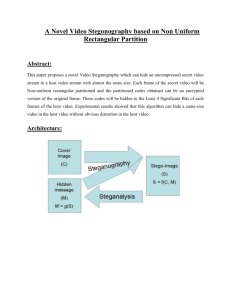
Intensity Based Substitution Technique using Images as Cover

International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT) – Volume 22 Number 2- April 2015
Intensity Based Substitution Technique using
Images as Cover
1
Renu Singla,
2
Mitali
1
Asst. Prof (CSE) ,Shri Ram College of Engg.,Palwal, India
2
M.Tech(CSE),Shri Ram College of Engg.,Palwal, India
2
Mitaliaggarwal90@gmail.com
Abstract:
In this paper, various image steganography techniques are analyzed for their merits and de-merits.
Even little distortion induced in an image may be noticeable if the color of pixel lies in the range to which human eye is highly sensitive. The paper motivates to intensity based substitution technique instead of traditional LSB technique.
Keywords : image, intensity, color, substitution.
I.
I NTRODUCTION
The increasing rate of usage of internet and the revolution that occurred in digitization of information; the overall structure of modern communication is changed. The revolution in software industry and semiconductor industry made it feasible that hardware as well as software are more user-friendly and flexible and enables consumers to communicate multimedia data.
Peoples are now able to transmit large multimedia files through broadband connection. Moreover, the transmission thus done is almost errorless [2]. Security of data to transmit is of high concern in today’s communication system. Data hiding is a technique of providing data security.
Steganography is the art and science of hiding information such that its presence cannot be detected[1].
The secret information is hidden in some carrier file and then transmitted. The carrier file can be an image, Audio file, text file, video file, etc.
On the basis of cover file used for embedding, the steganography techniques are divided into different categories. The focus will be on using image as cover file in this paper.
II.
R ELATED W ORK
Steganography is an art and science of hiding information in some cover media. The term originated from Greek roots literally means ‘covered writing’ [61].
Steganography can also be achieved by embedding secret data in an unsuspecting medium like image, video or audio, in such a way that the human-perceived quality of the unsuspecting medium is not altered [62]. The idea was first described by Simmons in 1983 [63]. More comprehension theory of steganography is given by
Anderson [64]. Steganography is different from
Cryptography which is about concealing the content of the message whereas steganography is about concealing the existence of the message itself [65]. Images provide excellent carriers for hidden information and many different techniques have been introduced [66]..
The popular and oldest method for hiding the message in a digital image is the LSB method[67]. In LSB method we hide the message in the least significant bits (LSB’s) of pixel values of an image. In this method binary equivalent of the secret message is distributed among the
LSBs of each pixel.
The problems with this technique is that it is very vulnerable to attacks such as image compression and quantization of noise.
ISSN: 2231-5381 http://www.ijettjournal.org
Page 44
International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT) – Volume 22 Number 2- April 2015
Advantages of LSB
1.
100 % chances of insertion.
2.
Easy to implement
Disadvantage of LSB
1.
One of the major disadvantage associated with
LSB method is that intruder can change the least significant bit of all the image pixels. In this way hidden message will be destroyed by changing the image quality, a little bit, i.e. in the range of +1 or -1 at each pixel position.
2.
Not immune to noise and compression technique.
3.
One of the basic techniques so more vulnerable to steganalysis.
Parvinder et al [68] obtained an algorithm to hide the message in 6 th
and 7 th
bit of pixel value.Here instead of
LSB bits 6 th
and 7 th
bit of pixel values are used to hide the secret data within an image. This novel proposed method overcomes the all disadvantages of LSB insertion method .However it has its own disadvantage ,that is the chance that the message bit will be inserted at pseudorandom location at first instance is less as compared to LSB.
Advantages
1.
49% chances,that when message bit is inserted, no change in pixel value is required.
2.
12.5% chances,that change in pixel value is required,when it is ignoring the location.
Disadvantages
1.
Not optimal chances of insertion.
2.
If intruder change LSB ,secret data may b effected.
3.
Not immune to compression and noise.
Gray level modification Steganography [69] is a technique to map data (not embed or hide it) by modifying the gray level values of the image pixels.
ISSN: 2231-5381 http://www.ijettjournal.org
GLM Steganography uses the concept of odd and even numbers to map data within an image. It is a one-to-one mapping between the binary data and the selected pixels in an image. From a given image a set of pixels are selected based on a mathematical function. The gray level values of those pixels are examined and compared with the bit stream that is to be mapped in the image.
Advantages of GLM
1.
Chances of insertion of data are optimal
2.
Easy to implement
Disadvantage of GLM
1.
Vulnerable to staganalysis
2.
Not immune to noise and compression.
III.
S UBSTITUTION T ECHNIQUE OF S TEGANOGRAPHY
Initially steganographic systems were developed for digital images and video.
The substitution technique is based on the idea that if a single bit or a few bits in each image pixel are replaced with the message bits then the change thus occurred will not be noticeable to the human eye (type of file matters). The capacity of this method is very high
(41,000 bps). The robustness of this method is very low.
This method is however easy to implement but susceptible to various attacks.
The prime reason for choosing this technique lies in the advantage of using substitution technique which is a very high capacity for hiding a message. When only single LSB replacement is done per host audio sample a capacity of 44.1 kbps can be achieved. However there are certain other techniques like spread spectrum (4 bps) having lesser capacity but they are more robust.
[10].
IV.
M OTIVATION AND P ROBLEM S TATEMENT
Steganography is a technique of sending secret messages by hiding in a carrier such that the existence of the message is concealed. Only the intended recipient is aware of the existence of the message. If any other is aware of the existence of the message in carrier then the purpose of Steganography is revealed.
Page 45
International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT) – Volume 22 Number 2- April 2015
LSB method of Steganography is very simple and easy to implement. But at the same side it is easy to detect also.
A person can get the LSB’s of each pixel an analyze them whether it gives some meaningful message or not.
Moreover the replacement of LSB of the pixel with the message bits will produce a little change in image. This change may be observable with the human eyes if the pixel is of greenish-yellow color as human eye is most sensitive to this color.
Among the eyes of Nature, the human eye is designed to distinguish colors. Cats eyes, for example are much better at detecting movement, the condor can see "death", and the dog can "read" our faces better than human can. But for colors, human seem to have the leading specimen eye.
And among the colors, which ones do our eyes seem most keen to observe? The 400 to 700 nm range of wavelengths is called "visible" because those are the wavelengths to which our eyes are sensitive. That range reflects the wavelengths of sunlight which reach the
Earth's surface with sufficient intensity to excite the cells on our retina. The physical process of seeing begins with the absorption of a photon by a pigment called "retinal"
[5].
From Fig4.1, it is clear that human eye is most sensitive to green color and more than 70% sensitive to greenish yellow color. Thus a slight change in the pixel of intensity lying between 520nm-600nm may be observable to the human eye.
V.
C ONCLUSION
However the replacement of LSB of the pixel with the message bits will produce a little change in image. This change may be observable with the human eyes if the pixel is of greenish-yellow color as human eye is most sensitive to this color. Using only those pixels to hide information to which our eye is less sensitive can be a better approach so that the change occurred after LSB insertion should not be observable by human eye.
R EFRENCES
[1].
Rohit Tanwar, Sunil Kumar, Narender Gautam, Ravinder
Gautam,”
A Spatial Domain Steganography Technique
Based on Optimal Solution Using Genetic Algorithm”,
January 2013,Page(s):228-232.ISBN:978-93-81583-82-1
[2].
Gunjan Nehru, Puja Dhar,”A detailed look of audio steganographic techniques using LSB and Genetic Algrithm approach”, IJCSI Vol.9, Issue1, No.2, January 2012
ISSN(online): 1694-0814.
[3].
Westfeld, Andrew. F5-a steganographic algorithm: high capacity despite better steganalysis. In Proceedings of the
4th Information Hiding Workshop, volume 2137 of
LNCS, pages 289{302. Springer, 2001.
[4].
Fridrich, J., Feature-based steganalysis for jpeg images and its implications for future design of steganographic schemes. In Proceedings of the 6th Information Hiding
Workshop, volume 3200 of LNCS, pages 67{81. Springer,
2004.
[5].
Yu, Lifang., Zhao, Yao., Ni, Rongrong., and Shi, Yun Q. A high-performance yass-like scheme using randomized bigblocks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International
Conference on Multimidea & Expo (ICME 2010), 2010.
[6].
Huang, Fangjun., Huang, Jiwu., and Shi, Yun Qing. An experimental study on the security performance of yass.
IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security,
5(3):374 { 380, 2010
[7].
Sallee, P.. Model-based steganography . In Proceedings of the 2nd Internation Workshop on Digital Watermarking , volume 2939 of LNCS , pages 154{167. Springer, 2003.
ISSN: 2231-5381 http://www.ijettjournal.org
Page 46
International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT) – Volume 22 Number 2- April 2015
[8].
Al-Ataby, Ali., Al-Naima, Fawzi. A modified high capacity image steganography technique based on wavelet transform.
The International Arab Journal of Information Technology,
7:358–364, 2010.
[9].
Westfeld, A., Ptzmann, A. Attacks on steganographic systems - breaking the steganographic utilities ezstego, jsteg, steganos, and s-tools-and some lessons learned. In
Proceedings of the 3rd Information Hiding Workshop, volume 1768 of LNCS, pages 61{76. Springer, 1999.
[10].
Fridrich, Jessica., Goljan, Miroslav., and Du, Rui. Reliable detection of lsb steganography in color and grayscale images. In Proceedings of 2001 ACM workshop on
Multimedia and security: new challenges, pages 27{30.
ACM Press, 2001.
[11].
Dumitrescu, S., Wu, X. L., and Wang, Z. Detection of lsb steganography via sample pair analysis. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 51(7):1995{2007, 2003.
[12].
Fridrich, J., Goljan, M. On estimation of secret message length in lsb steganography in spatial domain. In
IS&T/SPIE Electronic Imaging: Security, Steganography, and Watermarking of Multimedia Contents VI, volume
5306, pages 23{34. SPIE, 2004.
[13].
Ker, A.D. Fourth-order structural steganalysis and analysis of cover assumptions. In IS&T/SPIE Electronic Imaging:
Security, Steganography, and Watermarking of
Multimedia Contents VIII, volume 6072, pages 1{14.
SPIE, 2006.
[14].
Harmsen, J., Pearlman, W. Steganalysis of additive noise modelable information hiding. In IS&T/SPIE Electronic
Imaging: Security, Steganography, and Watermarking of
Multimedia Contents V, volume 5020, pages 131{142.
SPIE, 2003.
[15].
Huang, Jinggang., Mumford, David. Statistics of natural images and models. In Proceedings of IEEE Computer
Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition, volume 1, pages 541{547, 1999.
ISSN: 2231-5381 http://www.ijettjournal.org