The Law of Universal Gravitation Activity Purpose:
advertisement
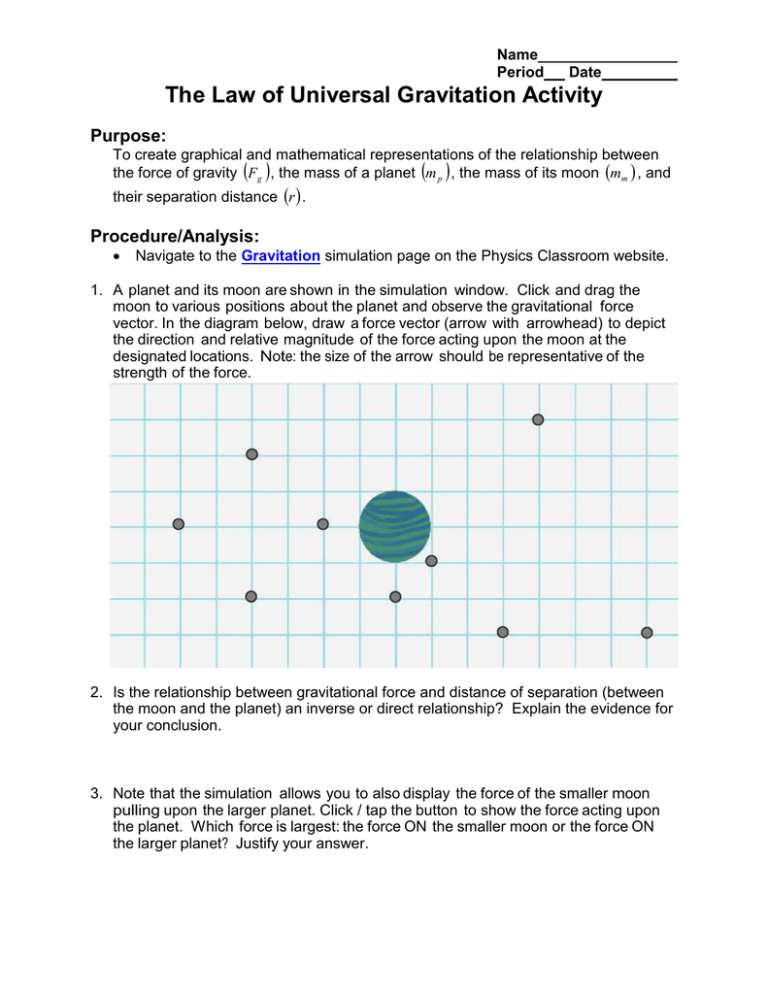
Name Period Date The Law of Universal Gravitation Activity Purpose: To create graphical and mathematical representations of the relationship between the force of gravity Fg , the mass of a planet m p , the mass of its moon mm , and their separation distance r . Procedure/Analysis: Navigate to the Gravitation simulation page on the Physics Classroom website. 1. A planet and its moon are shown in the simulation window. Click and drag the moon to various positions about the planet and observe the gravitational force vector. In the diagram below, draw a force vector (arrow with arrowhead) to depict the direction and relative magnitude of the force acting upon the moon at the designated locations. Note: the size of the arrow should be representative of the strength of the force. 2. Is the relationship between gravitational force and distance of separation (between the moon and the planet) an inverse or direct relationship? Explain the evidence for your conclusion. 3. Note that the simulation allows you to also display the force of the smaller moon pulling upon the larger planet. Click / tap the button to show the force acting upon the planet. Which force is largest: the force ON the smaller moon or the force ON the larger planet? Justify your answer. The Law of Universal Gravitation Activity page 2 While using the simulation in #4-10, consider the planet's surface to be a distance of one planet-radius 1R planet . 4. Now investigate the effect of varying the mass of the moon upon the gravitational force between the moon and the planet with constant separation distance and planet mass. Mass of Force of Use the sliders to alter the mass of the moon and the moon gravity record the force of gravity. (kg) (N) Graph the force of gravity vs. the mass of the moon. Sketch the graph and state the relationship 0 0 between the variables 5 x 1022 10 x 1022 20 x 1022 30 x 1022 40 x 1022 50 x 1022 Mass of the planet = 402 x 1024 kg Separation Distance = 3R planet 5. Use your observations to answer the following statements: If the mass of the moon is ... a. ... increased by a factor of 2, then the force of gravity is (increased, decreased) by a factor of _______. b. ... increased by a factor of 3, then the force of gravity is (increased, decreased) by a factor of _______. c. ... decreased by a factor of ¼, then the force of gravity is (increased, decreased) by a factor of _______. d. ... decreased by a factor of ½, then the force of gravity is (increased, decreased) by a factor of _______. The Law of Universal Gravitation Activity page 3 6. Now investigate the effect of varying the mass of the planet upon the gravitational force between the moon and the planet with constant separation distance and planet mass. Mass of Force of Use the sliders to alter the mass of the planet and the planet gravity record the force of gravity. (kg) (N) Graph the Force of gravity vs. the mass of the planet. 0 0 Sketch the graph and state the relationship between the variables 200 x 1024 302 x 1024 402 x 1024 502 x 1024 600 x 1024 Mass of the moon = 25 x 1022 kg Separation Distance = 3R planet 7. Use your observations to answer the following statements: If the mass of the planet is ... a. ... increased by a factor of 2, then the force of gravity is (increased, decreased) by a factor of _______. b. ... increased by a factor of 3, then the force of gravity is (increased, decreased) by a factor of _______. c. ... decreased by a factor of ¼, then the force of gravity is (increased, decreased) by a factor of _______. d. ... decreased by a factor of ½, then the force of gravity is (increased, decreased) by a factor of _______. The Law of Universal Gravitation Activity page 4 8. Drag the moon to various locations in order to determine the quantitative effect of separation distance upon the gravitational force. Examine the effect of doubling, tripling and quadrupling the distance of separation (as measured from the planet's center). Consider the planet's surface to be a distance of one planet-radius 1R planet . Separation Force of Use the table at the right to record the force of Distance gravity gravity for whole-number multiples of R planet . (m) (N) Graph the Force of gravity vs. the separation 2 R planet distance. Linearize the graph. You will have to do two 3R planet different modifications to the separation distance to linearize the graph! 4 R planet Sketch all three graphs (original, first attempt to 5 R planet linearize, final linearized graph) and state the relationship between the variables 6R planet 7 R planet 8 R planet 9 R planet 10 R planet 11R planet 12 R planet Mass of the moon = 25 x 1022 kg Mass of the planet = 402 x 1024 kg 9. Use your data to complete the following sentences. If the separation distance between the moon and the planet is ... a. ... increased by a factor of 2, then the force of gravity is (increased, decreased) by a factor of _______. b. ... increased by a factor of 3, then the force of gravity is (increased, decreased) by a factor of _______. c. ... increased by a factor of 4, then the force of gravity is (increased, decreased) by a factor of _______. d. ... decreased by a factor of ¼, then the force of gravity is (increased, decreased) by a factor of _______. Conclusion: Watch the video Law of Universal Gravitation to see how we can put together all three relationships into one math model relating the Force of Gravity, the masses of the objects and their separation distance!








