Psychosocial Theory
2nd Lecture
Theory that focuses on developmental task, focuses on EGO as this
develops from social interaction
The developmental tasks are sequential and depend on prior
successful mastery
An individual who fails to “master” the task at appropriate age may
return to work on mastery
Use of the theory in Nursing
Assessment can be done focusing on the psychosocial
development at specific age
Appropriate interventions can be selected based on task
Nurses can promote healthy behaviors and encourages hope that relearning is possible
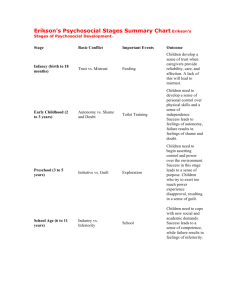
Erikson’s Psychosocial theory(Erik Erikson (1902–1994)
Trust versus mistrust
Autonomy versus shame and doubt
Initiative versus guilt
Industry versus inferiority
Identity versus role confusion
Intimacy versus isolation
Generativity versus stagnation
Ego integrity versus despair
Life Stages
I.
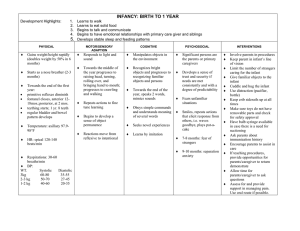
Trust vs Mistrust (0 – 18 months of age)
Child develops sense of trust or mistrust of others;
Shares openly and relates to others;
Interpersonal skills start to develop
1
II. Autonomy vs Shame and Doubt
18 months – 3 y/o;
Child learns self-control or becomes very conscious
and full of doubt;
Negativistic attitude;
Exhibits motor self-control and independence thru
negativism;
Parallel play is the social skill.
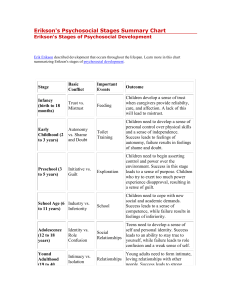
III. Initiative vs Guilt (3 – 5 y/o)
Child initiates spontaneous activities or develops fear of
wrongdoing;
Shows appropriate social behaviors;
Curiosity and exploration;
Social Skill:
Cooperative Play
IV. Industry vs Inferiority (6 – 12 y/o)
Child develops the social and physical skills necessary to
negotiate and compete in life;
Acquisition of competence;
Ability to cooperate and compromise;
Identification with admired others
2
(teachers, parents)
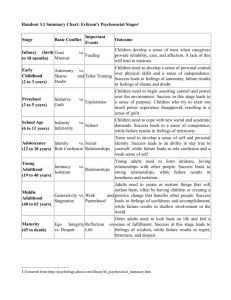
Identity vs Role Diffusion ( 12 – 20 y/o )
Teenager either integrates childhood experiences into a
personal identity;
May develop self-doubts about sexual or occupational roles;
Establish relationship with the opposite sex;
Fidelity with friends;
Also value importance of beauty or self-image;
Psychosocial Stage
VIRTUE
PATHOLOGY
T vs MT
HOPE
Psychosis Addiction
Depression
A vs S and D
WILL
Impulsivity Paranoia
Obs/Comp
Initiative vs G
PURPOSE
Conversion
Inhibition
Ind vs Inf
COMPETENCE
Creative inhibition
Identity vs RD
FIDELITY
Inti vs Iso
LOVE
Gender-related
identity disorders
Schizoid
G vs S
CARE
Midlife crisis
Integrity vs D
WISDOM
Despair
3
Phobia
Alienation
VI. Intimacy vs Isolation (18 – 25 or 30
The person develops commitment to work and to other
people;
Ability to give and receive love;
Responsible sexual behaviors;
4