillator disabling all other chip functions until the next hardware reset. ISSN: 2231-5381 (Fig 2) An ultrasonic based path finder robot with metal detection capability The case determine that robot move forward:Ultrasonic transmitter transmit the ultrasonic wave with frequency 40MHZ if there is no object found in between the path of waves then no waves reflect back from the object. Due to which ultrasonic receiver does not get any reading from reflected wave. Because of that receiver can’t be able to send signal to the microcontroller and microcontroller can’t be able to send any signal to the photo-transistor presented in opto coupler due to which both the transistor get ON (NPN and PNP) which resultant Cause clockwise movement to the motor and robot start moving in forward direction. http://www.ijettjournal.org Page 151 International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT) – Volume 34 Number 4- April 2016 (Fig 3) Flow diagram shows robot move forward The case determine that robot turns left at an angle of 0 to 90 degree: In this case ultrasonic transistor transmit the ultrasonic wave at same frequency if there is present any object in between the path of the waves the wave will reflect back by the object and this reflected wave received by the ultrasonic receiver. Ultrasonic receiver transmit the signal to the microcontroller that object is detected due to which microcontroller send negative pulse to the opto coupler. And opto coupler which control left motor in forward direction get turn OFF which resultant cause left turn. ISSN: 2231-5381 (Fig 4) Flow diagram shows robot turn left 3. WORKING PRINCIPLE FOR METAL DETECTOR Here is the pair of NPN and PNP transistors, variable register and a comparator LM 339. When the metal detector sensor is activated by the 5V power supply the transmitter start generating the electromagnetic field and transmit it if there metal is present the EMF react with metal and start generating induced current. This induced current is measured by the variable register for the generated voltage. This generated voltages is now compared by the comparator. Now the threshold voltage value for comparator is set to max. 5V and min. 2.5V now different condition. If generated voltage is 5V then it compare by the comparator. Because of 5V output of variable register the comparator output turn ON the PNP transistor which output turn on NPN transistor which gave negative output to the buzzer. The circuit have positive and negative signal both due to which buzzer get ON. The max. Range metal detector can detect the metal is 6 cm to 8 cm. http://www.ijettjournal.org Page 152 International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT) – Volume 34 Number 4- April 2016 Maximum threshold voltage Comment If metal is present then variable register gave around 5V output. 6. Buzzer beep Buzzer beep get ON 5V If metal is not present then variable register gave less than 2.5V output. Buzzer remain OFF 5V (Table 1)Describe metal detection process III. "Optimal path algorithms for autonomous vehicles," in Proc. 18th CIRP Manufacturing Systems Seminar, June 1986, Stuttgart, Germany. 7. Amy J. Briggs, Daniel Scharstein, Darius Braziunas, Cristian Dima, and Peter Wall. “Mobile Robot Navigation Using Self-Similar Landmark.” IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Pages 14281434, 2000. 8. Huosheng Hu and Dongbing GU. “Landmark-based Navigation of Industrial Mobile Robots.” International Journal of Industry Robot, Vol. 27, No. 6, pages 458 – 467. 2000. 9. Martin Samuelsson. “Artificial Landmark Navigation of an autonomous Robot.” Thesis work 20 credit D-level, Alcal´a de Henares, and Spain. Reg.code: Oru-Te-EXA37Mag109/05 rev. 3, 2005. 10. Y. Jang, S. Shin, J. W. Lee, and S. Kim, “A preliminary study for portable walking distance measurement system using ultrasonic sensors,” Proceedings of the 29th Annual IEEE International Conference of the EMBS, France, Aug. 2007, pp. 5290-5293. 11. Wail Gueaieb, and Md. Suruz Miah. “An Intelligent Mobile Robot Navigation Technique Using RFID Technology.” IEEE Transaction on Instrumentation and Measurement, Vol. 57, No.9, September 2008. 12. H. He, and J. Liu, “The design of ultrasonic distance measurement system based on S3C2410,” Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation, Oct. 2008, pp. 44-47. CONCLUSION The paper express the obstacle avoidance procedure introduced in the robot. Since the procedure heavily depends on the performance of the ultrasonic sensor and metal detector, these sensors and the effect of their working on the obstacle avoidance and metal detection procedure were discussed above. And we conclude that we can use the microcontroller for controlling the ultrasonic sensor and metal detector circuit. And ultrasonic sensor is the efficient way of finding path. And a metal detector which can be used for detecting metal. But the range for metal detecting is not very efficient and the range varies from 4 cm to 7 cm with this technological platform. IV. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. REFERENCES T. Lozano-Perez, "Automatic planning of manipulator transfer movements, "IEEE Trans. Syst., Man., Cybern., vol. SMC-11, pp. 681- 698, Oct. 1981. R. A. Brooks, "Solving the find-path problem by good representation of free space," in Proc. Nat. Conf. Artificial Intelligence, AAA/-82, Aug. 1982, pp. 381-386. D. M. Keirsey et at., "Algorithm of navigation for a mobile robot," in Proc. 1st Int. Conf. Robotics, Atlanta, GA, Mar. 1984, pp. 574-583. "Navigation for an intelligent mobile robot," CarnegieMellon University, The Robotics Institute, Pittsburgh, PA, Tech. Rep., Aug. 1984. C. Jorgensen, W. Halnel, and C. Weisbin, "Autonomous robot navigation," BYTE, pp. 223-235, Jan. 1986. ISSN: 2231-5381 http://www.ijettjournal.org Page 153