Earth’s Upper Atmosphere Qian Wu National Center for Atmospheric Research
advertisement

Earth’s Upper Atmosphere
Qian Wu
National Center for Atmospheric Research
High Altitude Observatory (HAO) – National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR)
The National Center for Atmospheric Research is operated by the University Corporation for Atmospheric Research
under sponsorship of the National Science Foundation. An Equal Opportunity/Affirmative Action Employer.
24 November 2005
Overview
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Mesosphere and lower thermosphere dynamics
Nightglow emissions
Ground based Fabry-Perot interferometer
Results from ground based Fabry-Perot interferometer
Spaceborne Fabry-Perot interferometer TIDI
Observation from TIDI
Summary
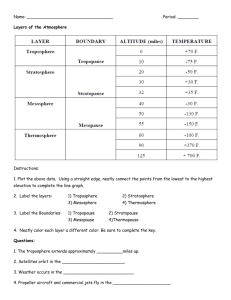
Upper Atmosphere
Forbes, Comparative Aeronomy, 2002
Mesosphere and Lower Thermosphere Tides
and Large Scale Waves
• Migrating tides
– Diurnal tide
– Semidiurnal tide
• Planetary Waves
• Non-migrating tides
H RT / g is the scale height,
a is the earth radius,
is the geopotenti al,
Dynamics
Equations
Du
u tan
(f
)v
X,
Dt
a
a cos
Dv
u tan
(f
)u
Y,
Dt
a
a
z H 1 Re z / H ,
[u ( v cos ) ]
a cos
D
Q,
Dt
( 0 w) z
0
0,
T ( p s /p ) ( R / c p 2/7) is
the potential
temp erature,
0 is the density
2 / Tday
f 2 sin
( , ) (longitude , latitude)
(u, v, w), velocity in
zonal, meridional , and vertic al
directions
D
u
v
w
Dt t a cos a
z
X , Y forcing term
Q heating source
Tidal Wave Function
~
{u~, v~, } e z / 2 H e ikz z exp i ( s t )
s is the zonal wavenumbe r
2
is the wave period in days
k z is the vertical wavenumbe r
t is the universal time
TL t
local time
~
z / 2 H ikz z
~
~
{u , v , } e
e exp i ( s (TL )) e z / 2 H e ikz z exp i (( s ) TL )
If s , then
~
{u~, v~, } e z / 2 H e ikz z exp i ( T ) is migrating tide
L
Migrating tides
Nonmigrating tides
Sun-synchronous
westward
non Sun-synchronous
westward, eastward, standing
zonal wavenumber: 1/period(days)
zonal wavenumber: any
radiative forcing, …
latent heat
PW/tidal interaction, …
comparable to / exceed
migrating tide
longitude modulation
the
Diurnal Tide in Zonal Winds
Aurora and Nightglow
Mesosphere and Lower Thermosphere
Nightglow Volume Emission Rates
120
O 2 (0,0)
lines
Altitude (km)
110
557.7 nm
100
90
80
70
589.3 nm
OH 892 nm
60
0.1
1.0
10.0
Volume emission rate (photons cm
solid=molecules, dashed=atoms
100.0
-3
s -1)
1000.0
Thermosphere Nightglow Volume Emission Rates
300
Altitude (km)
280
260
630.0 nm
240
220
200
0.1
1.0
Volume emission rate (photons cm
10.0
-3
100.0
-1
s )
Airglow Emission Sources
O 6300 Å red line
O 5577 Å green line
Electron impact
Electron impact
O e O(1S ) e
O e O(1D) e
Photodissociation of O2
Photodissociation of O2
O2 hv O O(1D)
O2 hv O O(1S )
Collisional deactivation of N2
Dissociative recombination
2
N 2 ( A3u ) O N 2 O (1S )
O e O O( D)
1
OH emission
16
H O3
OH (6 ' 9) O2
k
Fabry-Perot Interferometer
Plate
Post
Coating
Etalon
Incoming
Light
Optical
Axis
Fabry-Perot
Interferometer
Imaging
Lens
Image
Plane
Fabry-Perot Fringe Pattern
FPI Configuration
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Major Components
Sky scanner
Filters & filter wheel
Etalon & chamber
Thermal & pressure control
Focusing lens
Detector
Computer system
•
•
•
•
•
Highlights
Computerized micrometer
Daily laser calibration
High degree automation
Michigan heritage
NCAR enhancement
Instrument Operation
North
OH Airglow Layer
45 deg
FPI
West
Zenith
87 km
174 km
South
174 km
(a)
East
(b)
FPI at Resolute
FPI at Resolute
Instrument Electronics
FPI Operational Mode
Emission
Integration
time
Wind Errors
Altitude
OH 8920 A
3 minutes
6 m/s
87 km
O 5577 A
3 minutes
1 m/s
97 km
O 6300 A
5 minutes
2-6 m/s
250 km
Polar Cap Observatory 75N
Mesosphere Wind 12h Wave
Lower Thermosphere Wind 12h Wave
8-Hour Wave
Resolute OH Wind 10-Hour Wave
Thermosphere Wind
TIMED
A satellite mission to study
Thermosphere Ionosphere Mesosphere
Energetics and Dynamics (TIMED)
Instruments:
• TIMED Doppler Interferometer (TIDI)
• Global Ultraviolet Imager (GUVI)
• Solar Extreme Ultraviolet Experiment (SEE)
• Sounding of the Atmosphere using Broadband
Emission Radiometry (SABER)
TIMED Fact Sheet
The TIDI Instrument
The TIMED Doppler Interferometer (TIDI) is
a Fabry-Perot interferometer for measuring
winds in the mesosphere and lower
thermosphere.
Primary measurement: Global neutral wind
field, 60–120 km
Primary emission observed: O2 1 (0-0) P9
Additional emissions observed: O2 1 (0-0)
P15, O2 1 (0-1) P7, O(1S) “green line”
Telescope Assembly
Profiler
Limb-Scan Measurements
Airglow layer
TIDI Measurement Viewing Directions
4
1
3
2
9 minutes
Satellite
Travel direction
4
1
3
2
TIDI Local Time Coverage Day 80 2002
TIDI Neutral Wind Measurements
Neutral Winds From TIDI
TIDI Neutral Wind Observation
Observed Diurnal and Semidiurnal Tides
GSWM00 Tidal Amplitudes and Phases
Feb
Summary
• Earth’s upper atmosphere is very dynamic region, which is affected by
lower atmosphere and space weather.
• Fabry-Perot interferometer is an effective instrument for upper
atmosphere dynamics studies.
• Ground based instrument has a very high accuracy and can detect very
small tidal waves.
• Ground based instrument can only provide local coverage during
nighttime under clear sky.
• Satellite Fabry-Perot interferometer can provide a global view during
day and night.
• We need more observation in the mesosphere and thermosphere to
order to have a better understanding of the region.