Pelvic walls, vessels, and nerves Dr. Firas Mohammed Ghazi
advertisement

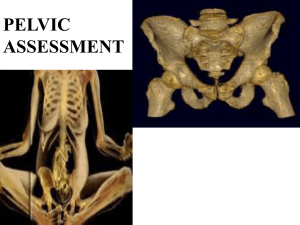
Pelvic walls, vessels, and nerves Dr. Firas Mohammed Ghazi The pelvis Cavity for Pelvic viscera Continuous with abdominal cavity Inlet, outlet, walls, and floor The pelvic bones AP Hip Sacrum Coccyx True Vs Falls pelvis • Pelvis is divided into true and falls by _______ which is formed by______________ Cavity of the true pelvis 1. 2. Between Inlet & Outlet Bounded by Ant., post., & lat. walls Floor Pelvic inlet • Transversely oval • Bounded by Vessels • Many structures pass through it Posterior wall 1. Anterior sacral foramina 2. Piriformis 3. Sacral plexus (sciatic N.) Lateral wall 1. 2. 3. 4. Sacrotuberous & sacrospinous ligaments Greater and lesser sciatic foramina Obturator foramen, membrane and canal Obturator internus The Pelvic outlet (Diamond shaped) Formed by 1. ____________ anteriorly 2. ____________ posteriorly Pelvic Floor (Pelvic diaphragm) Formed by 2 Muscles Gutter-shaped Separates pelvic cavity from ____ Openings: urethra ±vagina, rectum Perineal body?? Pelvic viscera Male Female Female pelvis is adapted to childbirth 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Roomier Inlet: Oval in women/ heart-shaped in men Cavity: wider and shorter in women Outlet: larger in women Sub-pubic angle: Wider in women Linings of the pelvis Pelvic fascia and peritoneum Parietal and visceral Reflections on viscera? Pelvic nerves &vessels lie outside Peritoneal reflections and spaces Rectovesical pouch Recto uterine pouch Female pelvis and labor Curved axis Fetal head rotates 2 times while descending Explain rotation of the fetal head !!! Major vessels of the pelvis Internal iliac artery and vein (± ovarian rtery) Run on the walls of the pelvis Pelvic fractures can lead to sever internal bleeding Obturator nerve and pelvic appendix • Run on the lateral pelvic wall covered by pelvic fascia and peritoneum