! " # $ "
advertisement

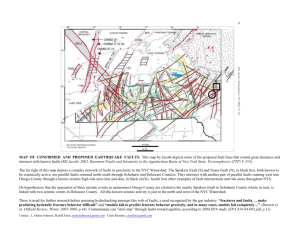
% ! " # & $' % $" ( ) *+ + *, - - . 1 / 0$ 0' 0 ' 0 $ 1 $ 2 $ $ 34 ( % 5 $ Protection components for local equipments Fast controllers for system-side effects 2 0 % 00 0 / $ %6$ ' 0 / 2 %6$ ' A relay is a safeguard of each major piece of equipment % 00 Relays sometimes malfunction by responding to overloads although there were not faults on the protected lines. This is a common mode of failure which accelerates the geographic spread of the cascading faults Relay malfunctioning is one of the major contributing factors to 70% of the major electric power outages and blackouts. 3 7 1 ( $'' ( $ / ' ' 0 8 ' 0 $ ' 0 $ ' ' 9 0 1 $ / $ 0 $ / ' ( : : 0 0 $ ' / 4 ; # 1 < 0 ' 7 / $ ' / $ 0 / $ 4 $ 7 / 5 0 7 : '' ' = 0 0 / $ magnitude of current, phase of current magnitude of voltage phase of voltage, real power reactive power # Relaxed condition: Normal condition and far away faults Stand-by condition: Zone 2 and Zone 3 faults Emergency condition: Zone 1 faults 6 ' ' ' 0 4 : ' 04 8 :9 $ '' ' 1 $' $ 0 Reactive Power > Real Power > Phase of Voltage > Magnitude of Voltage > Phase of Current > Magnitude of Current 04 $ Reactive Power + Real Power: 75% Reactive Power + Real Power + Phase of Current: 85% 7 $ $ 0 ' 4 $ 8 $ $ <+ ' 0<+ 0 0 6$ ' 0 # 1 ' / # ' 2 0 $ $ 0 $ . >? 1 @ >? 2 2 1 0 $ <+ 9 0 7 ; 0 0 = 6$ & 0 0 ( '' 2 0 1 $ / ' ' 0 00 ' $ 2 ' 2 Shorter simulation and training time Less data is needed to be kept in relay for training and updating; Quicker dynamic updating lower communication traffic load 10 = 7 : '' 7 + # < 1 , # < 1 Larger Networks ) # % < 1 0 11 $ $ ++@ 7 $ 12 % 00 4 6$ $ A A # 0 $ 0 $ 6$ ' 0 13 % % % +B 7 $ $ -3 4 x 10 simple isolation complex isolation 3 2 0.025 1 simple isolation complex isolation 0 0.015 -1 0.01 voltage current 0.02 -2 -3 0.005 0 -0.005 -4 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 -0.01 time $ 0 14 -0.015 +- ++ -0.02 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 time 0 $ 0 B > C 14 0.04 simple isolation complex isolation 0.03 0.02 current 0.01 0 -0.01 -0.02 -0.03 -0.04 -0.05 0 2 4 6 8 10 time 12 14 16 18 20 15 # / Instead of only working as a protect equipment, it may stabilize the system more quickly to trip extra relay(s) than just isolating the. Protection relays can be used as binary fast controllers Extract features from transient measurements Use continuous time series to do SVM 16 4 $ 4 0 # $ Max during fault; width during fault; min during fault; max after fault; width after fault 17 4 $ 4 0 $ Do log and curve fitting on function: 2 parameters for curve 1 and 2 parameters for curve 2 18 : $ 0 Serious effect: destroy equipment; make system unstable Moderate effect: may overloading equipment; potential harm Minor or none effect $ +B $ Class 1: generator faults; major line faults Class 2: moderate line faults Class 3: weak line faults Accuracy: 97.2% 19 $ $'' / 0 / ' ' / 2 Increase the dependability and security simultaneously May overcome the shortcomings brought by the invalid assumptions of conventional relays 2 # 0 ' $ = $ 0 $ $ $ / 0 # ' $ 0 " 20