Disability Research in a Developing Country
advertisement

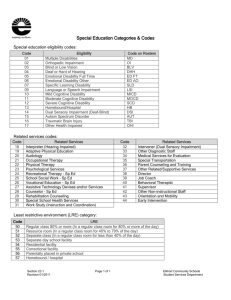
Disability Research in a Developing Country Naila Z. Khan, MBBS, FCPS, PhD (London) Child Development and Neurology Unit Bangladesh Institute of Child Health Dhaka Shishu Children’s Hospital Objective • Demonstrate how research can change the quality of child survival and human lives Presentation Plan • • • • Epidemiological Research: Cross Sectional Studies Evidence-Based Practice: Prospective Studies Public Health issues: Case Studies Future directions Epidemiological Research: Cross-Sectional Studies Newborn, Infant and Child Mortality Trend and Target in Bangladesh 200 180 173 160 152 139 140 120 133 117 116 105 100 80 96 87 94 75 63 60 88 82 66 60 52 48 40 42 65 41 65 52 51 37 35 21 20 0 1982-86 1985-89 1987-91 1989-93 U5MR IMR 1992-96 NMR 1995-99 1999-2003 2004-06 Target 2015 Bangladesh: Mortality declining Disability rising (per 1000) 160 150 140 Child Mortality Child Disability 120 120 100 children/1000 80 68 65 60 40 20 0 1980s Bangladesh Health Watch, 2006 2000s Strategies for Estimating the Prevalence of Disabilities in Populations • Administrative Record Review (schools, clinics, other social services) • Registries • Birth Cohort Studies • Household Censuses, Surveys • Key Informant Surveys • Utility approaches (e.g., DALY) • Two-Stage Prevalence Surveys Underestimates: -Underprivileged -Poor -‘Silent’ ‘Covert’ -Girl child -Very young -Inadequate info Two-Stage Design for Home-based Screening followed by Center-based Assessment of Children with Disabilities in Underserved Populations Screening of All Children Screened + (<20%) Clinical Assessment Disability “True Positive” No Disability “False Positive” Screened – (>80%) Clinical Assessment (10% of screened-) Disability “False Negative” No Assessment (90% of screened -) No Disability “True Negative” The Ten Questions: piloted in 10 countries; major surveys in Bangladesh, Jamaica and Pakistan. Zaman et al, 1990; Khan and Durkin, 1995; >30 publications. Most used instrument world-wide (Maulik and Darmstadt, Pediatrics, 2007) UNICEF, 2008: best measure of children at-risk for disability Only Stage One done in >30 countries 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 • 31 23 18 12 7 a sni o B a ai l h T c n esh oo bli d r u e a p l m ng Re Ca n Ba a ric f A al r t n Ce nd 23 22.3 21.8 22 Disability directly related to Poverty 21.4 21 % screened positive for 20 disability in 19 Bdesh 18 19 18.6 17 16 poorest 2nd 3rd wealth quintile 4th wealthiest Stage Two: Professional Assessment Tools Bangladesh, Jamaica, Pakistan: doctors, psychologists MEDICAL ASSESSMENT -General Developmental Assessment (GDA) PSYCHOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT -Psychometric Tests -Tests of Adaptive Behaviour DIAGNOSIS -Consensual Diagnosis -Impairment, Disability, Handicap (WHO,2001) Selected References: Studies funded by NIH; CDC, USA • • • • • • • • • • • Shrout PE, Newman SC, Design of two-phase prevalence surveys of rare disorders. Biometrics, 1989; 45:549-55. McNamee R, Efficiency of two-phase designs for prevalence estimation. International Journal of Epidemiology, 2003; 32:1072-8. Zaman S, Khan N, Islam S, Banu S, Dixit S, Shrout P, Durkin M, Validity of the Ten Questions for screening serious childhood disability: results from urban Bangladesh. International Journal of Epidemiology, 1990; 19(3):613-20. Durkin MS, Davidson LL, Hasan MZ, Hasan Z, Hauser WA, Khan N, Paul TJ, Shrout PE, Thorborn MJ, Zaman S. Estimates of the prevalence of childhood seizure disorders in communities where professional resources are scarce: results from Bangladesh, Jamaica and Pakistan. Paediatric and Perinatal Epidemiology. 6:166-180, 1992. Durkin M, Khan N, Davidson LL, Zaman SS, Stein ZA. The effects of a natural disaster on child behaviour: evidence for post-traumatic stress. American J Public Health. 83: 1549-1553, 1993. Durkin MS, Davidson LL, Desai P, Hasan ZM, Khan N, Thorburn MJ, Shrout PE, Wang W, Validity of the ten questions screen for childhood disability: results from population-based studies in Bangladesh, Jamaica and Pakistan. Epidemiology, 1994; 5:283-9. Durkin MS, Wang W, Shrout PE, Zaman SS, Hasan ZM, Desai P, Davidson, LL, Evaluating a Ten Questions screen for childhood disability: reliability and internal structure in different cultures. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 1995; 48:657-66. Durkin MS, Hasan ZM, Hasan Z, Uses and limitations of the Ten Questions screen for childhood disability in Pakistan. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 1995; 49(4):431-6. Durkin MS, Khan NZ, Davidson LL, Huq S, Munir S, Rasul I, Zaman SS, Prenatal and postnatal risk factors for mental retardation among children in Bangladesh. American Journal of Epidemiology, 2000; 152:1024-32. Abbey L Berg, Hemayetunnesa Papri, Shamim Ferdous, Naila Z Khan, Maureen S Durkin. Screening Methods for Childhood Hearing Impairment in Rural Bangladesh. Int J Ped Otorhinolaryngol. 2006; 70: 107 – 114. Naila Z. Khan, Shamim Ferdous, Robiul Islam, Afroza Sultana, Maureen Durkin, Helen McConachie. Behaviour problems in young children in rural Bangladesh. J Trop Peds. 2009 Jun; 55(3):177-82. . Evidence for Cross-Cultural Comparability of the 10 Questions Screen for Childhood Disability: Sensitivity 100 Bangladesh Jamaica Pakistan % of serious disability 50 identified 0 e ti iv n og C M or t o Se re u iz n o i is V H ng i r ea Disability Dynamics: Targeting Impairments World Health Organization, ICF, 2001 Normal Disease :body structure and function Reversible Impairment :temporary activity limitation Disability:permanent activity limitation:mild, moderate, severe Irreversible Handicap (poor social participation) WHO, 2001 Prevalence per 1000 Prevalence of Impairment vs. Disability in 5 sites in Bangladesh by PHC/CBR services 50 Good CBR; 40 Good PHC Poor CBR; Good PHC Poor CBR; Poor PHC Poor CBR; Poor PHC 49.18 32.77 31.4 30.21 30 Poor CBR; Very poor PHC 26.03 23.14 23.44 20 10.83 8.55 10 4.07 0 Dhamrai Savar Disability K'ganj N'shingdi Impairment Faridpur Limitations of TQ-based two stage survey 1. Does not address ‘impairments’, focuses on ‘serious’ disabilities 2. Does not screen <2 year olds 3. Stage Two requires multidisciplinary professional teams to assess 4. Stage Two assessment procedures need standardization, especially psychometric tools An Alternative Single Professional Approach: MDI assessment for 2-9 year olds field tested, awaiting publication 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 pr No impairment Impairment e r n g h n y r r x an efle oto oto isio rin eec itio vio izur r m m v ea sp gn eha se e h ss ne v co b iti gro fi im Impairment Khan, Muslima, Darmstadt et al, Pediatrics, 2010 Multidisciplinary professionals (physicians, therapists, special teachers) from Bangladesh, Bhutan and Australia (Fiji) attending the RNDA workshop, Dhaka, September, 2010 Khan, Muslima, McConachie, Darmstadt et al. Validation of home-based neurodevelopmental screening tool for <2 year olds, submitted to Pediatrics, October, 2010 Evidence-Based Practice: Prospective Studies Incidence by Diagnosis: CDC, DSH t men p o l e v al De m r o N PEM ba l /G lo c o r yd o c/H r c i is M ing it n e y/ M path o l a nt ph irme Ence a p n Im Visio nt irme a p m ing i r a e H s ob lem r p h ealt ta l h n e es M culti i MR/ f f i hd peec s / a i on as Aph ress i g e r / lay ic de f i c e lsy sp al Pa r Non b e Cer ep sy Epi l 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 % of children Data from 4800 children, Child Development Center, Dhaka Shishu Children’s Hospital, 2001 Advocacy: Pharmaceuticals restarted manufacturing phenobarbitone SH Banu, trained in GOSH, 1999-2003 How to reach unreached children? RCT: Distance Training Packages • • • Pictorial Manuals used as guidelines and reminders for parents Manuals for: Motor, Speech, Cognitive development, ADL Idea from a VSO, UK physiotherapist Distance Training Package: head control through play activities ↑ •Trained community workers working with mothers in a rural home McConachie, Zaman, Khan et al, J of Peds, 2000, funded by DFID, UK Functional outcomes for all children followed up for two years 2 Z scores on test for adaptive behavior 0 -2 -4 2 14 not as intended 34 34 as intended McConachie et al, J of Peds, 2000 Negative findings 1.One third had difficulty in attending sessions due to travel costs, family restrictions, cultural taboos (McConachie et al, CCHD, 2001) 2. Mortality highest among malnourished and tetraplegic group (Khan et al, DMCN, 1998) 3. Mothers became high risk for psychiatric morbidity (Mobarak et al, J Pediatric Psychology, 2001) (Similar finding PTBs FU: Khan et al, CCHD, 2009; funded by SNL) - most compliance mothers most at risk - ‘burden of caring’ eg. poor sleep, difficulty feeding; behavior problems increased stress - stress decreased in ‘no intervention’ group Seating and Feeding Clinic for children with Cerebral Palsy Outcomes:Before & after Mel Adams, field work in CDC, DSH, obtained PhD from London University, 2008 Adams M, Shilpi AB et al, 2009, submitted to DMCN ; low cost aids, Center for the Rehabilitation of the Paralyzed (CRP): Valerie Taylor Visual improvement by initial visual functions (best results in 6-13 month infants: Humaira Muslima et al, 2000) 45 42 40 35 30 % of 25 improvement 20 in vision 15 10 5 0 29 no functional vision some vision Early intervention for visual impairment (“Show me what my friends can see”: Dhaka Shishu Hospital, 2001) Neurodevelopmental Follow Up of Preterm Infants: Early Identification, Early Intervention Outcomes (Khan NZ, Muslima H, et al, Pediatrics, 2006) At 30 months At 1 month Low risk 6% High risk 55% Serious impairment 23% Moderate risk 39% Mild impairment 45% Normal 32% Rising maternal stress with increasing numbers of visits in a cohort of preterm infants (Khan, Muslima, Parvin, Bhattacharya et al, 2007, submitted to J of Pediatrics) # of vis its low risk high risk Risk for psychiatric morbidity in mothers Establishment of Shishu Bikash Kendra (CDCs) in 14 Government Medical College Hospitals 2008-2009 2009-2010 2010-2011 Public Health issues: Case Studies Media Campaign Against Leaded Petrol Media Campaign Against Leaded Petrol LEAD – FREE BANGLADESH Case Studies: followed by media campaign against leaded petrol Khan NZ, Khan AH. Lead poisoning and psychomotor delay in Bangladeshi children. Lancet.(letter) Feb 27; 353 (9154): 754, 1999 Child Protection: Study of CSA in CWDs Bangladesh Protibondhi Foundation, 2009 Funded by Save the Children, Sweden-Denmark Percentage of sexual abuse and types of disabilities : 111/216 (51%) abused or ‘possibility’ Distribution of age and possibility of sexual abuse and case of sexual abuse Age/Form of N Abuse (7-10) Possibility of Sexual Abuse Sexual Abuse Total % N (11-14) % N (15-18) % Total 24.3%(27) 14 12.61 11 9.90 2 1.80 32 28.28 28 25.22 18 16.21 75.7%(84) 46 40.89 39 35.12 20 18.01 100% (111) Future Directions Changing incidence of neurodevelopmental impairments recorded in the CDC: between 19912000 and 2001- 2006 seizures 36 behavior 43 31 13 cognition 55 28 speech 56 36 11 15 hearing 21 25 vision fine motor 43 34 gross motor 53 53 0 10 20 30 % 40 50 60 2001-2006 1991-2000 Conclusion • Epidemiology, clinical audit, evidence-based research are able to prevent and ameliorate disability • Research and publications based upon the above are able to provide government with valid direction for prevention and care • Changing scenarios need to be determined, at least once in every decade • International donors and researchers need to connect with national professionals, to be able to achieve sustainable changes in the public sector