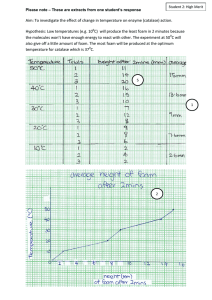
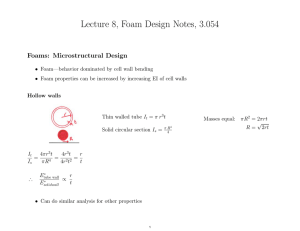
Foams: The parameters determining the characteristics of foams are the ratio... foam to that of unfoamed matrix ,and the cellar structure...
advertisement

Foams: The parameters determining the characteristics of foams are the ratio of bulk density of foam to that of unfoamed matrix ,and the cellar structure of foam. The foam can be open cell or closed cell or a mixture of the two. Figure(1) shows typical forms of compressive stress strain graph for polymeric foams. Over the initial straight line part of the graph the cell wall just bend under the action of the applied stress. The next stage is when the walls elastically buckle, often giving a plateau of deformation, the deformation is still elastic and finally the cell walls suffer irrecoverable buckling collapse. With cushion materials the foam is required to give continually increasing resistance to increasing load and so plateau in stress strain curve is not required.so the form shown in A is required. Foams used for packaging need to absorb the energy ivolved when packaging droped and so a plateau is highly desirable like that indicate in B. Et =Vs Es where Vs the fraction of the bulck volume of the foam that is solid matrix 𝑉𝑠= 𝑣𝑠 𝑣𝑠 + 𝑣𝑔 Where 𝑣𝑠 𝑖𝑠 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑓𝑜𝑎𝑚 𝑡ℎ𝑎𝑡 𝑖𝑠 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑖𝑑 𝑣𝑔 𝑖𝑠 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑓𝑜𝑎𝑚 𝑡ℎ𝑎𝑡 𝑖𝑠 gas, the bulck density𝜌𝑓 of the foam is 𝜌𝑓 = 𝑉𝑠 = 𝑚𝑠+𝑚𝑔 𝑣𝑠 + 𝑣𝑔 𝑣𝑠 𝜌𝑓 𝑚𝑠 + 𝑚𝑔 𝑚𝑔 is very small in comperation with 𝑚𝑠 𝑉𝑠 = 𝜌𝑓 𝜌𝑠 𝐸𝑓 = 𝜌 𝐸𝑓 =( 𝜌𝑓)n 𝑠 𝜌𝑓 𝜌𝑠