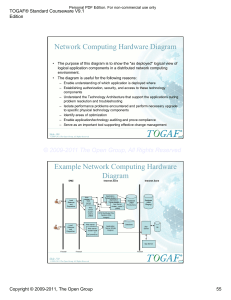
Building a prototype and testing system for processing GIFTS data
advertisement

Building a prototype and testing system for processing GIFTS data Maciek Smuga-Otto, SSEC Ray Garcia, Bob Knuteson, Erik Olson, Jason Otkin, David Tobin, CIMSS 2 5 th A N N I V E R S A R Y C I M S S GIFTS data processing: Background, Requirements, Architecture The Geosynchronous Imaging Fourier Transform Spectrometer (GIFTS) instrument will combine high spectral resolution soundings associated with Fourier Transform Spectrometers (FTS) with high spatial and temporal resolution, creating three-dimensional near-real time views of atmospheric radiance, temperature, water vapor, and winds. The Data Processing Pipeline Requirements for data processing software * High Throughput: process 1.5 Terabytes of data per day. * Low Latency: generate critical products within 5 minutes of gathering observation. * Flexibility: Allow for easy development, testing and staging of new processing algorithms. * Longevity: Software will evolve over a period of years to decades. * Reproducibility: Record detailed processing history of data. * Low Cost: Use off-the-shelf cluster hardware and leverage existing software technologies where possible. The Cluster Environment Master Node Monitoring Interface Data Channel Control Channel Audit Database Unprocessed Level 0 Data Input Delivery Monitoring Channel Processed Level 1 Data Output Delivery Worker Node Worker Node Worker Node Worker Node Worker Node Worker Node Worker Nodes Reference Database Science Pipeline Software Target Architecture Diagram System Design Snapshot Stream of incoming observations (interferograms) together with metadata Separate by band, (and optionally by scan direction and pixel) Data path: Interferograms Initial FFT (Ifg to Spectrum) Stage Complex Spectra Nonlinearity (and optionally, Tilt-correction) Stage create context from blackbody observations use context to apply correction create context from blackbody observations use context to calibrate Input Delivery Cluster for processing L0-L1 Pipeline Nonlinearity study Stage Design of software layout at a single compute node of the cluster 7 node research cluster at CIMSS Complex Spectra Radiometric Calibration Stage Front End Processor Metadata path: Retrieve records for time, band, scan direction, and (optionally) pixel index of incoming observations Data Dictionary Symbols Radiometric Calibration Study Stage requires refers to Connection Specification Data Bus Real Calibrated Spectra Capsule Interfaces: Ports, Function Specification requires implements satisfy refers to refers to Finite Field of View Correction Stage Pipeline Reference Database Instance(s) generates Flanging Compiler Cluster for processing L1-L2 Pipeline Data Archive and Distribution Real Calibrated Spectra Spectral Resampling Stage Real Calibrated Spectra generates Bundle reference (audit) metadata with outgoing calibrated spectra Breakdown of Pipeline Stages uses uses Connection Source code uses uses ESML describing binary protocols emits Connection Support Library generates describes Object code Baseline RDF Vocabulary Mosaic Generation Reshape Data Cubes Diagram of cluster deployment plan is published to is published to Build RDF Invocation Records include URI of assigns include Data UUIDs are recorded by is published to WWW server Deployment Framework uses generates includes URI of refers to Language Compiler includes URI of Template RDF Cluster processing of Winds Capsule Source Code uses generates represents Spectral Calibration Study Stage (Research) imports describes describes generates use context to calibrate responds to Binary Protocols consulted by Elements provided for every new pipeline configuration Audit Service Global Infrastructure elements provided once Automatically Generated elements Pre-existing thirdparty elements Graph of logical dependencies between all software components of system