قارعلا ةيروهمج يملعلا ثحبلاو يلاعلا ميلعتلا ةرازو لعفت ام قثو
advertisement

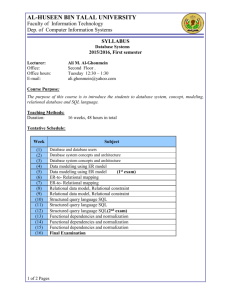
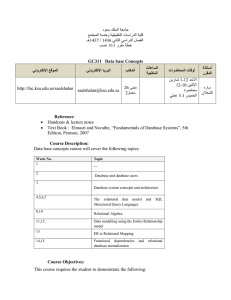
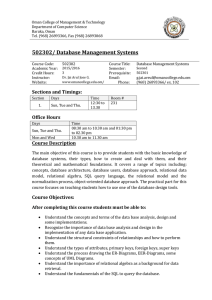
جمهورية العراق وزارة التعليم العالي والبحث العلمي وثق ما تفعل وافعل ما توثق جامعة بابل إدارة الجودة الشاملة كلية تكنولوجيا الحاسبات قسم شبكات المعلومات الدراسات األولية رقم المقرر الدولي: Curriculum and Process Design Evidence )CAPDE (7-3-1.2.3.-02-01 العدد: استمارة خاصة الطالع الطلبة على المقرر التاريخ: Course NO.: 1 مقدمة الى قواعد البيانات Introduction to database اسم المقرر اجباري اختياري X 2 عدد الوحدات 3 المرحلة الدراسية عدد الساعات االجمالي 4 4اسم التدريسي النوع فصلي X سنوي 5 النظري 3 العملي 2 الثانية أن ـوار جعفر موسى الشهادة واللقب العلمي ماجستير علوم حاسبات – مدرس مساعد التخصص الدقيق حاسبات 5لغة تدريس المقرر انكليزي برنامج المقرر اوال المقدمة Databases are at the heart of modern commercial application development. Their use extends beyond this to many applications and environments where large amounts of data must be stored for efficient update and retrieval. The purpose of this course is to provide an introduction to the design and use of database systems, as well as an appreciation of the key issues in building such systems. ()1 - 3 اهداف المقرر ثانيا Upon completion of this course, the student should be able to: 1. Explain database approach: its advantages, disadvantages, Evolution, and applications, define the basic terms in database management systems. Explain the advantages of database approach compared to conventional file processing. Identify categories of database. Describe the components of database environment . Identify costs and risks of the database approach. Appreciate the need of a data model 2. Identify the role of data model in database system Development. Extract the business rules, Differentiates between various data models, namely: Hierarchical, Network, Relational, Object Oriented. 3. Describe the three level schema architecture for Database. 4. Identify characteristics of a Relational Table, identify key terms in data modeling, Define integrity rules. 5. Apply relational set operators on database relations. 6. Understand what is Data dictionary and system catalog in database systems, Use various relationships in relational database model. 7. Eliminate data redundancy. 8. Understand indexes in database systems 9. Define the key terms in EER modeling (Entities, Attributes, Domains, Identifiers, Relationships), Develop ER model ,Transform ER model into Database. 10. Identify the need for normalization, Apply the normalization process in database design. 11. Apply demoralization when it is needed 12. Create database tables, Create database constraints 13. Add, modify, and delete data, Retrieve data 14. Design a database model. 15. Create database using SQL language, Query single database table using SQL مفردات المقرر او المحتوى Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Database Systems Introducing the Database and the DBMS Why Database Design is important Problems with File System Data Management Database System Environment Data Models The importance of Data Models Data model basic building blocks Business rules Data Models Types of Data Models and their evolution Data Models Degrees of data abstraction The Relational Database Model A logical view of data The Relational Model’s basic components Integrity rules The Relational Database Model Relational Algebra Relational set Operators Data dictionary and System catalog The Relational Database Model Relationships within the relational database Data redundancy Indexes The Entity Relationship (ER) Model The main characteristics of ER model )2 - 3( ثالثا مفردات المقرر او المحتوى ثالثا طرائق التدريس المعتمدة لتنفيذ المقرر 1. Lectures (Present by using MS-PowerPoint) 2. Discussion. 3. Interaction between the lecturer and the students by questions. رابعا توزع درجات المقرر وفق لواحد أو أكثر مما يأتي Active participation, homework assignments, Attendance, quizzes Practical Exams Final exam خامسا %20 %30 %50 Week 9 Week 10 Week 11 Week 12 Week 13 Week 14 Week 15 The Entity Relationship (ER) Model Developing an ER diagram ER relationships implementation Database design challenges Normalization of Database Tables The role of normalization in database design process Normalization of Database Tables Normal forms: 1NF, 2NF, 3NF Demoralization Introduction to Structured Query Language (SQL) Introduction to SQL The use of SQL for data administration Introduction to Structured Query Language (SQL) The use of SQL for data administration Introduction to Structured Query Language (SQL) The use of SQL for data manipulation Introduction to Structured Query Language (SQL) The use of SQL to query a database المصادر والمراجع سادسا * Hector Garcia-Molina, Jeffrey Ullman, Jennifer Widom. Database Systems: The Complete Book, Prentice-Hall, 2002. * Rob, Peter and Carlos Coronel, Database SYSTEMS – DESIGN, IMPLEMENTATION, AND MANAGEMENT, 7th edition, THOMSON-COURSE TECHNOLOGY, 2007 * Carolyn Begg & Thomas Connolly: Database Systems: A Practical Approach to Design, Implementation and Management (4th edition), Prentice Hall, 2004 * Ramez Elmasri and Shamkant B. Navathe, Fundamentals of Database Systems, 4th Ed. AddisonWesley, 2004 القسم.ر اسم التدريسي وسام سمير بهيه.د أنـوار جعفر موسى التوقيع التوقيع )3 - 3(