Momentum: Worksheet 4 Elastic Collisions
advertisement
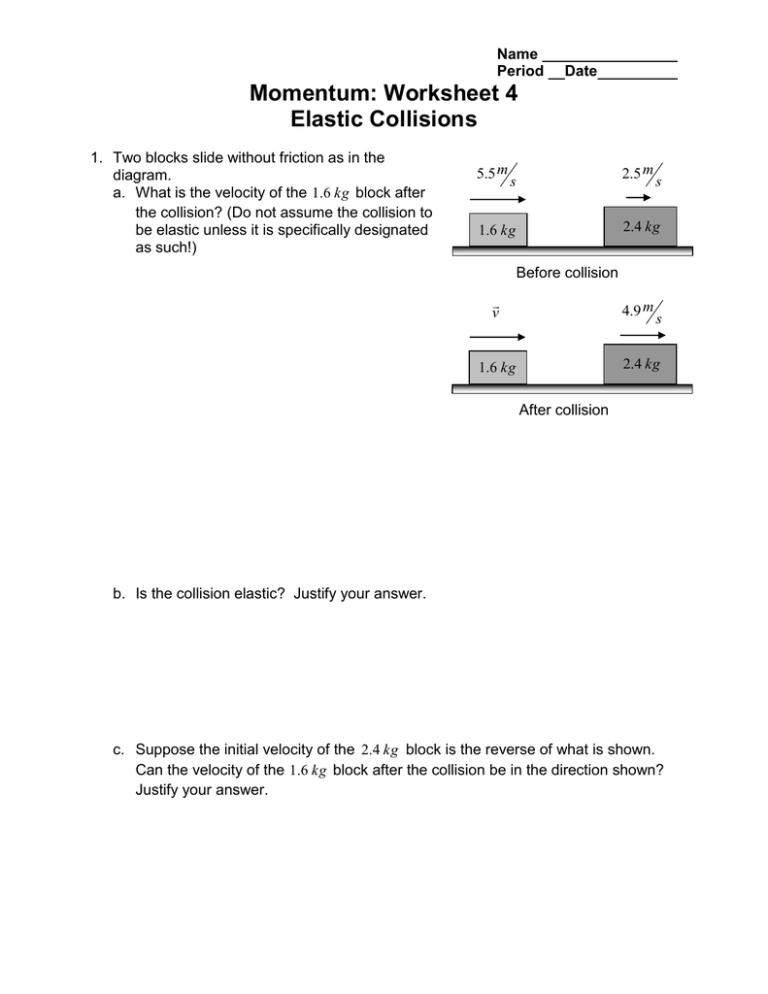
Name Period Date Momentum: Worksheet 4 Elastic Collisions 1. Two blocks slide without friction as in the diagram. a. What is the velocity of the 1.6 kg block after the collision? (Do not assume the collision to be elastic unless it is specifically designated as such!) 5.5 m 2.5 m s s 2.4 kg 1.6 kg Before collision v 4.9 m 1.6 kg 2.4 kg s After collision b. Is the collision elastic? Justify your answer. c. Suppose the initial velocity of the 2.4 kg block is the reverse of what is shown. Can the velocity of the 1.6 kg block after the collision be in the direction shown? Justify your answer. Momentum: Worksheet 4 Elastic Collisions page 2 2. A hovering fly is approached by an enraged elephant charging at 2.1 m . Assuming s that the collision is elastic, at what speed does the fly rebound? Note that the projectile (the elephant) is much more massive than the stationary target (the fly). 3. A proton (atomic mass 1u ) with a speed of 500. m collides elastically with another s proton at rest. The original proton is scattered 60. from its original direction. a. What is the direction of the velocity of the target proton after the collision? b. What are the speeds of the two protons after the collision? Momentum: Worksheet 4 Elastic Collisions page 3 1 Frictionless k h 2 4. Block 1 of mass m1 slides from rest along a frictionless ramp from height h 2.50 m and then collides with stationary block 2, which has mass m2 2.00m1 . After the collision, block 2 slides into a region where the coefficient of kinetic friction k is 0.500 and comes to a stop in distance d within that region. a. Calculate the b. Calculate the velocity c. What is the value of the distance d if the velocity of block 1 of block 2 immediately immediately before after the collision if the collision is elastic? the collision. collision is elastic. d. Calculate the velocity of block 2 immediately after the collision if the collision is completely inelastic. e. What is the value of the distance d if the collision is completely inelastic? Momentum: Worksheet 4 Elastic Collisions page 4 5. A steel ball of mass 0.500 kg is fastened to a cord 70.0 cm long and fixed at the far end, and is released when the cord is horizontal as in the diagram above. At the bottom of its path, the ball collides elastically with a 2.50 kg steel block initially at rest on a frictionless surface. a. What is the speed b. What is the speed and c. What is the speed and of the ball just direction of the ball just direction of the block before the collision? after the collision? just after the collision? After the collision the block runs into a horizontal spring of spring constant 60.8 N d. What is the maximum compression of the spring? m .