Excess free energy :it is possible to divide thermodynamic properties... parts the part which would be exhibited by an ideal...
advertisement

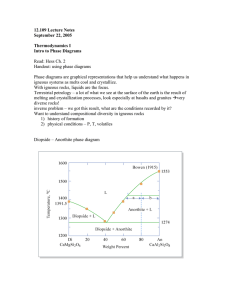
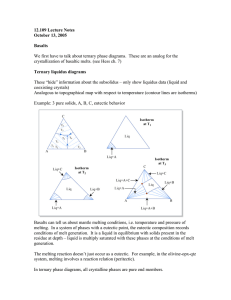
Excess free energy :it is possible to divide thermodynamic properties of a solution into two parts the part which would be exhibited by an ideal solution and the excess part which expresses the deviation from ideal solution: FOR ASYSTEM in which ideal solution are formed in both liquid and solid states, the free energy curves for both states will determined.at very high temperature the liquid free energy curve lies below that of the solid at all composition. With decreasing temperature the free energies of both liquid and solid state intersect. At melting temperature of metal A the free energy for liquid and solid state is equal where pure solid A and pure liquid A at equilibrium. By decreasing temperature the free energy of liquid and solid state intersect at some intermediate composition. Under these circumstances it may be demonstrated that with in a certain composition range a mixture of two solutions one liquid and one solid is more stable than either liquid solution or solid solution. The eutectic system diagram can be calculated by drawing the free energy of all phases( phase and liquid phase) at different temperatures.