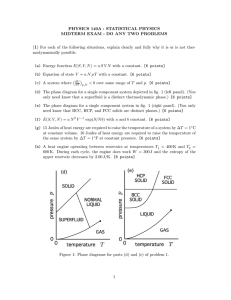
Chapter 2

Chapter 2
Entropy:-
Clausius (1854) introduced another most important thermodynamic function called entropy to make more clear and thorough understanding of the second and law of thermodynamics. Entropy of a system is a measure of randomness or disorder of the system and is denoted by the symbol S. it is a state function (that is, the change in entropy is independent of path). It can also be regarded as the measure of unavailable energy. The change in entropy of a system (or a reaction) is given by
Entropy is expressed in joule degree
-1
(J K
-1
mol
-1
).
Second law of thermodynamics states a spontaneous process is always accompanied by an increase in the total entropy of the system and its surroundings.
THE THIRD LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
This law, stated by Nernst in 1906, state that "at absolute zero, the entropy of a perfectly crystalline substance is taken as zero.".At absolute zero, the kinetic energy is zero, and the substances are in rigid state, thereby providing them complete order. Due to the total lack of disorder, the entropy of pure elements and compounds at absolute zero is zero. This law is true only for the substances that exist in perfect crystalline form at 0 k. however, if there are imperfections at 0 k, then entropy will be larger than zero
Zero Law of Thermodynamics
It is also known as law of thermal equilibrium. According to this law "if two systems A and B separately are in thermal equilibrium with another system C, then the system A and B will also be in thermal equilibrium with each other ". in other words, if system A and B, which are in thermal equilibrium with
C, are place in contact with each other, no exchange of heat will take place. This law was established after the establishment of first and second law but it put forward before first law of thermodynamics because it is based upon strong logic.