University Of Northern Iowa Division of Physical Education
advertisement

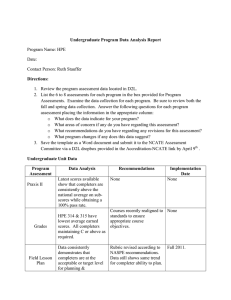
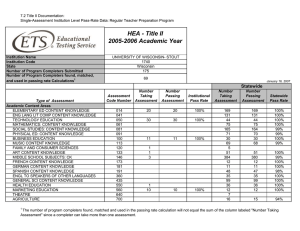
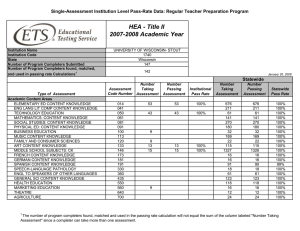
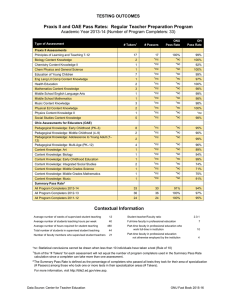
University Of Northern Iowa School Of Health, Physical Education and Leisure Services Division of Physical Education Outcomes Assessment for Teaching Majors Benchmarks for student outcomes assessments. The benchmarks for the Physical Education program are based on student outcomes and performance. This requires us to systematically collect data on student performance that is then analyzed, interpreted, and discussed in the context of program improvement. As such, the Physical Education – Teaching program outcomes include: Outcome I. Outcome II. Outcome III. Outcome IV. Outcome V. Be knowledgeable about concepts and principles relating to Human Movement. Be able to perform a variety of movement skills. Understand students and the process of learning. Demonstrate the ability to teach effectively to both groups and individuals. Understand responsibilities and opportunities in order to continue to develop as teachers and leaders throughout their careers. Procedures. Performance data reported here are based upon the following procedures. Outcomes I, II, and IV were assessed during student teaching. Evaluation forms were completed as to the student’s competence. Competencies were measured using rubrics describing abilities demonstrated during their student teaching experience. They were assessed on a five-point scale from unsatisfactory (1), to competent (3), to outstanding (5). Outcome II was assessed by measuring levels attained on four tests of physical fitness- body composition, curl-ups, push-ups, and a one-mile jog. Passing the fitness test was based on the cut-off point for the highest of the average/moderate fitness category (Dolgener & Hensley, 19??). Outcome V was assessed based on the number of students participating in professional associations, conferences, and physical education experiential learning course opportunities. Additional survey results were obtained from the Renaissance Group Survey administered to UNI student teachers. The UNI Placement and Career Services Graduate Follow-up Report was used to obtain data on the employment of recent physical education graduates. NOTE: (Outcome I was assessed using the Overall Mean of Question #1 on the Student Teaching Evaluation form.) (Outcome II was assessed using the Overall Percentage of Students passing each physical fitness test. In other words, the results of each test were totaled to provide an overall percentage. Starting in 2000, these tests were administered as part of 420:053.) (Outcome III was assessed using the Overall Mean of Questions #2, #3, and #4 on the Student Teaching Evaluation form.) (Outcome IV was assessed using the Overall Mean of Questions #5, #6, #7, and #8 on the Student Teaching Evaluation form.) (Outcome V was assessed as part of 420:173. The assessment was based on the number of students participating in professional activities. The competency rubric consisted of Unacceptable, Acceptable, and Outstanding. Students not completing professional activities for classes and not doing additional experiences were categorized as Unacceptable. Students completing all required professional activities and attending local or state conferences/speakers not required for class were rated as Acceptable. Students completing all acceptable requirements plus attending a National Convention/Conference, service as PE Club officer, or volunteering time in a physical activity leadership role was classified as Outstanding.) C. Findings. Outcome I. Be knowledgeable about concepts and principles relating to Human Movement. Year 2002-2003 2003-2004 Findings rating Analysis Modifications Outcome II. Be able to perform a variety of movement skills. Year 2002-2003 2003-2004 Findings % passed % at risk % passed % at risk Analysis Modifications Outcome III. Understand students and the process of learning. Year 2002-2003 2003-2004 Findings rating Analysis Modifications Outcome IV. Demonstrate the ability to teach effectively to both groups and individuals. Year 2002-2003 2003-2004 Findings rating Analysis Modifications Outcome V. Understand responsibilities and opportunities in order to continue to develop as teachers and leaders throughout their careers. Year 2002-2003 Findings % Outstanding % Acceptable % Unacceptable Analysis Modifications 2003-2004 D. Results. A review of the outcomes assessment findings suggests that E. Planned modifications. Planned modifications to the undergraduate physical education program include adding two new courses: Introduction to Physical Education (420:0XX) and Senior Seminar in Physical Education (420:1XX). The purpose of the introductory course will be to develop an awareness of the types of programs and their requirements available in the field, introduce student outcome assessment and portfolios, discuss technology in physical education, and provide an overview of various professional associations and journals. The Senior Seminar will serve as a capstone course in which students present portfolios, learn about licensure and evaluations, and discuss program promotion and professionalism upon entering the field. Faculty will continue to discuss and evaluate the curriculum to ensure that the student’s needs are being met. Specifically, both the disciplinary knowledge core and the skill/activity content areas will be reevaluated. With the proposed change in student outcomes assessment explained in the following paragraphs, the infusion of technology into the curriculum will receive even greater emphasis. The present student outcomes procedure is also being modified to meet the NASPE/NCATE Standards as the Division prepares for NASPE/NCATE accreditation. The Division has identified three critical stages for student outcome assessment. These are pre-admission, pedagogical content, and student teaching stages. The following lists the benchmarks for each critical stage and current data available. This data will be collected for the next five years in preparation for future NASPE/NCATE accreditation efforts. During the Pre-admission Stage teacher education candidates demonstrate competence for NASPE Standards: Standard 1: Content Knowledge, Standard 2: Growth and Development, Standard 8: Reflection, and Standard 9: Technology and Standard 10: Collaboration. Teacher candidates address these Standards by completing the following tasks. Benchmark % program completers unacceptable level Pre-admission Stage % program completers acceptable level % program completers target level Basic Skill analysis project Skill competence & proficiency Observational Analysis of Children Motor Behavior Task Field Experience Reflections on Diversity Use of Technology Engage in Professional Opportunities During the Pedagogical Content Stage teacher education candidates demonstrate competence for NASPE Standards: 1: Content Knowledge, Standard 2: Growth and Development, Standard 3: Diversity, Standard 4: Management and Motivation, Standard 5: Communication, Standard 6: Instruction, Standard 7: Student Assessment, Standard 8: Reflection, Standard 9: Technology, and Standard 10: Collaboration. These standards are addresses by teacher education candidates by completing the following tasks. Benchmark Pedagogical Content Stage % program % program % program completers completers completers target unacceptable level acceptable level level Mechanical Analysis Philosophical Statement Planning for Developmental Stage Teaching based on Learning Styles Planning based on Individual Differences Management Plan Teaching of Special Needs Students (Adapted Physical Ed.) Teaching at Price Laboratory School (Methods) Power Point Presentation Assessment Plan Reflections on Teaching & Student Learning Collaboration with Teachers in the Field During the Student Teaching Stage teacher education candidates demonstrate competence in all of the NASPE Standards by completing a Teacher Work Sample Project. This project requires student teachers to design and teach a comprehensive unit. Before they teach the unit, they describe contextual factors, identify learning goals based on NASPE and district content standards, create an assessment plan designed to measure student performance before (pre-assessment), during (formative assessment), and after (post-assessment), and plan for their instruction. After they teach the unit, they analyze student learning and reflect upon and evaluate their teaching as related to student learning. Benchmark Student Teaching Stage % program % program completers completers unacceptable level acceptable level % program completers target level Teacher Work Sample The University via the department of their major recommends students for teacher licensure. Teacher education candidates that do not meet the predominance of the preceding outcomes at the acceptable level will not be recommended for licensure.