Cancer immunotherapy - Immune checkpoint
advertisement

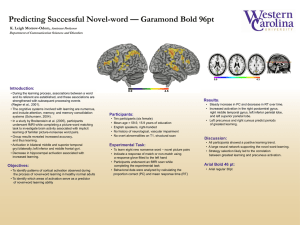
Cancer immunotherapy - Immune checkpoint T cell activation is regulated by stimulatory and inhibitory signals that fine-tune the response and maintain the balance between appropriate recognition and destruction of tumors and inappropriate overstimulation of immune responses. Please see the table for a list of targets that regulate T cell activation. CD28 T cell is activated when: CD80/86 T-cell receptor recognizes an antigen on the surface of the antigen presenting cell (APC). Activated T cell Dendritic cell Co-stimulatory interaction occurs between T cell and APC. PD-1/PD-L1 interaction reduces cytokine production and suppresses T cell proliferation. Tumor cells exploit this immune checkpoint pathway as a mechanism to evade detection and inhibit the immune response. This leads to cancer progression. Antigen TCR T cell activation by dendritic cell Tumor cell - Growing Inhibited T cell Activated T cell Inhibited T cell PD1 PDL1 Dendritic cell T cell inhibition by tumor cell Naive T cell T cell activation PDL1 PD1 T cell inhibition by dendritic cell T cell proliferation T cell priming Activated T cell T cell is inhibited when: Cancer immunity cycle Co-inhibitors of T cell are bound to their receptors on APC. Cancer immunotherapy strategies involve blocking of key immune checkpoint inhibitors to ensure immune responses remain effective against cancer. Immunotherapies against PD-L1 and PD-1 reveal promising results against some cancer types. Through these interactions the immune system is regulated to minimize autoimmune inflammation. Dendritic cell Antigen Presenting Cell T Cell T Cell Regulation PD-L1 PD-1 Inhibition PD-L2 PD-1 n/a CD80 / CD86 CD28 Activation CD80 / CD86 CTLA4 Inhibition B7RP1 (ICOSL) ICOS Activation B7-H3 (CD276) n/a Inhibition B7-H4 (VTCN1) n/a Inhibition B7-H5 CD28H Activation n/a VISTA Inhibition HVEM BTLA Inhibition CD40 CD40L Activation OX40L OX40 Activation CD137L CD137 Activation CD70 CD27 Activation GAL9 TIM3 Inhibition GITRL GITR Activation MHC-II LAG-3 Inhibition Copyright © 2015 Abcam, All rights reserved. RabMAb® is a registered trademark of Abcam. *Adapted from Pardoll, et al., 2012 Tumor cell Antigens T cell activation by immunotherapy Tumor apoptosis PD-L1 [28-8] RabMAb® knockout validated antibody Blocking PD-L1 with a monoclonal antibody interferes with T cell inhibition and active immune response leads to tumor cell death. Activated T cell Tumor cell Key features Knockout (KO) cell line validated in key applications: IHC, FC, WB Highly specific for human PD-L1; no cross-reactivity with human PD-L2 Wild Type L2987 Cells PD-L1 KO L2987 Cells Tested with pathologically validated positive and negative controls Generated using extracellular domain of PD-L1 protein – observed membrane specific staining Tumor cell death Extensive validation in automated protocols (Phillips et al., 2015) Reference B-CAP Cells - High Discover more at abcam.com/cancer Antigen capture Tumor cell - Dying HCC70 Cells - Medium ES-2 Cells - Low COLO205 Cells - None (Cancer cell lines with varying levels of PD-L1 expression) Phillips, T., Simmons, P., Inzunza, H., Cogswell, J., Novotny, J., Taylor, C. and Zhang, X. (2015). Development of an Automated PD-L1 Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Assay for Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology, 23(8), pp.541-549. E-914 Regulators of T cell activation* Activated T cell Tumor infiltration