Danielle Duffourc, Ph.D. Director for Institutional Effectiveness and Assessment Xavier University
advertisement

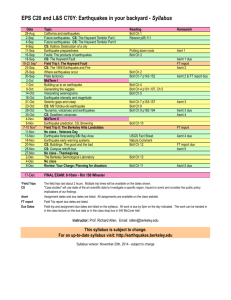
Danielle Duffourc, Ph.D. Director for Institutional Effectiveness and Assessment Xavier University Today’s workshop will focus on understanding how curriculum maps can be used as a tool to link program outcomes with program curriculum. ◦ How do we document, communicate and demonstrate coherence of program curricula to SACSCOC reviewers and other stakeholders? While each faculty member may be familiar with their own coursework: ◦ Do you know if/how the courses you teach relate to those taught by peer faculty? ◦ Do you know if the sequence of courses taken by students add up to a coherent learning experience? ◦ When you alter a course, do you know the impact that adding and removing components will have on the program curriculum as a whole? Curriculum mapping offers the “ability to look at programs in a holistic way – at a level beyond individual courses – and make sure that program curriculum provides appropriate conditions for student achievement of intended learning outcomes” (Palomba & Banta, 1999). Needed ◦ Course List ◦ Student Learning Outcomes Optional (for depth) ◦ Relationship of Course to Outcome ◦ Level of Instruction in Course to Outcome ◦ Feedback and Assessment Program Outcome 1 Course 1 X Course 2 X Course 3 X Program Outcome 2 Program Outcome 3 X X X Course 5 X Course 6 X Course 7 X Program Outcome 5 X Course 4 X X X Course 8 X Course 9 X Course 10 Program Outcome 4 X X Program Outcome 1 Program Outcome 2 Rel Level Asmt Course 1 X I E Course 2 M I Course 3 M R E Rel X Level Asmt I Program Outcome 3 Rel Level Asmt X I E X R E M A E Course 4 Course 5 Course 6 X R Course 7 M A X R Course 8 M A Course 9 X R X = Explicit M = Implicit I = Introduced R = Reinforced A = Advanced E E = Embedded Asmt Explicit (X)= Outcome is directly expressed in the course syllabus. ◦ Program Outcome: Scientific Reasoning ◦ Course Outcome: “Students will describe how the scientific method is used to understand phenomena.” Implicit (M)= Outcome is indirectly expressed in the course syllabus. ◦ Program Outcome: Communication ◦ Course Outcome: “Students will articulate and defend American foreign policy viewpoints and influences.” Introduced (I)= Students are introduced to the outcome. Reinforced (R)= The outcome is reinforced and students afforded opportunities to practice. Advanced (A)= Students have had sufficient practice and can demonstrate mastery. *NOTE: Advanced level not in TracDat Student readiness level Instruction and learning activities Scope of outcome coverage Embedded Course Assessment (E): Students will have opportunities to demonstrate what has been learned and receive feedback. Program Outcome 1 Program Outcome 2 Rel Level Asmt Course 1 X I E Course 2 M I Course 3 M R E Rel X Level Asmt I Program Outcome 3 Rel Level Asmt X I E X R E M A E Course 4 Course 5 Course 6 X R Course 7 M A X R Course 8 M A Course 9 X R X = Explicit M = Implicit I = Introduced R = Reinforced A = Advanced E E = Embedded Asmt Are program outcomes communicated in individual courses? Do students have enough opportunities to meet program outcomes? Is content organized in a logical manner to reflect progression? (Introduced before reinforced). Are students provided feedback to achieve program outcomes? Do courses integrate multiple program outcomes? While faculty collectively select courses to be mapped, they must individually complete the map for courses they teach. ◦ If several faculty members teach the same course, they may choose to work collectively. The assessment coordinator or department head compiles the program map using a predesigned template. Faculty collectively analyze and interpret the map. Curriculum mapping is a tool to stimulate campus-wide reflection and discussion. ◦ Results are “food for thought and discussion” not “information for action.” ◦ Ultimate purpose is to help organize thinking about how curricula aligns with student achievement and success. TracDat has a built-in module that can help track curriculum mapping, but it is generally better to draft the map in Excel or Word. Once information is entered, you can go to Reports Curriculum Map to print the report. Hamilton, L., Okala, C. and Zapatero, E. G. (2013). Curriculum Mapping: A Process to Define, Document, Demonstrate and Improve the Pathways to Student Success. (SACS Workshop) http://learn.nsu.edu/curriculum-mapping.html