Essentials of Heterocyclic Chemistry-III Heterocyclic Chemistry Baran, Hafensteiner, Richter Indazoles:
advertisement
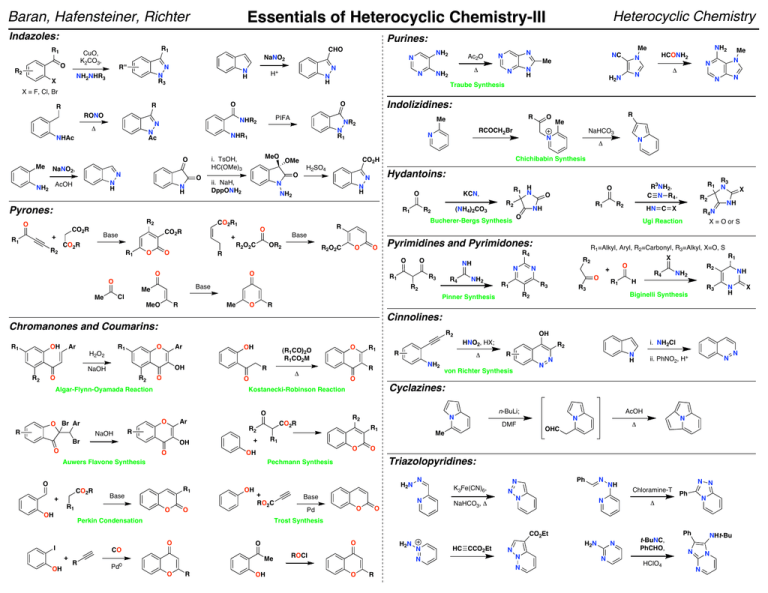
Indazoles: Purines: R1 R1 CuO, K2CO3, O R2 Heterocyclic Chemistry Essentials of Heterocyclic Chemistry-III Baran, Hafensteiner, Richter NaNO2 R'' N N R3 NH2NHR3 X CHO N H NH2 N N H+ N N H Ac2O Δ NH2 NC Me N H N NH2 Me N N Me N N Δ N H2 N Traube Synthesis HCONH2 N N N X = F, Cl, Br RONO N Ac NHAc NaNO2, N O N H AcOH NH2 N R1 MeO i. TsOH, HC(OMe)3 N H O R1 O CO2R R2 CO2R Base + R1 CO2R1 R2O2C R1 O O OR2 R2O2C R O O R1 Base Me R1 H2O2 R Me Ar OH (R1CO)2O R1CO2M R O Ar R OH OH O R1 Base O O OH OH N H X + RO2C i. NH2Cl N N H N n-BuLi; ii. PhNO2, H+ N DMF Me AcOH N N Δ OHC O Triazolopyridines: Base N K3Fe(CN)6, N O Pd O NaHCO3, Δ Ph N N N N NH N N N Chloramine-T Ph N Δ Ph CO2Et O O CO R NH Trost Synthesis O + R3 Biginelli Synthesis R2 R von Richter Synthesis N H2N Perkin Condensation I NH2 H Cyclazines: Pechmann Synthesis O Δ NH2 R1 OH O R1 R4 R2 OH R R1 + Auwers Flavone Synthesis + R1 R2 CO2R R2 Br CO2R O O O O O Kostanecki-Robinson Reaction O NaOH R1 R3 R2 R1 X O R3 HNO2, HX; R Δ O Algar-Flynn-Oyamada Reaction R X = O or S R O OH O Br Ar R4N R1=Alkyl, Aryl, R2=Carbonyl, R3=Alkyl, X=O, S R2 N R1 R2 NaOH R2 HN C X X NH Cinnolines: O O R2 NH2 R2 Chromanones and Coumarins: Ar R4 N Pinner Synthesis MeO OH R3 Cl Me R1 NH R2 Ugi Reaction R4 O R2 O + O O R1 NH R R1 N3 R3NH2, C N R4 , O O Pyrimidines and Pyrimidones: O O R2 Bucherer-Bergs Synthesis Base + CO2R (NH4)2CO3 R2 R O R1 H N KCN, O Pyrones: R2 N Δ Chichibabin Synthesis N H NH2 NaHCO3 Hydantoins: N N R Me N CO2H OMe O RCOCH2Br N H2SO4 ii. NaH, DppONH2 R Me NR2 NHR1 O Me PIFA NHR2 N Δ Indolizidines: O O R R Me H2N ROCl N N Pd0 HC CCO2Et N N N O R OH O R N H2N N t-BuNC, PhCHO, HClO4 NHt-Bu N N N N Essentials of Heterocyclic Chemistry-III Baran, Hafensteiner, Richter Useful Methods of Forming Aryl C–N and C–O Bonds: Useful Methods of Forming Aryl C–N and C–O Bonds: FeCl2 ArMgCl + Ar'NO2 "Pd Source" ArNHAr' NaBH4 + ArX J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 9390 RYHZ X = I, Br, Cl Y = N, O, S Z = C, H Electron-donating and electron-withdrawing functional groups are tolerated on both coupling partners. "Cu Source" ArB(OH)2 + RYH Y = NH, O, S Heterocyclic Chemistry ArYR Base Applicable to a wide variety of nucleophilic partners, including phenols, amines, anilines, amides, imides, ureas, carbamates, sulfonamides, thiols, and thiophenols. Can use a variety of heterocycles, including imidazoles, pyrazoles, triazoles, tetrazoles, benzimidazoles, and indazoles. Even styryl boronic acids are tolerated in the reaction. α-Amino esters can be arylated in good yields and purines have been shown to react selectively at N-9. Catalytic reactions can be performed and a wide variety of copper sources, ligands, and bases can be used. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 2933 Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 2937 Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 2941 Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 2019 Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 3415 Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 1691 Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 3359 ArYRZ Base Applicable to a wide variety of nucleophilic partners, including amines, amides, silyloxides, sulfonamides, anilines, carbamates, ureas, alkoxides, vinylogous amides, phenoxides, cyclopropylamines, tert-butylcarbamates, sulfoximes, hydrazines, hydrazones, and imines. Various heterocycles can be N-arylated including indole, pyrrole, imidazole, carbazole, benzotriazole, and phenoxazole. A variety of aryl donors are tolerated, including electronrich, electron-poor, hindered, unhindered, and heterocyclic. A tropone has even been aminated using this procedure. Five and six (not seven) membered heterocycles can routinely be formed via intramolecular cyclizations. "Cu source" ArB(OH)2 + PhthNOH Pyr, DCE ArONPhth Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 139 A wide variety of boronic acids are tolerated and hydrazinolysis reveals the O-arylhydroxylamine. Requires two equivalents of the boronic acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 10539 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 12459 + ArX RYHZ ArYRZ Base Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 2657 X = I, Br, Cl Y = N, O, S J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 670 Z = C, H Tetrahedron Lett. 2000, 41, 1283 Applicable to a wide variety of nucleophilic partners, including anilines, phenols, thiophenols, Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 4791 aliphatic alcohols, thiols, amines, amino alcohols, amino acids, amino esters, guanidines, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 7727 amides, diamines, hydrazones, carbazoles, imidazoles, indoles, acylhydrazides, pyrroles, Synlett. 2002, 231 pyrazoles, benzimidazoles, indazoles, azaindoles, and carbamates. The aryl ring can be a Synlett. 2002, 427 wide variety of heterocycles and the reaction tolerates a wide range of substituents, including Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 581 electron-donating and electron-withdrawing groups. Inter- and intramolecular reactions are both possible. Unprotected functionality of all sorts is tolerated. Various ring sizes can be Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 973 formed/are tolerated in the reaction. A wide variety of copper sources and oxidation states work Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 3517 in the reaction. A variety of bases and ligands can be used and the reaction can even be run Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 3703 with catalytic copper loadings. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 7421 J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 5164.Tetrahedron, 2005, 61, 6553. Synlett, 2006,18, 3105. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 11684 Tetrahedron, 2006, 62, 4435. Tetrahedron, 2006, 62, 4756. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 2737. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 793 Tetrahedron Letters, 2007, 48, 6573. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 934. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 133 J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 3863. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 643. Tetrahedron Letters, 2007, 48, 7199. "Cu Source" ArSnR3 YNHZ Z = C, H ArNYZ Base Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 3091 Applicable to a wide variety of aryl stannanes. Nucleophilic partners include amines, anilines, indazoles, benzimiazolones, pyridones, and aryl amides. ArX Ni(0) + NaOR X = Cl, Br J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 5413 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 199, 6054 ArOR R = alkyl Various nucleophilic parters can be used, specifically alkoxides, silyloxides, anilines, and amines. A variety of electron-withdrawing and electron-donating groups are tolerated on the aromatic ring. R + F M M = Cr(CO)3 FeCpPF6 RuCpPF6 i. Base HN X R N ii. Demetalate X = NH, CH2 X Tetrahedron Lett. 1993, 34, 1395 J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 6581 Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 8487 Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 5123 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 6488 For chromium: will tolerate electron-donating groups on the aromatic ring and a variety (lack of) protecting groups on the piperazine. For iron: a range of amine nucleophiles can be used and some susbstitution on the aromatic ring is tolerable. R R + Br R'NH2 + X = Cl, O2CR' RYHZ Tetrahedron Lett. 1986, 27, 3615 Synthesis. 1994, 775 Tetrahedron. 1997, 53, 4137 Tetrahedron. 1999, 55, 1341 ArYRZ Y = N, O Z = C, H Can use with various substituted aryl groups, however phenyl is the most common. The nucleophilic partner can be an amide, aniline, alcohol, phenol, amine, or hydrazone. EWG EWG + Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 7343 J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1. 1997, 2229 J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 3874 Base R2NH NR2 F Various amines and electron-withdrawing groups can be used. R' R' + Base R2NH J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 5101 OMe NR2 A variety of amines can undergo the displacement. Electron-withdrawing groups are not required on the aromatic ring. "Cu Source" + Cu(II) Ar3BiX2 Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 3609 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1995, 34, 1348 J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 1133 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 7215, 7217 J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 7240 Tetrahedron 1996, 52, 7525 J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 1264, 1268 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 3395 J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 5413 Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 6367 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 827 Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 5731 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 9722 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 3224 Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 3543 J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 5575 Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 219 Tetrahedron. 2001, 57, 2953 Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 4381 Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 1109 Base J. Org. Chem. 1987, 52, 2619 NHR' Ammonia, primary, and secondary amines can be used. Gives regioisomeric product mixtures if unsymmetrical. R' R' + OMe TMSX X = N3, OAc, SCN, SPh X PIFA OMe Tetrahedron Lett. 1991, 32, 4321 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 3684 Synlett. 1995, 211 J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 7144 Pure Appl. Chem. 1996, 68, 627 A variety of substitution can be tolerated on the aromatic ring. R can be either alkyl or methoxy. The reaction has even been performed in the absence of methoxy group. For Reviews on the Subject See: 1. Ley, S. V.; Thomas, A. W. "Modern Synthetic Methods for Copper-Mediated C(aryl)–O, C(aryl)–N, and C(aryl)–S Bond Formation" Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 5400 – 5449. 2. Koser, G. F. "C-Heteroatom-Bond Forming Reactions" Top. Curr. Chem. 2003, 224, 137 – 172. 3. Muci, A. R.; Buchwald, S. L. "Practical Palladium Catalysts for C-N and C-O Bond Formation" Top. Curr. Chem. 2002, 219, 131 – 209. 4. Hartwig, J. F. "Palladium-Catalyzed Amination of Aryl Halides: Mechanism and Rational Catalyst Design" Synlett. 1997, 329 – 340. 5. Hartwig, J. F. "Transition Metal Catalyzed Synthesis of Arylamines and Aryl Ethers from Aryl Halides and Triflates: Scope and Mechanism" Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 2046 – 2067. 6. Wolfe, J. P.; Wagaw, S.; Marcoux, J.-F.; Buchwald, S. L. "Rational Development of Practical Catalysts for Aromatic Carbon–Nitrogen Bond Formation" Acc. Chem. Res. 1998, 31, 805 – 818. 7. Hartwig, J. F. "Carbon–Heteroatom Bond-Forming Reductive Eliminations of Amines, Ethers, and Sulfides" Acc. Chem. Res. 1998, 31, 852 – 860. 8. Frost, C. G.; Mendonça, P. "Recent developments in aromatic heteroatom coupling reactions" J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1. 1998, 2615 – 2623. 9. Yang, B. H.; Buchwald, S. L. "Palladium-catalyzed amination of aryl halides and sulfonates" J. Organometallic Chem. 1999, 576, 125 – 146. 10. Belfield, A. J.; Brown, G. R.; Foubister, A. J. "Recent Synthetic Advances in the Nucleophilic Amination of Benzenes" Tetrahedron. 1999, 55, 11399 – 11428. 11. Hartwig, J. F. "Approaches to catalyst discovery. New carbon-heteroatom and carbon-carbon bond formation" Pure Appl. Chem. 1999, 71, 1417 – 1423. 12. Prim, D.; Campagnew, J.-M.; Joseph, D.; Andrioletti, B. "Palladium-catalysed reactions of aryl halides with soft, non-organomettalic nucleophiles" Tetrahedron. 2002, 58, 2041 – 2075.