PH113 Physics III Name _________________________ Test IV
advertisement

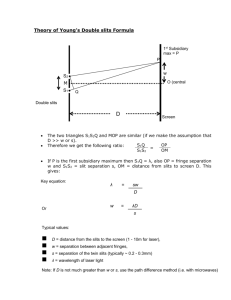
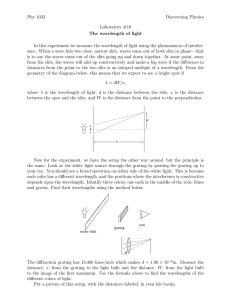
PH113 Physics III Test IV Spring 1996/97 Name _________________________ (Please print in UPPER CASE BLOCK letters) Section (hour) __________________ No books or paper notes are allowed. A one page formula sheet is attached as the last page of this test. It may be removed and need not be handed in. You may use your laptop and any resources residing on your hard drive. This includes Maple and Working Model. No network connections are allowed. Any student with a physical connection between the computer and the network outlet during the test will receive a zero on the test. Show all your work. No credit will be given for answers appearing without supporting calculations. Partial credit may be awarded based on clarity and completeness of solution. 1. A laser beam with wavelength 633 nm is incident normally on two identical, closely-spaced slits. The resulting interference pattern falls on a screen 2.50 m in front of the slits. A photograph of the pattern is shown below along with a millimeter scale. (a) Calculate the distance between the slits. (b) Calculate the width of each individual slit. PH113 Physics III Test IV Spring 1996/97 Name _________________________ (Please print in UPPER CASE BLOCK letters) 2. The photos at the right show interference patterns from five different pairs of double slits. (Each pattern is pictured at three different exposures (short, medium, and long), so that details in the central maximum and details on the fainter “wings” can both be observed.) In all of the photographs the wavelength of light was 633 nm, and the film was 2.50 m from the double slit. Circle the correct response in (a) and (b). (a) In the sequence of five sets of photos, the width of the slits used (i) increases from top to bottom (ii) decreases from top to bottom (iii) is the same from all five pairs of slits (b) In the sequence of five sets of photos, the distance between slits (i) increases from top to bottom (ii) decreases from top to bottom (iii) is the same from all five pairs of slits Now consider a set of four diffraction patterns as shown below. Each pattern is formed by shining a HeNe laser through a set of slits as done in class. For each pattern the distance between the slits and the screen is identical. The dark marks in the figure represent the red “dots” seen in the classroom demonstrations. (c) For which of the patterns A through D are the slits the greatest distance apart? (d) For which pattern A through D is the number of slits illuminated the greatest? PH113 Physics III Test IV Spring 1996/97 Name _________________________ (Please print in UPPER CASE BLOCK letters) 3. At the right is a photograph of a soap film as viewed in reflected green light of wavelength 555 nm. Gravity causes the soap film to gradually increase in thickness from top to bottom. Assume the index of refraction of the soap film is n = 1.40 (a) At the top of the film, no light is reflected. (The film is present! It just doesn’t reflect light) Explain why no light is reflected. Use a diagram to aid you explanation. Say what you can about the thickness of the soap film. (b) Farther down where the film is thicker is a horizontal band where once again no light is reflected. Explain why this band occurs. Use a diagram to aid your explanation. Calculate the thickness of the film in this band. PH113 Physics III Test IV Spring 1996/97 Page 4 of 4 Name _________________________ (Please print in UPPER CASE BLOCK letters) 4. Light of wavelength 555 nm is emitted from a point source located 100. m from a circular aperture of diameter 2.00 mm. Behind the aperture is a lens of focal length 2.20 cm. In the focal plane of the lens is a screen. The image on the screen of the distant point is blurred by diffraction. (a) Calculate the diameter of the central bright spot of the pattern formed on the screen. (This diameter is defined as twice the distance from the center of the pattern to the first zero in the diffraction pattern.) (b) If the diameter of the aperture is increased to 6.00 mm, what happens to the diameter of the central diffraction bright spot? (A qualitative answer is all that is required.)