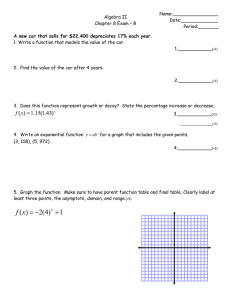
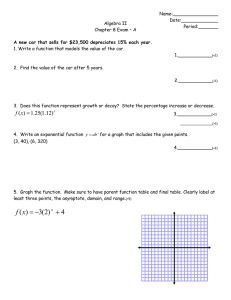
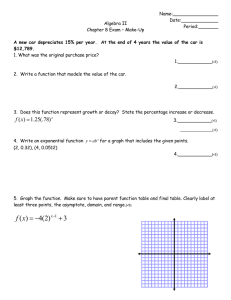
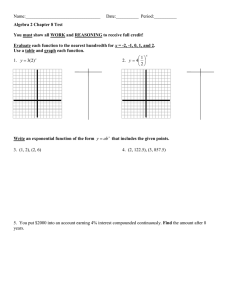
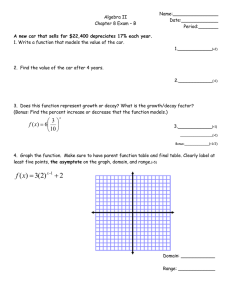
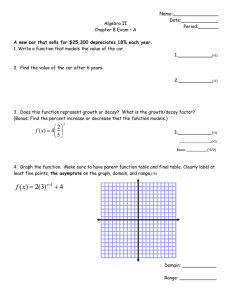
Precalculus Sec 3.2 Logarithmic Functions a is the inverse of an exponential function
advertisement
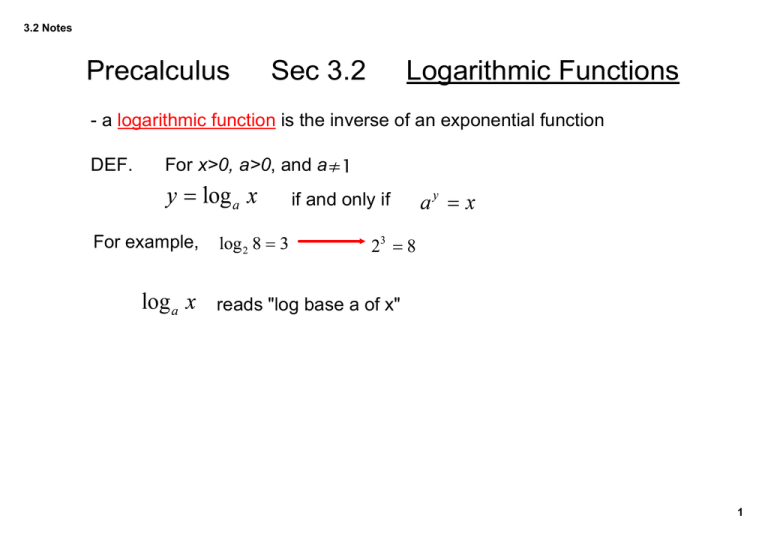
3.2 Notes Precalculus Sec 3.2 Logarithmic Functions ­ a logarithmic function is the inverse of an exponential function DEF. For x>0, a>0, and a≠1 if and only if For example, reads "log base a of x" 1 3.2 Notes Examples 2 3.2 Notes ­ The base of a logarithm can be any positive number except 0 and 1, there are two that are used the most, base 10 and base e. we don't need to write the base 10, it is implied a log base e is called the natural logarithm and written as Properties of logarithms with any allowed base 1) 2) 3) 4) If then End Day 1 3 3.2 Notes Sec. 3.2 Day 2 The graph of comes from the fact that logarithms are inverses with Domain: x>0 Range: all real x­intercept: x=1 increasing throughout domain V.A.: x=0 4 3.2 Notes Transformations ­ same rules as before for shifts, reflections EXAMPLE Parent: is the parent function after being... ­ When graphing the logarithm function, concentrate on the vertical asymptote for the shifts left and right, and the x­intercept for the shifts up and down. Sketch g(x) from above. 5 3.2 Notes Finding Domain of logarithmic functions You can not take the log of a negative number or of zero. EXAMPLE Find the domain, x intercept and the vertical asymptote of 6