Advanced UNIX programming Fall 2002 Instructor: Ashok Srinivasan Lecture 23
advertisement

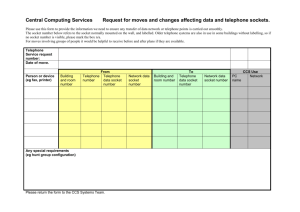
Advanced UNIX programming Fall 2002 Instructor: Ashok Srinivasan Lecture 23 Acknowledgements: The syllabus and power point presentations are modified versions of those by T. Baker and X. Yuan Announcements • Reading assignment – Chapter 7 • Sections 7.1 – 7.6 and 7.9 – 7.11 – Chapter 8 – Midterm next Monday Week 9 Topics • Socket options – getsockopt, setsockopt – fcntl – ioctl • Introduction to UDP – TCP vs UDP – UDP interface Socket options • getsockopt, setsockopt – General socket options – IP options – TCP options • fcntl • ioctl getsockopt, setsockopt – #include <sys/socket.h> int getsockopt (int sockfd, int level, int optname, void *optval, socklen_t *optlen); int setsockopt(int sockfd, int level, int optname, const void *optval, socklen_t optlen); • The level includes general socket options (SOL_SOCKET) and protocol-specific options (for IP, TCP, etc). • Option value can be of different types: pointers to int, in_addr, timeval, etc General socket options • level = SOL_SOCKET, optnames = – SO_BROADCAST • Permit sending broadcast datagram – SO_KEEPALIVE • For TCP only, automatically send a keepalive message when inactive for 2 hours (can be modified) – SO_LINGER • for TCP only, determines behavior on close – SO_RCVBUF, SO_SNDBUF • Send and receive buffer size General socket options (continued) • level = SOL_SOCKET, optnames = – SO_RCVLOWAT, SO_SENDLOWAT • low watermark – affects the select system call – SO_RCVTIMEO, SO_SNDTIMEO • Inherent timeout time (disabled by default) – SO_TYPE • Socket type: SOCK_STREAM and SOCK_DGRAM – Etc. IP options • Allows packets sent through a socket to have certain behavior – For example, source routing – level = IPPROTO_IP • optname (manipulating IP header fields) – IP_OPTIONS – IP_RECVDSTADDR – IP_RECVIF – IP_TOS – IP_TTL – Etc. TCP options • level = IPPROTO_TCP, optname = – TCP_KEEPALIVE • Set the time – TCP_MAXRT • Maximum retransmission time – TCP_MAXSEG • Maximum segment size • See example1.c fcntl and ioctl • fcntl – File control on open files • Set file descriptor flags (FD_CLOEXEC) • Non-blocking mode, etc. • ioctl – Some I/O control operations