Bronchial asthma :--
advertisement

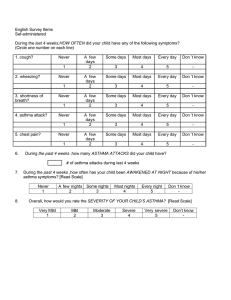
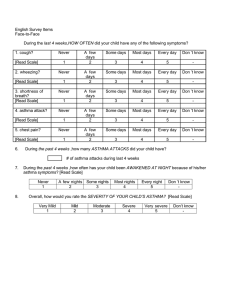
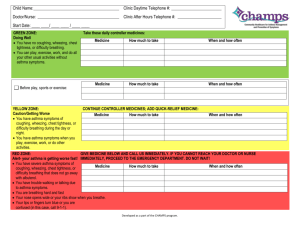
Bronchial asthma :-is chronic inflammatory condition of the lung air way resulting in a episodic air flow obstruction ( this is resulting heightens the twitchiness of the air way ( air way hyper responsiveness to .provocative exposure Or is defined as a paroxysmal , diffuse obstructive lung dis with hyper-reactivity of the air way to variety of stimuli & high degree of reversibility of the obstructive Process which may occur either spontaneously or by ---treatment . ---1 Asthma management is aimed of reducing air way inflammation :-1- minimizing post inflammation environmental exposures. ) 2- using daily controller ( anti inflammatory medication , control comorbid condition that can worsen asthma ( rhinitis -3 • ) sinusitis & G.O.R .Less inflam is better control with fewer exacerbation • :--Trigger factors of asthma • respiratory tract infection like RSV, influenza & para influenza, - 1-1 • • rhino virus , aero allergen in sensitized asthma like ( animal dander -2 indoor allergen(dust mite , molds, cockroaches ) , seasonal aero ) allergen ( trees , grass , weeds • environmental tobacco smoke -3 air pollution ( sulfure dioxide ,dust , wood , coal burning -4 • )smoke & endotoxin cold & dry air 6- exercise 7-strong & noxious odor-5 fumes. 8- comorbid condition 9-drug administration • • • • .(aspirin, NSAID, B-blocker • ;risk factors for persistant asthma in early childhood parental asthma . 2-allergy ( eczema ,allergic rhinitis , food allergy-1 3-severLRTI as in pneumonia and bronchiolitis 4- wheezing apart • Attack of asthma occurs in 30% in Ist year of life & 80-90% within 45years of age . If onset in first year of age & there is family history of asthma or allergic :- disorder • those patients have :-- 1- growth retarded unrelated to corticosteriod 2- chest deformity secondary to hyper.inflation & persistant abnormality of PFT :--Fate of asthma • • :--in general , the prognosis is good in young children • of all patients are virtually free of symptoms within 10- 50%- 1 .20years but recurrence are common in adulthood • children who have mild asthma with onset between 2year & -2 puberty , the remission rate is about 50% & only 5% experience .sever asthma • children with sever asthma characterized by steroid - 3 dependant with frequent hospitalization rarely improved & about . 95% become adult asthma • ----3--- Etiology :-the cause of childhood asthma has not been determined , implicated a combination of environmental exposures , biological , genetic & . immunological factors :--Mediators release causing broncho-spasm by • • direct action on smooth muscle 2-stimulation of vagal-1 .sensory receptor :-Viral infection trigger asthma through • • afferant vagal receptor-1 • IgE response to RSV which occur in both infant & children -2 ( RSV & PIV trigger asthma in early life while rhino virus & influenza .virus trigger in adult asthma : ----Types of asthma :-- classify into • • a- recurrent wheezing : ( trigger by common respiratory viral ) .infection in early childhood • b- chronic asthma : associated with allergy that persist into later .childhood and often adulthood .C- 3rd type emerge in female who experience obesity ,early puberty • :--Or classify into • • extrensic asthma ( allergic type) (has positive skin test & increased-1 IGE& specific IGE agaist allergen 2- intrinsic asthma( non Pathophysiology ;-- on overhead ClF :-- into 2 forms ;-a- acute episode :-occurs within minutes which commonly .happen at night due to decreased patency of air way • it is usually follow exposures to irritant like cold air , naxious .fumes like smoke , wet paint , allergen & drug like aspirin • b- insidious episode :- usually proceeded by viral infection :-ClF is variable from mild to sever as • • respiratory distress , wheezing ( S.T without wheezing )just ,cough , may associated with abdominal pain , excessive sweating .Vomiting is common • In mild chronic asthma , patient is entirely normal in between attack • :-In sever attack ( associated with danger sign ) :- characterized by • • silent chest 2- inability to talk or walk-1 • tripod position 4-cynosis 5- exhaustion -3 :--In chronic asthma : characterized by • • barrel chest 2- harrison sulci 3- antero lateral -1 depresion of thorax at insertion of diaphragm 4-clubbing of .fingers which suggest cystic fibrosis --5-- • Diagnosis :-1- clinical diagnosis by a- recurrent episodic of wheezing or + ) coughing ( S.T only persistent cough • + b-rapid improvement with using bronchdilator • c-+ve family history of atopy • :-laboratory evaluation- 2 • a-eosinophil in blood & sputum • IgE is increased in allergic type • b-skin test & RAST • exercise test- 3 chest x-ray :- ( as hyper-inflation of chest , some time atelactasis as small- 4 • .patches or may associated with pneumothorax or pneumomediastinum • :-- indication CXR in the following a- first attack of wheezing b- associated with high fever c- suspected cx like pneumothorax or pneumo mediastinum d- if resp rate of more than 60 & pulse rate of more than 160 e- localized wheeze or rales or decreased breath sound )blood gas analysis ( elevation of pco2 is ominous sign- 5 • ---6-- • • • • • pulmonary function test :-important in :-- 5 a- asses degree of air way obstruction & disturbances of gas exchange b- in measuring response of air way to inhaled allergen , exercise , chemical • c-asses response to therapeutic agent • d-in evaluation of long term course of diseases :-Measuring PEFR & FEV1 before therapy & after broncho-dilator • • if increased 10% strongly suggestive asthma :--Failure of response is not exclude asthma due to • • status asthmaticus 2- near maximal PFT -1 Note :-it is feasible to monitor PEFR 2-3 times per day which • .provide objective measuring of degree of air way obstruction :--DD :--of wheezy chest • • ,infection 2- anatomical & congenital ( G.O.R, H-type fistula- 1 • cystic fibrosis , vascular ring ) 3- vasculitis • others like F.B , broncho- pulmonary dysplasia ,psychogenic -4 cough , pul thrombo embolism • --thank you ---7