The new programme of EU funding for research and innovation UKRO’s Mission:
advertisement

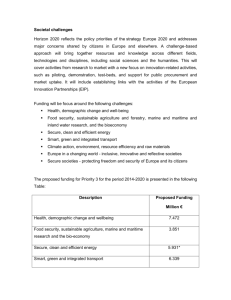
The new programme of EU funding for research and innovation Eevi Laukkanen University of Warwick, 21 November 2013 UKRO’s Mission: “To promote effective UK engagement in EU research, innovation and higher education activities” The Office: • Is based in Brussels, was established in 1984 • Is sponsored by the seven UK Research Councils • Around 130 research organisations subscribe to UKRO UKRO services: offering a suite of quality services to help subscribers and sponsors to make informed decisions on participating in EU programmes Policy work: supporting UK input into European research policy development and implementation Brussels liaison: establishing and maintaining contacts with the European Institutions and other major Brussels stakeholders in research and innovation. 1 UKRO Portal: tailored news articles and clear and accessible web pages on the latest in EU funding Enquiry service: individual support through your dedicated European Advisor Annual briefing visits: bespoke training for your institution Meeting room: a venue in Brussels Tailored news articles on EU funding • Calls for proposals • Funding and policy news • Events, partner searches, job opportunities Web pages on EU research programmes and policy Email alert function/ news by topic Daily, weekly, only on your discipline? Personalise your account to best meet your needs! Create your profile today! 2 UK National Contact Point: • Marie Curie Actions www.ukro.ac.uk/mariecurie • European Research Council www.ukro.ac.uk/erc European RTD Insight: Free monthly publication funded by the British Council UKRO training and development programme: complementing annual UKRO Annual Conference: a key event for EU policy and networking visits Introduction - 10 year strategy aimed at making the EU more dynamic and competitive - Three key drivers: Smart, sustainable and inclusive growth Headline targets 75% of the population aged 20-64 should be employed 3% of the EU's GDP should be invested in R&D The share of early school leavers should be under 10% and at least 40% of younger generation should have a tertiary degree The "20/20/20" climate/energy targets should be met 20 million fewer people should be at risk of poverty 3 Seven flagship initiatives: Innovation Union Youth on the move A digital agenda for Europe Resource efficient Europe An industrial policy for the globalisation era An agenda for new skills and jobs European platform against poverty The European Union’s funding instrument for research and innovation from 2014-2020 • Budget of € 70.2 billion • From research to innovation – from basic research to bringing ideas to the market • Focus on societal challenges EU society is facing (e.g. health, clean energy, food security, integrated transport) • Promise of simplified access for all Horizon 2020 overarching priority: Exiting the economic crisis and sustainable growth Key features: • Concentrates on key societal challenges • Focuses resources on areas of high growth and innovation potential • Key measures to support industrial leadership, particularly innovative SMEs • Leverage private investment in key technologies (PPPs, Joint Technology Initiatives) • Encourages pooling of resources through Public Public partnerships / ERA-NETs • Help overcome the innovation divide 4 Key features are complemented by: • More open, bottom up areas • Significant investment in excellence • European Institute of Innovation and Technology: building Knowledge and Innovation Communities (KICs) • Work of the Commission’s own Joint Research Centre (JRC) for scientific support to policy FP7 Framework Programme Research themes SME participation important Growing importance of innovation Range of funding rates, complex rules Horizon 2020 Integrates FP, EIT, CIP Societal Challenges Strong industry focus overall Covering the entire cycle from basic idea to market Single reimbursement rate for all 28 EU Member States (Croatia joined in 2013) Associate Countries (similar list to FP7 expected) • Still under negotiation • Some might not sign agreement in time for Horizon 2020 start but can still apply as long as the agreement is signed in time for grant signature. Third countries (funding will depend on GDP) • BRIC no longer eligible for automatic funding 5 2014-2016 Strategic Programme Aims at ensuring a coherent, evidence-based implementation Will guide the preparation of the work programmes Defines areas of special focus for the first work programmes 2014-2015 Work Programmes Two-year work programmes Common topics structure: “Specific challenge”, “Scope”, “Expected Impact”, “Type of action” Smart cities and communities Sustainable food security Water innovation Personalising health and care New ideas for Europe Blue growth Disaster resilience Competitive lowcarbon energy Digital security Waste Mobility for growth Energy Efficiency Excellent Science Industrial Leadership Societal Challenges Health and Wellbeing European Research Council (ERC) Leadership in Enabling and Industrial Technologies (LEIT) ICT, KETs, Space Future and Emerging Technologies (FET) Food security Transport Energy Marie Skłodowska-Curie Actions (MSCA) Climate action Access to Risk Finance Research Infrastructures Societies Security Innovation in SMEs Widening Participation; Science with and for Society European Institute of Innovation and Technology (EIT) EURATOM Joint Research Centre (JRC) 6 Pillar 1 – Excellent Science Total budget = €21.6 billion Overall objective: “to strengthen the excellence of European research” European Research Council 7 The ERC seeks to fund the best ‘frontier research’ proposals submitted by excellent researchers, with excellence as the single peer review criterion. Will fund projects led by a Principal Investigator, if necessary supported by a team (no need for pan-European collaboration). Will operate on a ‘bottom-up’ basis, without pre-determined research priorities. 25 panels in 3 domains which proposals can be submitted to: Physical Sciences and Engineering Life Sciences Social Sciences and Humanities Starting Grants 2-7 years postdoc Up to €1.5-2m for 5 years Consolidator Grants 7–12 years postdoc Up to €2-2.75m for 5 years Advanced Grants Leading researchers Up to €3-3.5m for 5 years Synergy Grants 2 – 4 PIs Up to €15m for 6 years Proof of Concept ERC grant holders €150k for up to 18 months Horizon 2020 general funding rate of 100% direct + 25% indirect costs applies Marie Skłodowska-Curie Actions 8 Operates in a ‘bottom-up’ basis Open to all research and innovation domains – from basic research to market take-up Mobility is a key requirement Aim: develop new knowledge / enhance skills of people behind research and innovation Dissemination and public engagement through public outreach activities Total budget: €6.2bn (compared with €4.7bn in FP7) FP7 ITN Horizon 2020 ITN Innovative Training Networks (Early Stage Researchers) IEF IOF IIF IF Individual Fellowships (Experienced Researchers) CIG IAPP IRSES COFUND RISE COFUND Research and Innovation Staff Exchange (Exchange of Staff) Cofunding or regional, national and international programmes Also: Researchers’ Night Future Emerging Technologies 9 Expanded from ICT and Energy in FP7 to be used as cross-cutting funding scheme Supports alternative ideas, concepts or paradigms of risky or nonconventional nature but with a technological concreteness Open, light and agile Roadmap based research FET Open FET Proactive •‘Fostering novel ideas’ FET Flagships •‘Nurturing emerging themes and communities’ •Individual research projects •Open research clusters •Early ideas and promising new areas •3 topics: Global Systems Science (GSS); Knowing, doing being: cognition beyond problem solving; Quantum simulation •‘Tackling grand Interdisciplinary science and technology challenges’ •Common research agendas •Graphene •Human Brain •Support to Flagships High-Performance Computing (HPC) Strategy Developing the next generation towards exascale 2 call topics Characteristics Types of project • Long Term Vision and breakthrough S&T targeted • Foundational – develop the basis for a new kind of technology • High-Risk – complex projects that cross multiple disciplines • Novelty – new ideas and concepts, not incremental • Interdisciplinary • Non-topical and non-descriptive • Involve new and high-potential research and innovation players • Impact through leading-edge S&T that is more open, collaborative, creative and closer to society Objectives • Early Proof of Principle of a new technological possibility, together with its scientific basis, as foundational contribution for a radically new line of science and technology research; or • Establish a solid baseline of feasibility and potential for a new technological direction, ready for early take-up with an early-stage emerging innovation ecosystem of high-potential actors. Three topics Exploratory: to stimulate the exploration of a variety of directions by building up critical mass of researchers and groups 1. Path finding: translating science into concrete technological directions by projects that build on proof of concept, while high risk, to take them to the next level of development 2. Knowing, doing, being: cognition beyond problem solving • • Renewing ties between disciplines studying knowledge and cognition from various perspectives Potential to boost innovation potential in robotics, materials and cyber systems Global Science System • Improve way scientific knowledge can stimulate and help societal responses to global challenges such as climate change • Highly interdisciplinary • Strong policy implications Quantum simulation 3. • Quantum computation, simulation, communication, metrology, sensing 10 Call Opens Closes Budget FET Open 11 Dec 2013 30 Sep 2014 31 March 2015 29 Sep 2015 77 M 37 M 40 M FET Proactive 11 Dec 2013 1 April 2014 10 + 15 + 10 M FET HPC 1 11 Dec 2013 25 Nov 2014 94 M FET HPC 2 11 Dec 2013 25 Nov 2014 4M FET HPC 3 11 Dec 2013 25 Nov 2014 2M All are single stage applications Research Infrastructures ESFRI Roadmap – identifies new pan-European RIs or major upgrades to existing ones ERIC – legal instrument at EU level to facilitate the joint establishment and operation of RI of European interest Background information at: • http://ec.europa.eu/research/infrastructures 11 FP7 supported: • 73 Integrating Activity networks supporting access to c. 800 RIs for about 7000 users per year • 67 e-Infrastructure projects • 18 design studies for new RIs • 45 preparatory phases of ESFRI projects • Support for construction of ESFRI projects Developing the European Research Infrastructures (RI) for 2020 and beyond: Developing new world class RIs Integrating and opening national RIs of pan-European interest Development, deployment and operation ICT based eInfrastructures Foster innovation potential of RI and their human capital Reinforcing European RI policy and international co-operation Call Opens Closes Developing new worldclass RIs 11 Dec 2013 2 Sept 2014 Budget 70 M Integrating and opening RIs of European interest 11 Dec 2013 2 Sept 2014 90 M E-Infrastructures -Open Access - All others 11 Dec 2013 15 Apr 2014 2 Sept 2014 13 M 82 M Support to Innovation, Human Resources, policy and international operation 11 Dec 2013 2 Sept 2014 22 M All are single stage applications 12 Pillar 2 – Industrial Leadership (€ million, 2014-2020) Strategic investments in key technologies (e.g. advanced manufacturing, micro-electronics) underpin innovation across existing and emerging sectors Europe needs to attract more private investment in research and innovation Europe needs more innovative SMEs to create growth and jobs Emphasis on combining enabling technologies to find solutions for societal challenges – particularly energy efficiency targets, sustainability and climate change objectives 13 Strong focus on industrial involvement and applied research Developing industrial capacity in focus areas: • Key Enabling Technologies (KETs) Micro- and nano-electronics Photonics Nanotechnologies Advanced Materials Biotechnology Advanced Manufacturing and Processing KETs - Combining several key enabling technologies for advanced products TRL 1 Basic principles observed TRL 2 Technology concept formulated TRL 3 Experimental proof of concept TRL 4 Technology validated in lab TRL 5 Technology validated in relevant environment (industrial environment in the case of KETs) TRL 6 Technology demonstrated in relevant environment (industrial environment in the case of KETs) TRL 7 System prototype demonstration in operational environment TRL 8 System complete and qualified TRL 9 Actual system proven in operational environment (competitive manufacturing in the case of KETs; or in space 14 Nanotechnology and Advanced materials • Bridging the gap between nanotechnology research and market • Nanotechnology and advanced materials for more effective Healthcare • Nanotechnology and advanced materials for low carbon energy technologies and energy efficiency • Cross-sector potential of Nanotechnology and Advanced Materials to drive competitiveness and sustainability • Safety of nanotechnology-based applications and support for the development of regulation • Addressing generic needs in support of governance, standards, models and structuring in nanotechnology, advanced materials and production NB: Based on draft. Subject to change Biotechnology • Cutting-edge biotechnologies as future innovation drivers Synthetic biology New bioinformatics • Biotechnology based industrial processes driving competitiveness and sustainability Widening industrial application of enzymatic processes Downstream processes unlocking biotechnological transformations • Innovative and competitive platform technologies Metagenomics as innovation driver NB: Based on draft. Subject to change Micro- and nano-electronics Photonics Advanced Manufacturing and Processing Contained in ICT work programme • Implemented through three PPPs: Factories of the Future: FoF Energy Efficient Buildings: EeB Sustainable Process Industries: SPIRE • Roadmaps of PPPs in public domain Also contribution topics to Societal Challenges • Waste – moving towards a circular economy through industrial symbiosis • Transport – next generation of batteries for fully electric automotive applications 15 New generation of components and systems Advanced Computing Future Internet Content technologies and information management Robotics Micro- and nano-electronic technologies/ Photonics Cross-cutting and horizontal activities and International Co-operation Robotics PPP Advanced 5G PPP Photonics PPP To foster a cost-effective competitive and innovative space industry and research community to develop and exploit space infrastructure to meet future Union policy and societal needs • Develop innovative space technology from idea to demonstration in space • Use space data, incl. Earth Observation data, for scientific, public and commercial purposes • Work with Member States’ and European Space Agency research activities • Boost Space industry competitiveness and capacity for innovation • Use European space infrastructure to full capacity • International cooperation in space science and exploitation Note that infrastructure development of Galileo and GMES (now Copernicus) funded outside Horizon 2020 Funding for single beneficiaries for investment in research and innovation projects. Two types of funding will be provided: Debt funding: loans and guarantees for investment in a project Equity funding: investment of capital in a project Funding is mainly designed for early stage SMEs, or in some cases at the expansion stage Some risk financing for a basic or applied research project by a public organisation (university, research institute) is also planned, under the new ‘Risk-Sharing Finance Facility’ Funds will be managed by the European Investment Bank 16 “The specific objective is to stimulate growth by means of increasing the levels of innovation in SMEs, covering their different innovation needs over the whole innovation cycle for all types of innovation, thereby creating more fast-growing, internationally active SMEs.” Replaces Research for SMEs instrument (R4SME) Dedicated SME instrument, only SMEs can apply and hold grants Target highly innovative SMEs looking to develop and grow in international environment Single company or consortia of SMEs only Allows for out-sourcing of research through subcontracting Three stage support through innovation cycle One project can access all three in order One application per year, in all fields across LEIT and Societal Challenges Stage 1: Feasibility • 6 month project • ~ €50k lump sum funding • to assess technological / commercial potential of project Stage 2: Innovation Activity • 12 – 24 month duration • €1m - €3m funding • Emphasis on demonstration and market replication, encouraging the involvement of end users or potential clients Stage 3: Commercialisation phase • No direct funding • Simplified access to debt and equity financial instruments • Assistance with IPR protection Pillar 3 – Societal Challenges 17 Concerns of citizens and society + EU policy objectives Breakthrough solutions come from multi-disciplinary collaborations, including social sciences and humanities Addressing challenges requires full research & innovation cycle, from research to market Focus on policy priorities without predetermining technologies or types of solutions to be developed fewer but broader and less prescriptive topics Total budget €26.2 bn Societal Challenges € bn SC1 Health, demographic change and wellbeing 6.6 SC 2 Food security, sustainable agriculture, marine and maritime research & the Bioeconomy 3.4 SC3 Secure, clean and efficient energy 5.2 SC4 Smart, green and integrated transport 5.6 SC5 Climate action, environment, resource efficiency and raw materials 2.7 SC6 Inclusive, innovative and reflective societies 1.2 SC7 Secure societies 1.5 Food Challenge Energy Challenge Transport Challenge Climate Challenge Health Challenge Security Challenge IIR Challenge 18 Health, demographic change and wellbeing Horizon 2020 Health - Context JPIs EIP Active and Healthy Ageing Work programme Health, Demographic Change and Wellbeing Health for Growth Commission healthcare programme Ambient Assisted Living MS and EU Joint Programme Research Innovation Deployment Draft Work Programme for 2014-2015: Calls divided into the 8 specific activity areas Understanding health, ageing and diseases Effective health promotion, diseases prevention, preparedness and screening Improving diagnosis 3 topics / €120M Innovative treatments and technologies Advancing active and healthy aging Integrated, sustainable, citizen-centred care 6 topics / €302M 6 topics / €119M 3 topics/€207.2M 4 topics / €73.6M 7 topics/€185.6M 5 topics / €84M Improving health information, data exploitation and providing an evidence base for health policies and regulation Co-ordination activities e.g. AHA EIP; More years, Better 15 topics / €67M Lives; Global Alliance for Chronic Diseases Note: Many two stage applications – reflects broad response base sought 19 Innovative Medicines Initiative homepage http://www.imi.europa.eu/ European and Developing Countries Clinical Trials Partnership homepage - http://www.edctp.org/ More Years Better Lives homepage - http://www.jpdemographic.eu/ Joint Programme on Neurodegenerative Disease homepage http://www.jp-demographic.eu/ Joint Programme on Antimicrobial Resistance homepage http://www.jpiamr.eu/ Food Security, Sustainable Agriculture, Marine and Maritime Research and the Bio-economy 2014-2015 Calls divided into 3 specific activity areas: 1. Sustainable food security • Sustainable food production systems • Safe food and sustainable consumption • Global drivers of food security 2. Blue Growth: Unlocking the potential of the Oceans • Sustainably exploiting the diversity of marine life • New offshore challenges • Ocean observation technologies/systems • Horizontal aspects, socio-economic sciences, innovation, engagement with society and ocean governance 20 3. Innovative, sustainable and inclusive bioeconomy • Sustainable agriculture and forestry • Sustainable and competitive bio-based industries • Cross-cutting actions covering all activities + Contributions to other focus areas: Waste Useful links: European Commission pages on EU-funded research on the bioeconomy, plus details of new EU Bioeconomy Strategy: http://ec.europa.eu/research/bioeconomy/policy/ European Commission pages on EU ‘Blue Growth’ strategy: http://ec.europa.eu/maritimeaffairs/policy/blue_growth/index_en.htm European Innovation Partnership on Agriculture: http://ec.europa.eu/agriculture/eip/ Joint Programming Initiative on Agriculture, Food Security and Climate Change (UK among the participating countries): http://www.faccejpi.com/ Secure, Clean and Efficient Energy Draft Work Programme 2014-2015 Calls divided into 3 specific activity areas: 1. Energy efficiency Bring to mass market technologies and services for a smart and efficient energy use Unlock the potential of efficient and renewable heating-cooling systems Foster uptake of energy efficiency technologies in industry Innovative finance for sustainable energy 2. Low-cost, low-carbon energy Accelerating the development of transformative energy technologies Renewable electricity and heating/cooling Modernising the single European electricity grid Enhanced energy storage technologies Sustainable biofuels and alternative fuels for transport Sustainable use of fossil fuels Social, environmental and economic aspects of the energy system 3. Smart Cities and Communities Commercial-scale solutions with a high market potential, integrating energy, transport and ICT sectors 21 European Commission, DG Research & Innovation / Energy website SET Plan webpages European Commission, DG Energy website Fuel Cells and Hydrogen Joint Technology Initiative (FCH JTI) Knowledge and Innovation Community on InnoEnergy http://ec.europa.eu/research/energy/index_en.cfm http://ec.europa.eu/energy/technology/set_plan/set_plan_en.htm http://ec.europa.eu/energy/index_en.htm http://www.fch-ju.eu/ http://www.kic-innoenergy.com/ Climate Knowledge and Innovation Community Smart Cities and Communities EIP http://www.climate-kic.org/ http://ec.europa.eu/energy/technology/initiatives/smart_cities_en.htm Smart, green and integrated transport Aviation Four broad lines of activity: 1) Resource-efficient transport that respects the environment and public health Rail Mode of transport Road 2) Better mobility and accessibility, less congestion, more safety and security Waterborne Urban mobility 3) Global leadership for the European transport industry 4) Socio-economic and behavioural research and forward looking activities for policy making Transport integration Logistics Intelligent transport systems Infrastructures 22 European Commission’s Transport website http://ec.europa.eu/research/transport/index_en.htm Transport Research & Innovation Portal http://www.transport-research.info/web/index.cfm The European Green Cars Initiative website http://www.green-cars-initiative.eu/public/ Clean Sky website http://www.cleansky.eu/ 2011 Transport White Paper - Roadmap to a Single European Transport Area http://ec.europa.eu/transport/themes/strategies/2011_white_paper_en.htm 2012 Transport Communication – Research and Innovation for Europe’s Future Mobility http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=COM:2012:0501:FIN:EN:PDF Flightpath 2050 – Europe’s Vision for Aviation (2011) http://ec.europa.eu/transport/modes/air/doc/flightpath2050.pdf Climate action, resource efficiency and raw materials Fighting and adapting to climate change Protecting the environment, sustainably managing natural resources and ecosystems Sustainable supply of nonenergy and nonagricultural raw materials To achieve: Transition to a green economy through eco-innovation + Global environmental observation and information systems Contributing to focus areas Waste: a resource to recycle, reuse and recover raw materials Water innovation: boosting its value for Europe 23 1. Waste: A resource to recycle, reuse and recover raw materials • Addressing whole production and consumption cycle – waste prevention, design of processes and products for recyclability, reuse, waste management 2. Water innovation: Boosting its value for Europe • Integrated approaches to water and climate change • Bringing innovative water solutions to the market 3. Fighting and adapting to climate change • Better understanding of climate change and reliable projections • Innovative adaption and risk prevention measures • Climate change mitigation policies 4. Sustainably managing natural resources and ecosystems • Functioning of ecosystems, interactions with social systems and their role in sustaining economy and human beings • Support for decision making and public engagement 5. Ensuring the sustainable supply of non-energy and nonagricultural raw materials • Better knowledge on availability • Promotion of sustainable supply (exploration, extraction, processing, recycling and recovery) • Alternatives for critical raw materials • Improve social awareness 6. Enabling the transition towards a green economy through ecoinnovation • Strengthen eco-innovation and market uptake • Innovative policies and societal changes • Resource efficiency through digital systems 7. Developing comprehensive and sustained global environmental observation and information systems European Commission pages on EU-funded Environmental research http://ec.europa.eu/research/environment/index_en.cfm European Innovation Partnership on water: • http://ec.europa.eu/environment/water/innovationpartnership/index_en.htm Joint programming initiatives: • Water: http://www.waterjpi.eu/home • Oceans: http://www.jpi-oceans.eu/home • Climate: http://www.jpi-climate.eu/home Life+ programme: • http://ec.europa.eu/environment/life/funding/lifeplus.htm 24 Europe in a Changing World: Inclusive, Innovative and Reflective Societies Overcoming the crisis: new ideas, strategies and governance structures Young generation in an innovative, inclusive and sustainable Europe Reflective societies: cultural heritage and European identities To achieve: inclusive and innovative European societies in a context of unprecedented transformations and growing global interdependencies Europe as a global actor New forms of innovation 1. Overcoming the crisis: new ideas, strategies and governance structures for Europe • The reform of the EU economic governance structure to better secure financial and economic stability • The social, political and cultural consequences of and responses to the crisis • Understanding the evolution of the crisis • The impacts of broader global trends on the EU’s economy 2. Young generation in an innovative, inclusive and sustainable Europe • The situation of young people, their capabilities, prospects and needs – from the economic, social and individual perspective • How to ensure the full participation of young people in an innovative, inclusive and sustainable Europe? 25 3. Reflective societies: cultural heritage and European identities • European diversities, cultural heritage and identity formation - ‘Unity in diversity’ • Intellectual, artistic and historical legacy of the EU • Digital technologies for European cultural heritage 4. Europe as a global actor • International cooperation in research and innovation • Research to support Europe’s role as a global actor 5. New forms of innovation • Social and public sector innovation, new business models • Modernisation of public administration, incl. ICT-enabled open government • Uptake of technologies in education, training and inclusion European Commission pages on Socio-economic Sciences and Humanities research http://ec.europa.eu/research/social-sciences/index_en.html European Commission pages on the Innovation Union http://ec.europa.eu/research/innovation-union/index_en.cfm EU vision for ‘Deep and Genuine Economic and Monetary Union’ http://ec.europa.eu/commission_20102014/president/news/archives/2013/04/20130430_1_en.htm Youth on the move http://ec.europa.eu/social/main.jsp?catId=950&langId=en Joint Programming Initiative (JPI) on Cultural Heritage http://www.jpi-culturalheritage.eu/ Secure Societies – Protecting Freedom and Security of Europe and its Citizens 26 Fighting Crime and Terrorism • Forensics topics • Law enforcement capabilities • Urban Security • Ethical /Societal Dimension Border security & External security • Maritime border security • Border crossing points • Supply chain security • Information management • Conflict prevention and peace building • Ethical/societal dimension Digital security: cybersecurity, privacy and Disaster-resilience trust • Crisis Management • Privacy • Disaster resilience & Climate • Access control Change • Secure information sharing • Critical infrastructure protection • Trust eServices • Communication technologies and interoperability • Risk management and assurance models • Ethical / Societal Dimension • The role of ICT in critical infrastructure protection European Commission pages on EU-funded research on Security: • http://ec.europa.eu/enterprise/policies/security/index_en.htm EU Security Industrial Policy Communications • http://ec.europa.eu/enterprise/policies/security/industrialpolicy/communication/index_en.htm EU Internal Security Strategy • http://ec.europa.eu/dgs/home-affairs/what-we-do/policies/internalsecurity/internal-security-strategy/index_en.htm EU Cyber Security Strategy • http://ec.europa.eu/dgs/home-affairs/what-we-do/policies/internalsecurity/internal-security-strategy/index_en.htm Cross-cutting aspects: Science with and for Society, Social Sciences and Humanities, ICT 27 Objective is to “build effective cooperation between science and society, recruit new talent for science and pair scientific excellence with social awareness and responsibility” Better alignment of the research and innovation process and its outcomes with the values, needs and expectations of European society = Responsible Research and Innovation Cross-cutting issue in Horizon 2020 + dedicated work programme to further develop, disseminate and support good RRI practices all across Europe 1. Making science education and careers attractive for young people 2. Promoting gender equality in research and innovation 3. Integrating Society in Science and Innovation 4. Developing governance for the advancement of Responsible Research and Innovation (RRI) 5. Networking and sharing knowledge about Science with and for society European Commission pages on Science in Society: http://ec.europa.eu/research/science-society/index.cfm “Social sciences and humanities (SSH) research will be fully integrated into each of the general objectives of Horizon 2020” Excellent Science Base • SSH fully supported under the ERC, MCSA and research infrastructures • FET calls for “intense collaboration across disciplines…cognitive sciences, social sciences or economics…and with the arts and humanities” • “Societal engagement on responsible nanotechnology” Industrial Leadership • “Innovative materials for creative industries” • “Developing smart factories that are attractive to workers” • “Human-centric digital age” 28 “SSH will be mainstreamed as an essential element of the activities needed to tackle each of the societal challenges” Health Food security • “Individual empowerment for selfmanagement of health” • “A systems approach for the reduction, recycling and reuse of food waste” • “Promoting mental wellbeing in the ageing population” • “Optimising the efficiency and effectiveness of health care systems and reducing inequalities” • “Unlocking the growth potential of rural areas through enhanced governance and social innovation” • “Transport societal drivers” • “The human factor in the energy system” • “Consumer engagement for sustainable energy” • “Tackling malnutrition in the elderly” Transport • “Traffic safety analysis and integrated approach towards the safety of Vulnerable Road Users” Energy • “Socio-economic research on energy efficiency” Climate action • “More effective ecosystem restoration in the EU” • “The economics of climate change and linkages with sustainable development” Generally referred to in call topics Skills sets necessary Security • “The role of new social media networks in national security” • “Better understanding the links between culture and disaster” • “Impact of climate change in 3rd countries on Europe’s security” • economics, sociology, dissemination, market research, implementation and acceptability planning, management of market change, behaviour and social interaction studies, ethical studies etc. • 25% of technological change is new science • 75% of technological change is achieving acceptance (Vilnius) Inter / multidisciplinary approach Problem solving dimension to calls 29 Excellent Science ICT in bottom up schemes: ERC, MSCA, FET, and eInfrastructures Industrial Leadership Societal Challenges ICT in LEIT – micronano-electronics KET and photonics KET ICT embedded in Societal Challenges Health: e-health, self management of health, improved diagnostics, improved surveillance, health data collection, active ageing, assisted living; • “Advancing active and healthy ageing with ICT: Service robotics within assisted living environments” • “Advancing active and healthy ageing with ICT: early risk detection and intervention” • “Advanced ICT systems and services for integrated care” • “self-management of health and disease: decisional support systems and patient empowerment supported by ICT Food: • Ocean observation technologies “Acoustic and imaging technologies” • “Forecasting and anticipating effects of climate change on fisheries and aquaculture” • “Improved data and management models for sustainable forestry” Energy: smart cities; energy efficient buildings; smart electricity grids; smart metering; • “New ICT based solutions for energy efficiency” • “Modelling and analysing the energy system, its transformation and impacts Transport: smart transport equipment, infrastructures and services; innovative transport management systems; safety aspects • “Intelligent infrastructure” • “Connectivity and information sharing for intelligent mobility” • “System modelling and life-cycle cost optimisation for waterborne assets Climate: ICT for increased resource efficiency; earth observation and monitoring • “Integrated approaches to water and climate change” • “Harnessing EU water research and innovation results for industry, policy makers and citizens” • “Making Earth Observation Data usable for ecosystem modelling and services” 30 Societies: Digital inclusion; social innovation platforms; e-government services; eskills and e-learning; e-culture • • • • • “Advanced 3D modelling for accessing and understanding European cultural assets” “Innovation ecosystems of digital cultural assets” “Innovation in the public sector by using emerging ICT technologies” “ICT-enabled open government” “Platform for ICT for learning and inclusion” Security: Cyber security; ensuring privacy and protection of human rights on-line • “Cybercrime on Industrial Control systems protection” • “Tools and infrastructure for the fusion, exchange and analysis of big data for forensic investigation” • “Internet Forensics to combat organized crime” • “Detection and analysis of terrorist generated content on the Internet” • “The role of new social media networks in national security” • “Secure Information Sharing” • “The role of ICT in Critical Infrastructure Protection” How does it work in practice? Official programme launch 1 January 2014 Before then: First Calls for Proposals expected on 11.12.2013 Draft 2-year Work Programme published in the autumn at: http://ec.europa.eu/research/horizon2020/index_en.cfm?pg=h2020 -documents European Commission Participant Portal: to become the main entry point for EU research and innovation funding • Calls will be deposited here, with improved search function! • Proposal submission via Participant Portal • Will also be used for negotiations, project management, evaluators, documentation… 31 Calls SEARCH TOPICS F U N D I N G G U I D E Horizon 2020 COSME Search keywords: climate change Search Search Topics Call Updates Other Funding Opportunities Previous Framework Programmes (FP7 & CIP) Horizon 2020 predefined criteria: Cross‐cutting Key‐Enabling Technologies (KETs) International cooperation ERA‐NET SME Instrument Gender 3 results Socio‐economic science and Humanities Filter options: ◎ Open calls ○ Closed calls ○ Forthcoming calls Sort by: ○Publication date ◎Deadline ○Title ○Call ID Topic: SFS 7 - 2014: Optimising external nutrient inputs in intensive crop production systems in Europe European crop production is facing more and more difficulties in remaining competitive in the global market for many reasons. One of these reasons is certainly the high cost of external nutrient inputs necessary More… Call title: Sustainable Food Security Call identifier: H2020-SFS-2014/2015 Status: Open Deadline: 2014-03-18 Topic: WATER 2 – 2014/2015: Integrated approaches to water and climate change The rising demands of a growing world population for food, water, materials and energy will put increasing pressures on land use, water resources and ecosystems. Energy consumption is expected to increase, More… Call title: Water Innovation: Boosting its value for Europe Call identifier: H2020-WATER-2014/2015 Status: Open Deadline: 2014-03-18 Topic: WATER 5 – 2014/2015: Strengthening international R&I cooperation in the field of water Stay informed RSS feed iCal Email notification Developing countries, especially in Africa, are facing serious challenges for sustaining its development. Sustainable water supply and sanitation is fundamental to the food security, health, survival More… Call title: Water Innovation: Boosting its value for Europe Call identifier: H2020-WATER-2014/2015 Status: Open Deadline: 2014-03-18 32 Publication of work programmes and calls for proposals: • The first work programme will cover 2014 and 2015 Work programme explains what is funded (topics, grant schemes) and the expected policy impact Calls for proposals give details on the timeline (deadline, evaluation, results) and the eligibility criteria Topics structure: “Specific challenge”, “Scope”, “Expected Impact” Structure reflects challenge based approach • Specific challenge Sets context, the problem to be addressed, why intervention is necessary • Scope Delineates the problem, specifies the focus and the boundaries of the potential action BUT without overtly describing specific approaches • Expected impact Describes the key elements of what is expected to be achieved in relation to the specific challenge Evaluation (and therefore success) reflects this structure State any specific requirements • international component, involvement of SME/other stakeholder, use of specific data source (eg GMES), open access/open data pilot Suggest budget required to do the action State what kind of action (i.e. project) is called for Explain any unusual evaluation criteria State whether it is a one or two-stage application process 33 Research and innovation actions (R&I) Innovation actions Co-ordination and support actions (CSA) Prizes Fast-track to innovation SME instrument ERA-NET Cofund Pre-Commercial Procurement (PCP) Public Procurement of Innovative Solutions (PPI) Description • “Action primarily consisting of activities aiming to establish new knowledge and/or to explore the feasibility of a new or improved technology, product, process, service or solution” Funding rate: 100% + 25% indirects Multi-beneficiary • Minimum: three legal entities each of which established in a different Member State or associated country Respond to challenges set in the Societal challenges or Industrial Leadership pillars Bottom up in FET open (directed in FET proactive) Description • “Action primarily consisting of activities directly aiming at producing plans and arrangements or designs for new, altered or improved products, processes or services. For this purpose they may include prototyping, testing, demonstrating, piloting, large-scale product validation and market replication” Funding rate: 70% (100% for non-profit) + 25% indirects Multi-beneficiary • Minimum: three legal entities each of which established in a different Member State or associated country Respond to challenges set in the Societal challenges or Industrial Leadership pillars 34 Description • “Action consisting primarily of accompanying measures such as standardisation, dissemination, awareness-raising and communication, networking, coordination or support services, policy dialogues and mutual learning exercises and studies, including design studies for new infrastructure” Funding: 100% + 25% indirects Mono or Multi-beneficiary • Minimum one legal entity established in a Member State or Associated Country Respond to direction given in the Societal Challenges or Industrial Leadership pillars, and in FET Horizon 2020 collaborative projects are different ! • A strong challenge-based approach – broader topics • Covers whole research to close-to-market continuum • Strong involvement of industry, especially SMEs • Applicants have considerable freedom to come up with innovative solutions – less prescription • Strong emphasis on expected impact • More cross-cutting activities (e.g. SSH, gender, international collaboration) Cross-cutting theme in H2020 LEIT: Factories of the Future Challenge 6: Cultural heritage and European identities Challenge 3: Secure, Clean and Efficient Energy Challenge 6: Europe in a changing world LEIT: Advanced materials Challenge 2: Food Security Challenge 1: Health, demographic change and wellbeing Challenge 6: Europe as a global actor Challenge 5: Climate action Challenge 4: Smart, Green and Integrated Transport 35 Sign up to the UKRO portal and you will receive: Updates on the likely funding priorities for Horizon 2020 in each planned area Updates on key events Updates on call dates and management/financial issues Updates on opportunities to feed in to the programme’s development (i.e. formation of expert advisory groups, evaluator registration, other calls for expressions of interest) ‘UKRO understands’: early information New: UKRO Horizon 2020 Factsheets! Info Day on Horizon 2020 Health Challenge 22 November 2013 Horizon 2020 Energy Challenge – Infoday and brokerage event 5-6 December 2013 Public-Private Partnerships under Horizon 2020 16-17 December 2013 Info Day Horizon 2020 Smart, Green and Integrated Transport challenge 18 December 2013 Info day 2014 Horizon 2020 calls for proposals – Societal Challenge 2 and LEIT Biotechnology 17 January 2014 36 Questions? Contact Email: Eevi.Laukkanen@bbsrc.ac.uk Phone: +32 2 286 9055 37