Document 12839673
advertisement

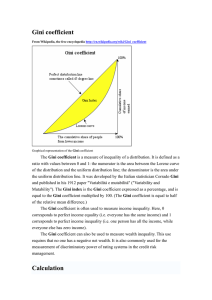
Substantial rise in inequality during the 1980s Gini Coefficient 0.40 0.35 0.30 0.25 0.20 Source: IFS Top of income distribution races away 6.00 Ratio 5.00 4.00 3.00 2.00 1.00 90/10 Source: IFS 50/10 99/50 Gini – Mid 80s Gini - Mid 2000s Source: OECD. Figures not directly comparable with those on other slides. Mid 80s Germany refers to West Germany. OE CD ex ic o M US A Ire la nd tra lia Au s Ita ly UK ad a Ca n Ja pa n an ce Fr Ge rm an y 0.50 0.45 0.40 0.35 0.30 0.25 0.20 0.15 0.10 0.05 0.00 Sw ed en Gini Coefficient The Gini: international comparisons Real earnings growth Sweden (1980-2005) Avg annual earnings growth 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 -0.5 -1.0 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 -0.5 -1.0 USA (1980-2005) Source: OECD Notes: Full-time male workers only France (2000-2005) Avg annual earnings growth Avg annual earnings growth 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 -0.5 -1.0 Avg annual earnings growth UK (1980-2005) 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 -0.5 -1.0 Lowest Income Highest Lowest Income Highest Lowest Income Highest Lowest Income Highest Lowest Income Highest Lowest Income Highest Lowest Income Highest Lowest Income Highest Lowest Income Highest Lowest Income Highest Lowest Income Highest Lowest Income Highest Lowest Income Highest Lowest Income Highest Inequality (log variance x 1000) 350 Employment Status Health 300 Ethnic group 250 Education 200 Age 150 Gender 100 Household type Region 50 Residual 0 1968 1972 1976 1980 1984 1988 1992 1996 2000 2004 Source: HBAI Data (FES and FRS) and authors’ analysis What we do not know (and why it matters) How much can government affect inequality? How much can government affect labour market outcomes?