Human Visual System (HVS) • Eye. • Brian.
advertisement

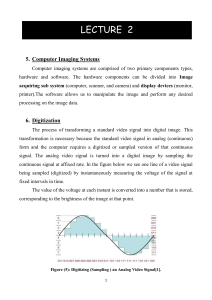
Human Visual System (HVS) The Human Visual System (HVS) has two primary components: • Eye. • Brian. * The structure that we know the most about is the image receiving sensors (the human eye). the brain can be thought as being an information processing unit analogous to the computer in our computer imaging system. These two are connected by the optic nerve, which is really a bundle of nerves that contains the path ways for visual information to travel from the receiving sensor (the eye) to the processor (the brain). Computer Imaging Systems(Digital Image Processing System) Computer imaging systems are comprised of two primary components types, hardware and software. The hardware components can be divided into image acquiring sub system (computer, scanner, and camera) and display devices (monitor, printer).The software allows us to manipulate the image and perform any desired processing on the image data. 1 A simple image model: • To be suitable for computer processing, an image f(x,y) must be digitalized both spatially and in amplitude. • Digitization of the spatial coordinates (x,y) is called image sampling. • Amplitude digitization is called gray-level quantization. Digitization The process of transforming a standard video signal into digital image .This transformation is necessary because the standard video signal in analog (continuous) form and the computer requires a digitized or sampled version of that continuous signal. The analog video signal is turned into a digital image by sampling the continuous signal at affixed rate. In the figure below we see one line of a video signal being sampled (digitized) by instantaneously measuring the voltage of the signal at fixed intervals in time. The value of the voltage at each instant is converted into a number that is stored, corresponding to the brightness of the image at that point. Note that the image brightness of the image at that point depends on both the intrinsic properties of the object and the lighting conditions in the scene. 2 Figure (3) Digitizing (Sampling ) an Analog Video Signal What's an image? • An image refers to a 2D light intensity function f(x,y), where (x,y) denote spatial coordinates and the value of f at any point (x,y) is proportional to the brightness or gray levels of the image at that point. • A digital image is an image f(x,y) that has been discretized both in spatial coordinates and brightness. The image can now be accessed as a two-dimension array of data , where each data point is referred to a pixel (picture element) pixels. 3 • Two-dimensional function f(x,y) or matrix • x, y, f(x,y) are discrete and finite • Image size = maxx x maxy -- e.g. 640x480 • Pixel intensity value f(x,y) ∈ [0, 255] Where x represent columns and y represent rows The digital image is 2D array as: 4 f(0,1) ...........................f(0 , N - 1) f (0,0) f(1,0).... .........................................f(1, N - 1) . ... ........................................ ........................................ . ... . ... ........................................ f(N - 1, N - 1) f(N - 1,0) f(N - 1,1) In above image matrix, the image size is (NXN) [matrix dimension] then: Where Ng denotes the number of gray levels m is the no. of bits contains in digital image matrix. • The storage and processing requirements increase rapidly with the spatial resolution and the number of gray levels. Example :If we have (6 bit)in 128 X 128 image .Find the no. of gray levels to represent it ,then find t he no. of bit in this image? Solution 5 6
![[Type the document title]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/012643359_1-f3f273ee619f414513db75d7a1f76d45-300x300.png)