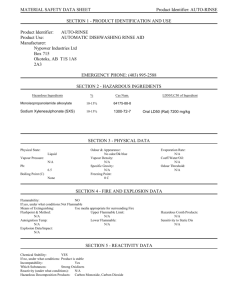
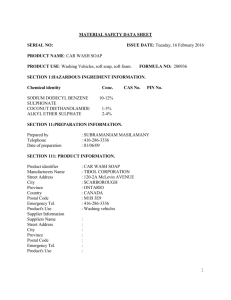
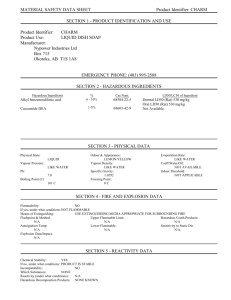
GLOSSARY OF COMMONLY USED MSDS TERMS
advertisement
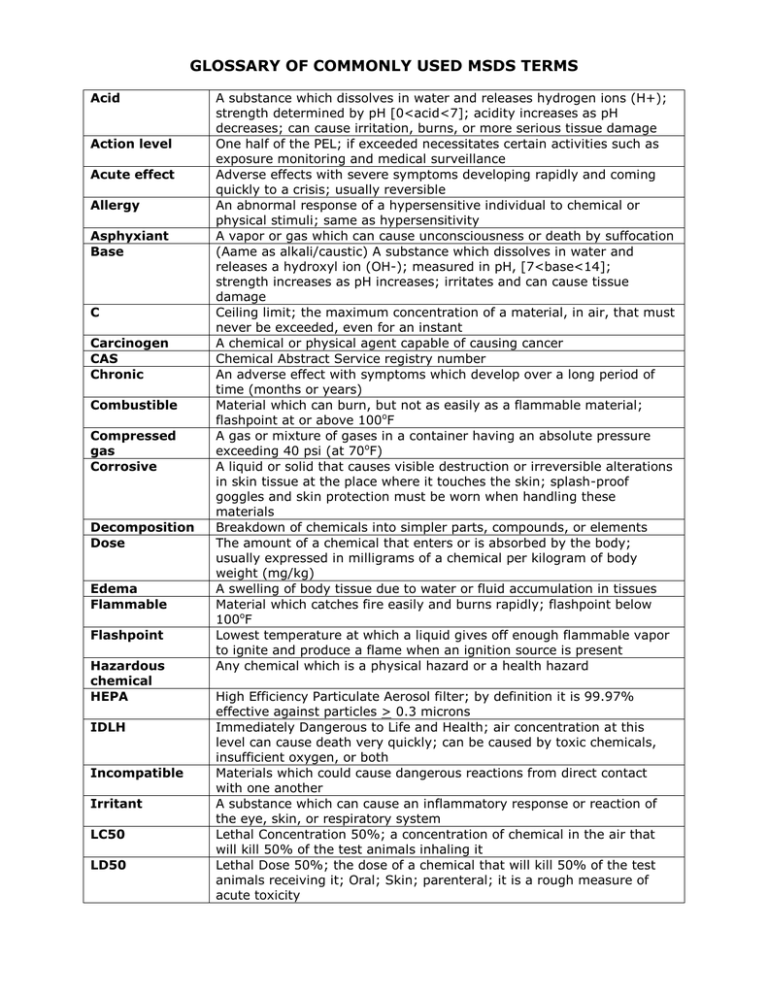
GLOSSARY OF COMMONLY USED MSDS TERMS Acid Action level Acute effect Allergy Asphyxiant Base C Carcinogen CAS Chronic Combustible Compressed gas Corrosive Decomposition Dose Edema Flammable Flashpoint Hazardous chemical HEPA IDLH Incompatible Irritant LC50 LD50 A substance which dissolves in water and releases hydrogen ions (H+); strength determined by pH [0<acid<7]; acidity increases as pH decreases; can cause irritation, burns, or more serious tissue damage One half of the PEL; if exceeded necessitates certain activities such as exposure monitoring and medical surveillance Adverse effects with severe symptoms developing rapidly and coming quickly to a crisis; usually reversible An abnormal response of a hypersensitive individual to chemical or physical stimuli; same as hypersensitivity A vapor or gas which can cause unconsciousness or death by suffocation (Aame as alkali/caustic) A substance which dissolves in water and releases a hydroxyl ion (OH-); measured in pH, [7<base<14]; strength increases as pH increases; irritates and can cause tissue damage Ceiling limit; the maximum concentration of a material, in air, that must never be exceeded, even for an instant A chemical or physical agent capable of causing cancer Chemical Abstract Service registry number An adverse effect with symptoms which develop over a long period of time (months or years) Material which can burn, but not as easily as a flammable material; flashpoint at or above 100oF A gas or mixture of gases in a container having an absolute pressure exceeding 40 psi (at 70oF) A liquid or solid that causes visible destruction or irreversible alterations in skin tissue at the place where it touches the skin; splash-proof goggles and skin protection must be worn when handling these materials Breakdown of chemicals into simpler parts, compounds, or elements The amount of a chemical that enters or is absorbed by the body; usually expressed in milligrams of a chemical per kilogram of body weight (mg/kg) A swelling of body tissue due to water or fluid accumulation in tissues Material which catches fire easily and burns rapidly; flashpoint below 100oF Lowest temperature at which a liquid gives off enough flammable vapor to ignite and produce a flame when an ignition source is present Any chemical which is a physical hazard or a health hazard High Efficiency Particulate Aerosol filter; by definition it is 99.97% effective against particles > 0.3 microns Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health; air concentration at this level can cause death very quickly; can be caused by toxic chemicals, insufficient oxygen, or both Materials which could cause dangerous reactions from direct contact with one another A substance which can cause an inflammatory response or reaction of the eye, skin, or respiratory system Lethal Concentration 50%; a concentration of chemical in the air that will kill 50% of the test animals inhaling it Lethal Dose 50%; the dose of a chemical that will kill 50% of the test animals receiving it; Oral; Skin; parenteral; it is a rough measure of acute toxicity mg/m3 MSDS Mutagen NFPA NIOSH PEL pH Polymerization ppb ppm psi Pyrophoric Oxidizer Reactivity Respirator Route of entry/exposure STEL Teratogen TLV TWA A way of expressing dose; milligrams of a substance per cubic meter of air Material Safety Data Sheets; a form that lists the properties and hazards of a product or a substance A chemical or physical agent able to change the genetic material in the cells National Fire Protection Agency National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health Permissible Exposure Limit; legal limit of chemical exposure a worker can be exposed to based on an 8 hour work day for 40 hours per week based on 30 years of employment Expresses how acidic or alkaline a solution or chemical is; range is from 0 to 14; water is neutral at pH=7; see acid/base A chemical reaction in which small molecules (monomers) combine to form much larger molecules (polymers); hazardous when this takes place at a fast rate with large amounts of energy released Parts per billion; a measure of concentration Parts per million; a measure of concentration Pound per square inch; a unit of pressure A chemical that will ignite spontaneously in air at a temperature of 130oF or below Any substance which will react chemically either by supplying oxygen or removing electrons; oxidizers must not be stored near flammable or reactive materials The ability of a substance to undergo a chemical reaction (such as combining with another substance) A device worn to prevent inhalation of hazardous substances; UCSD has an official program in which all respirator users must be enrolled The way in which a chemical enters the body; ingestion, inhalation, skin absorption or injection Short Term Exposure Limit; indicates the maximum average concentration allowed for a continuous 15 minute exposure A chemical or physical agent which can lead to malformations in the fetus and birth defects in children (live born offspring) Threshold Limit Value; suggested chemical exposure limit as determined by the American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists [ACGIH]) Time-Weighted Average; the average concentration of a chemical in the air over the total exposure time- usually a 8-hour work day