Sharing good practice - recruiting women into engineering roles #jobs4boys? t
advertisement

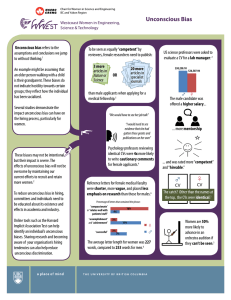
Sharing good practice recruiting women into engineering roles #jobs4boys? For more information contact Jan.Peters@katalytik.co.uk 0797 4011278 #jobs4boys? Event supporters Sagent Recruitment Women’s Engineering Society #jobs4boys? Welcome DR SARAH PEERS #jobs4boys? UCL and Engineering Education DR JOHN MITCHELL #jobs4boys? Engineering – A Diverse Cohort? Intake from State Section – 75% (UCL 65%) Socio-economic groups 4-8 – 29% (UCL 20%) Low participation Neighborhoods – 6.5% (UCL 3.9%) Male : Female – 75% : 25% (UCL 51:49) BME – 60.6% (41.6%) What is Engineering? engineering ….the art and practice of changing the physical world for the use and benefit of mankind Prof Chris Wise, UCL Civil, Environmental and Geomatic Engineering and Expedition Engineering Wrap up Research DR JAN PETERS #jobs4boys? From anecdote to evidence Action research Questions Anecdote: Women don’t perform as well at assessment centres • Evidence the numbers • Explore assessment centre performance by gender • Explore graduates’ experience by survey FACT: In 2006/07, twice the proportion of men graduating with undergraduate qualifications in STEM entered SET professional or associate professional occupations (41.8 per cent) compared with women (21.0 per cent) #jobs4boys? Outputs • short report • inclusive assessment centres – good practice guide Adaptation and use of the resources and activities •Workshops and training •Further collaborative research and diaries •Leadership and engineering discussions #jobs4boys? Full time students completing first degree courses in 2009/10 Subject Female Aeronautical Engineering 10.5% Chemical Engineering 27.0% Civil Engineering 16.3% Electronic Engineering 13.7% General Engineering 20.4% Mechanical Engineering 8.8% Production Engineering 23.6% Computing Science 28.6% #jobs4boys? Data source: UCAS Research elements • Secondary analysis of HESA data, including DLHE data • On-line survey investigating the variation of undergraduates’ career intentions through the course of study. – 4,624 cleaned responses – 1,200 from women #jobs4boys? Student expectations Fact Fact Around three quarters of men and women undergraduate engineers aspire to a career in engineering or technology Half of men and two fifths of women make that transition 80 74 72 70 60 Male 50 Female 40 % 30 20 16 10 10 12 8 0 E&T Role #jobs4boys? Non-E&T Role Further study Main activities of graduates in engineering subjects in 2008/09 and 2009/10 60 50 50 Male Female 39 40 % 30 27 23 19 20 16 10 7 9 0 E&T Role #jobs4boys? Non-E&T Role Further study Work and further study Transfer of graduates from their degree into relevant employment A CRITICAL TRANSITION POINT #jobs4boys? Findings • • • • Behaviours of students Course content on teaming and leadership Where students want to go and where they go Support resources to help facilitate learning for employability skills so students get the jobs that are right for them #jobs4boys? • In general women are less likely to enter SET roles even though both men and women are equally likely to state that they wish to • This appears to be related to the lower “career confidence” of women E&T students #jobs4boys? • Key actions are around building the confidence of women engineering and technology students #jobs4boys? HE actions #jobs4boys? Employer actions Tonight’s focus ASSESSMENT CENTRES #jobs4boys? Awareness Fact When you are focused on one thing you can ignore other important information going on right in front of you. Act Assessor briefing #jobs4boys? Minority behaviours Fact Minorities need to work extra hard to get their point over Fact It’s hard to be authentic in a minority Act When welcoming candidates to your assessment centre set out behaviour standards in your workplace and the standards expected during the assessment • politeness and respect towards all other participants • assess these behaviours #jobs4boys? Behaviours Fact Act Act Act You don’t tolerate bullying at work. Don’t tolerate bad behaviour in your Assessment Centre Ensure behaviours of male assessors towards female candidates are professional and respectful and vice versa Ensure that someone on the panel is assigned to make note of any bullying behaviours During observations monitor how the male candidates listen to the female candidates #jobs4boys? Visual representation Fact Act Act Act Role models are important Female assessors present Images in literature, posters, photos Use female employees – technical where possible #jobs4boys? Interviews Fact Act Fact Act Fact Act Every individual has their own biases and everybody will have some unconscious bias Each candidate to see a range of male and female assessors so that individual biases can be averaged out. This is particularly important if you use 1:1 interviews Women tend to have lower career confidence than men Encourage female candidates An interview panel of all women or all men can be intimidating For larger panels, try to have a balance of men and women on every panel. For smaller panels try to include at least one women and one man #jobs4boys? Tests Fact Act Act Sometimes assessment tests have inbuilt gender biases Ensure that your assessment tests have been rigorously tested for gender biases Make sure that the results of tests are analysed by gender to check whether in general men or women do better. Remember that correlation does not necessarily mean causation but if you find any issues investigate them further #jobs4boys? Group work 1 Fact Act Act Act Research shows male students can dominate and domineer in group and project work Spend time thinking about the makeup of groups Ensure that you are clear what behaviours/skills you are assessing and try to design group work to minimise the effects of other factors such as gender Monitor participation for boorish or domineering behaviour #jobs4boys? Group work 2 Fact Act Inclusion and respect are important elements at work Add into group work or role play exercises some diversityrelated incidents #jobs4boys? Monitoring 1 Fact Fact Fact Act Act Act Women are in a minority among engineering and technology graduates Female engineering and technology graduates are less likely than male engineering and technology graduates to work in engineering and technology roles Within engineering and technology courses, a higher percentage of women than men get 1st class degrees Number of women in your pool Be proactive If you collect data, use it. Make cross year comparisons and anonymise it to avoid breaching data protection #jobs4boys? Monitoring 2 Fact Act Act Act Everyone is a product of their environment and will display some biases whether they are aware of it or not Monitor the % of men and women at each stage Assess the same behaviours or criteria twice and make comparisons. Actively look for gender differences and gender biases When you are making comparisons between men and women – look to see what the gender of the assessor was. Women can be biased against women too #jobs4boys? Findings • • • • Behaviours of students Course content on teaming and leadership Where students want to go and where they go Support resources to help facilitate development of wider skills so students get the jobs that are right for them #jobs4boys? HE actions #jobs4boys? Employer actions Unconscious Bias GREET BROSENS #jobs4boys? www.sagentrecruitment.com @sagentrec Greet Brosens & Michele Garrigan Founders and Directors UNCONSCIOUS BIAS AND ENGINEERING Apple Developer Conference Bias: Some Examples 58% of male CEOs of Fortune 500 companies are over 6’ tall versus 14.5% of men in the general American population. (source: Malcolm Gladwell, Blink) Bias: Some Examples Bias comes in different forms Explicit Stereotypes that we openly admit to Implicit Stereotypes that we are unable or unwilling to admit Explicit bias? “A brain type that leans towards strong systemising is more common in males” Professor Simon Baron-Cohen “Why Men Don’t Listen and Women Can’t Read Maps” Allan & Barbara Pease Explicit bias? “The underrepresentation of female scientists at elite universities may stem in part from innate differences between men and women” Larry Summers, former president of Harvard University Conscious versus Unconscious bias Unconscious Bias at Play Automatic stereotyping Ingroup favouritism Consequences of Unconscious Bias Stereotype Threat: Girls perform under their ability in STEM tests Misperception: Men are assertive, women are aggressive What can we do? Create awareness with relevant stakeholders: IAT test (gender-career and gender-science) Identify areas within the business where unconscious bias is at play • Recruitment and selection • Performance review • Promotion Eliminate opportunities for unconscious bias Examples for the workplace Recruitment & Selection • Blind applications • Multiple interviewers involved in the process • Multiple channel attraction programme (abolish reliance on referral programmes) Performance Reviews • Keep comparative data of performance ratios for men and women and report back • Coaching for managers; coaching for women • Women’s groups Internal Mobility • Celebrate diversity to remove unconscious bias • Mentoring Programmes • Identify sponsors for high flyers early in career THE FUTURE: Will we achieve gender equality in engineering? JOHN ALLPORT #jobs4boys? The Cummins “Staircase of Talent” and how it relates to encouraging female engineers John Allport Talent Development Leader 22 July 2013 Cummins Global company – World’s largest independent supplier of Diesel engines Over 45000 employees Large proportion of female engineers everywhere except in the UK “Hire to Develop” strategy – 75% of new starters from graduates or apprentices 51 7/23/2013 Cummins Confidential Where to start? Support from the top 52 7/23/2013 Cummins Confidential Next steps Good role models Hiring large number of graduate engineers Graduate recruits all start at same level – Less gender bias – Can reach critical mass quickly due to large intake – Word spreads – More female applicants 53 7/23/2013 Cummins Confidential Need a general model “Pipeline of talent” theory already common Didn’t quite fit the model needed Modified to “Staircase of Talent” 54 7/23/2013 Cummins Confidential Still not enough females applying, what next? Develop further down the “staircase” Closer links with universities, particularly with womens engineering groups 55 7/23/2013 Cummins Confidential “Boots on ground” approach works much better than advertising, especially in schools 56 7/23/2013 Cummins Confidential Key points All students respond better to direct personal approach, especially female to female A consistent approach is much better than having a “token example female” 57 7/23/2013 Cummins Confidential Comments from female engineers on good practices Large percentage of women Work life balance Made to feel part of a team / welcome / wanted Flexibility regarding work patterns Facilitating return to work after maternity Pleasant environment – nice offices Relaxed but efficient atmosphere 58 7/23/2013 Cummins Confidential Comments from female engineers on good practices Social opportunities Interesting challenging work Not treated differently Decent / Helpful work colleagues Opportunity for career progression Opportunity for Professional Development Opportunity to do voluntary work / community involvement Good training 59 7/23/2013 Cummins Confidential MARY-CLARE RACE #jobs4boys? Recruitment Approach and Challenges Mary-Clare Race 22nd July 2013 Our current position •34% of total recruits since Feb 2012 •32% of graduate recruits in 2012 Highlights of our approach • Winning Awards and raising our profile – positioning Arup as the organisation of choice for women from a STEM background • Our senior female role models • Relationships with external partners e.g. UKRC / WES • Linking with universities and schools through outreach activities Highlights of our approach •Offering a ‘whole of self’ employment package •E.g. Development opportunities based on social support mechanisms •A more flexible employment offering •Targeting women in our recruitment approach •Female undergraduate days •Training our managers in unconscious bias •Our values and culture – shaping a better world #jobs4boys? DISCUSSION PANEL #jobs4boys?