Chapter 6 Essential Organic Chemistry Isomers and Stereochemistry Paula Yurkanis Bruice
advertisement

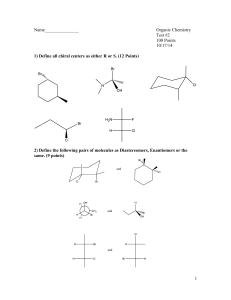
Essential Organic Chemistry Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 6 Isomers and Stereochemistry Disampaikan oleh : Dr. Sri Handayani 2013 Review of Isomerism Isomers – Compounds that have the same molecular formula but do not have identical structures. Constitutional Isomers – differ in the way their atoms are connected. Stereoisomers – differ in the way their atoms are arrange in space. Constitutional Isomers 6.1 Cis-trans isomers Differ in the arrangement of their atoms in space (cannot interconvert)- Alkenes. 6.1 Cis-trans isomers Cyclic structure. 6.2 Chirality Chiral – Nonsuperimposable on its mirror image. Achiral – Superimposable on its mirror image. If a molecule (or object) has a mirror plane or an inversion center, it cannot be chiral. Chiral or Achiral? Brandy snifter achiral achiral Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Chiral or Achiral? Shears chiral Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Chiral or Achiral? Beer mug achiral Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Chiral or Achiral? Hiking boot chiral Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Chiral or Achiral? Baseball glove chiral Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Chiral or Achiral? Boat propeller chiral Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Chiral or Achiral? Desk chair achiral Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Chiral or Achiral? School desk chiral Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Chiral or Achiral? cis-1,3-dimethylcyclopentane achiral mirror plane Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Chiral or Achiral? trans-1,3-dimethylcyclopentane chiral Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Chiral or Achiral? 1,1-dimethylcyclohexane achiral Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 6.3 Asymmetric centers An asymmetric center is an atom that is bonded to four different groups. Chiral or Achiral? Asymmetric center 2-butanol chiral mirror image Chiral or Achiral? 2-bromopropane achiral 6.4 Isomers with one asymmetric center 6.4 Isomers with one asymmetric center Enantiomers A chiral compound and its mirror image are called enantiomers. 2-butanol: enantiomers Enantiomers Asparagine: O C mirror plane OH H2N C H H2N HO C O H C NH2 CH2 CH2 C C O L-asparagine O NH2 D-asparagine (from asparagus) (from vetch) bitter taste sweet taste enantiomers 6.5 How to draw enantiomers 6.6 Naming enantiomers: the R,S system Absolute Configuration R and S • Assign priorities to the remaining groups based on atomic numbers. • Clockwise (highest to lowest priority) R • Counterclockwise S HO OH H C = CH3 (R)-2-butanol 2 1 CH 2CH3 CH2CH3 C CH3 3 Absolute Configuration Assign priority: • Atomic number of atom directly bonded. • If the same atom is bonded, go to the next atom, etc. • Groups containing multiple bonds are treated as though multiple atoms were attached: N C C O = C O O C C N = C N N C Absolute Configuration Determine the absolute configuration of the following compounds: 1 3 H3C F 4 H C Cl Br S 2 C CH DR 2 3 3 1 O 2 (CH3)2CHCH2 4 H C Cl S CH3CH2CH2CH2 1 3 4 H 1 H C 4 H C C N CH3CH2 R 2 3 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Absolute Configuration Determine the absolute configuration of the following compounds: CH3 CH3 1 2 CH3O CH 4 H C 2 CH3 S 3 CH CH3CH2 CH3O CH CH3CH2 C 1 CH3 R CH 3 OCH3 OH 1 CH2=CH 4 H 2 CH2=CH 4 H C 2 CH3 S CH3CH2 3 4 H C C CH S (CH3)2CH 1 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 6.7 Chiral compounds are optically active Plane-polarized light is produced by passing normal light through a polarizer. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Optical Activity When plane-polarized light passes through a solution of achiral molecules, the light emerges from the solution with its plane of polarization unchanged. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Optical Activity However, when plane-polarized light passes through a solution of a chiral compound, the light emerges with its plane of polarization changed. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Optical Activity Optical Activity – The ability of a compound to rotate the plane of polarized light. A compound that rotates the plane of polarization is said to be optically active. Chiral compounds are optically active and achiral compounds are optically inactive. A polarimeter is used to make such measurements: Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.