E N E R G Y ... F S
advertisement

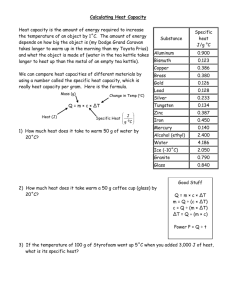
E NE RG Y MAT TER S FACT SHEET 1: WHAT IS ENERGY? It seems an obvious and simple question, though the generally accepted answer – the capacity to do work – asks more questions than it answers. For example, what is work? Its generally accepted definition is as mechanical work: movement of an object. Mathematically it is the value of the distance that an object is moved multiplied by the force acting on it. sound etc, but that between stored and released energy. Stored energy contains the ability (potential) to do work. Released energy does the work. EXERCISE 3 What are some examples of stored energy? Energy creates force which does work. EXERCISE 1 Consider a windmill or wind turbine. How does the above definition apply to this specific case? Stored energy when it is released will produce movement in some form, whether it is visible to the observer or not. EXERCISE 4 When the examples in Exercise 3 release their stored energy, where is the movement produced? EXERCISE 2 When you heat water in a kettle, you are quite definitely using energy. However, nothing seems to be moving, just that the water increases in temperature. Why is this not violating the definition of energy? Forms of energy The most important distinction between the various forms of energy, is not as you might expect, the difference between heat, Energy changes Energy cannot be created or destroyed, the First Law of Thermodynamics says, only converted into different forms. When energy is expended to do work, the amount of energy is much greater than the work done. This is because the conversion of energy into moving the object is not very efficient. Some of the energy is converted into other forms, such as heat, light and sound. EXERCISE 5 Classify the following general forms of energy as stored or released. Form Type Heat boils water From To Electrical Steam turns turbines Chemical From Nuclear To Gravitational Generation of electricity Heat From Light To Sound Boiling water in the kettle Kinetic From EXERCISE 6 Trace the energy interconversions from the formation of coal through to heating water in an electrical kettle. To Growth of plants From To Formation of coal From To Burning of coal in power station furnace From To Every time energy is converted from one form to another, some is lost, which means a lot of sunlight has gone into making your cup of coffee! Power Another relevant term here is power. It is the rate at which energy is used or converted into a new form. Running consumes more energy in a given time than does walking, therefore your power is greater. The heat energy required to boil a litre of water is a constant. However, the rate at which it reaches boiling point is not, and depends on the amount of energy per second that is being supplied to the water. Trying to boil the water with a lit match will take a very long while compared to the much higher powered electric kettle.