Page 7 Roy Silen, PNW
advertisement

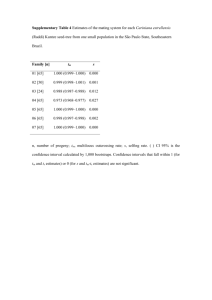
Page 7 BURNT WOODS COOPERATIVE--MAPPING GEOGRAPHIC GENETIC VARIATION Roy Silen, PNW Following methods of marping geographic genetic variation developed i 1978-1979 for the Vernoni . a and Molalla Cooperatives, a similar map of the Burnt Woods Cooperative area was mate from recent 10-year progeny . height data. The Burnt Woods Cooperative is a 70,000 acre forest area west of Corvallis owned . by Starker Forest and State of Oregon. The 10-year progeny measurements apply to families from 161 parent trees allotted among 5 sets of 31 to 33 families tested on 8 sites. Progeny av raged about 16 feet in height. The top 20 percent were 7.5 percent taller than mc·an height and an estimated 17 percent greater in volume as shown in Table l. In the earlier analyses we used computer programs to produce a response surface, then drew in i.soheight heights : ines to make the maps of progeny wen (see IFA TIN 1138). Expected average plotted for parents located within 500 meter square areas. One program produced an equation by a stepwise regression for a predicted height at the la itude, longit11de., and elevation of the parent. smoothing technique called Krieging, The other program uses a in which mean heights of one 500 meter square area was averaged with a weighting of mean values in adjacent 500 meter squares. Isoheight contours from hoth methods produced maps that are interpretable in _erms of influence of topographic features. The smoothing method produced a clearer map Of geogra;1hic genetic variation in height within the breeding zone. This map is shown in Figure 1. Fastest inherent growth was associated with parents from low ridges, and slowest with parents in the rain shadow of Little Grass Mountain, the highest ridge in the ownership. Like the Vernonia and Molalla geographic variation maps, this map supports the suggestion that adaptation to a locale is precise. Progeny height, range, Table 1. Burnt _ Woods Trf'e Improvement 10-J'.ear height data. shown by set and by overall average. average, and percent dif fererh:e from average are Set I TI3iI1 Set 2 Set 3 Set 4 Set 5 (3 (31) (32) (32) x 536 Tallest 529 54 7 512 529 542 Top 20% 523 537 521 533 531 529 Average 494 501 485 95 487 492 Shortest 395 454 437 435 450 434 % difference -in ht. 5.9 7.1 7.4 7.7 9.0 7.5 I 3.5 J6 1 16.8 17.2 20.4 16.8 from top 20% -in vol. '!:./ . l/ Number of families in the set. '!:./ Estimated from Vernonia Tree Improvement Cooperative 10-year data. Page 8 MAP OF GE.NE'r1c VARIA7i10N 5"1°011-i£i.J C f'?O,/\/ 7" I"' s-10 ) ... - .. ye,.,,-:: /NC;) F He NT 8vR.Nr Wooos CooP£ A7" Y£" -­ ·­ · .,, · - • • • • Isoheight contour map of inherent growth rate for Burnt Woods Tree Figure l. Contours display 10 cm differences in growth of Improvement Cooperative area. progeny (about 3.5 percent differences} in period between 5 and 10 years. Small figures are Lines are solid within ownership area and dashed between. coding of periodic height growth in 10 cm intervals from 250 cm (1) to 310 cm (7) for the 500 meter squares in which parent trees are represented.