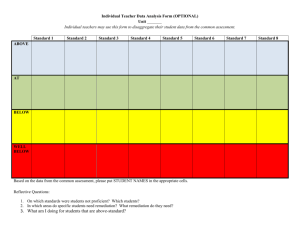
Develop Installation Restoration Design Technical Guidance Remediation Alternatives Data Draft
advertisement

Develop Installation Restoration Design Technical Guidance Remediation Alternatives Data Draft May 21, 1996 Requests for this document shall be referred to: Commander, U.S. Army Armament Research Development & Engineering Center Industrial Ecology Center ATTN: AMSTA-AR-ET, Building 172 Picatinny Arsenal, NJ 07806-5000 Contract No. DAAA21-93-C-0046 Task No. N.073 CDRL No. A005 Submitted by Concurrent Technologies Corporation 1450 Scalp Avenue Johnstown, PA 15904 Table C-1. Ground Water Pump and Treat with Air Stripping Site Characteristics Site Name Municipal Water Plant Eaton Corporation Site Location Soil Type Vanport Municipality, PA Beaver, PA Depth to Water Table Size of Site at least 0.75 mi plume 90 ft Alluvial deposits and fill material, fractured bedrock, interbedded mudstone/siltstone/s andstone Shales 4-20 ft BG Aiken, SC Sand, clay 100 ft. Langley, VA Fine sand, silts, shell beds 4-6 ft. water table; 400 ft. upper aretsian; 700 ft. principle aretsian Contaminants Present TCE 400 ft x 300 ft; 30 ft BG 700 ft x 700 ft; 125 ft BG TCE 4,000 ft. horizontally 40 ft. BG PCE; TCE; 1,2-DCE; Vinyl chloride 150 ft, horizontally 1200 acres 1,000 ft x 2,000 ft TCE; PCE; TCA Naval Air Warfare Center, Aircraft Division, Trenton Trenton, NJ US Department of Energy, Kansas City Plant Savannah River Site A/M Area Langley AFB, IRP Site 4 Kansas City, Missouri Fort Drum Fuel Dispensing Area 1595 McClellan AFB Watertown, NY BTEX Sacramento, CA Twin Cities Army Ammunition Plant New Brighton, Minnesota TCE; cis-1,2-DCE; PCE; 1,2-DCA 1,1-DCE; 1,1-DCA; 1,2-DCE; Chloroform; 1,1,1-TCA; TCE; PCE; TRCLE;1,1,1TCE; TCLEE Fractured bedrock, sand, clay, till layers 10,000 ft x25 Clean-up Level Achieved Clean-up levels achieved TCE 1,2-DCE Vinyl chloride BTEX; Total petroleum HCs Reduced VOCs below discharge level Depends on extent of treatment... 30 yrs. - 5 ppb TRCLE or 50-70 yrs. - 17 ppb Table C-1. Ground Water Pump and Treat with Air Stripping Site Characteristics (Continued) Site Name Site Location Tobyhanna Army Depot Tobyhanna, PA Naval Construction Battalion Center Gulfport, MS Naval Air Warfare Center Naval Air Engineering Center Lakehurst, NJ, Area H Lakehurst, NJ Site No. 28, Area E Soil Type Poorly graded medium-grained sands with some fines. Depth to Water Table 187 ft. aquifer #1; 375-450 ft. aquifer #2 6 ft. Size of Site Contaminants Present <1 mile horizontally TCE 200 ft. horizontally 35 ft. vertically Volatile (e.g. Vinyl Chloride, 1,1,1-TCE, Toluene) Semi-Volatile (e.g. Naphthalene) Pesticides Dioxins Inorganics (e.g. Cd, Cr, Ni) Naphthalene; 2-methylnaphthalene; Toluene; o-xylene; Ethylbenzene; Benzene Clean-up Level Achieved Concurrent Technologies Corporation Ground Water Pump and Treat with An Air Stripper nav_rem2.doc 3/20/97 Purpose: Concurrent Technologies Corporation (CTC), in conjunction with the Naval Facilities Engineering Command (NAVFAC), is collecting real-life design information on remediation technologies involving Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper. The collected information will be compiled into a technical design guidance document that will indicate if a specific selected remediation technology will be effective at a given site, the design criteria that should be considered for that site, and lessons learned from past users of these technologies. The guidance document will provide the information necessary to effectively design the selected remediation technology. Point of Contact concerning questionnaire: Heather Fennessey Phone number/E-mail: 814-269-6479/fennesse@ctc.com Date entered: 4/23/96 SITE VISIT Date updated: I. GENERAL INFORMATION A. B. Installation Information 1. Type of Installation (e.g., Navy): Municipal 2. Facility Name: Municipal Water Plant 3. Address: Vanport Municipality, PA Information Source 1. Name: Jeff Forshner 2. Address: Westinghouse Electric Corporation 11 Stanwix Street Pittsburgh, PA 15222-1384 3. Phone: 412-642-4959 4. Fax: 412-642-3318 5. E-mail Address: Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper II. Page 2 SITE CHARACTERISTICS A. B. Vadose Zone 1. Soil Type: 2. Unified Soil Classification: 3. Moisture Content: 4. Depth to Water Table: Saturated Zone Aquifer 1 C. 1. Soil Type: 2. Unified Soil Classification: 3. Hydraulic Conductivity: 4. Transmissivity: 5. Depth to Water Table: 6. Hydraulic Gradient: 7. Aquifer Type: 8. Capillary Fringe Height: Aquifer 2 Contaminants Present 1. Source of Contamination (e.g., gasoline spill): Solvent Spill at other site (0.75 mile away) Refer to Eaton Corporation, Bevaer, PA 2. Horizontal Extent of Site: 3. Vertical Extent of Site: 4. Temperature Range at Site: 5. Contaminant Names and Concentrations in Ground Water (ppm): TCE Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper III. PILOT OR BENCH SCALE TESTS A. Pump Test 1. Type (e.g., step test, continuous discharge): 2. Test Duration: 3. Pump Test Rate: 4. Pumping Well 5. 6. B. a. Type: b. Screened Interval: c. Packer Depth: Observation Well a. Type: b. Screened Interval: c. Packer Depth: d. Method of Data Collection: Method of Analysis: Pilot Test 1. Goals: 2. Other: Page 3 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper IV. TECHNOLOGY DESIGN Typical System Components: Extraction Wells (Section A) Oil Water Separator (Section B) Air Stripper (Section C) Carbon Treatment (Section D) Other A. Extraction Wells 1. Design Goals a. 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. g. B. Provide ________ GPM to treatment system Pipe Type: Pipe Diameter: Depth: Screen Interval: Screen Type: Number and Spacing: Other: 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Oil and Water Separator 1. Design Goals: 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. 3. Flow Rate: Efficiency: Other: Design Tools: Page 4 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper C. 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Air Stripper (2- total of 1.2 million gallons water/day treated) 1. Design Goals: Remove TCE in contaminated water at 1,800 GPM 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. g. D. Page 5 Stripper Height: 35 ft; stainless steel Stripper Diameter: 10 ft Blower Rate: 5000 CFM/tower Packing Material: 20 ft of packing Pretreatment Requirements: Add Aquimag ( Phosphate-based material prevents fouling), to control solubility of Fe and Mn. Packing balls and sieve tray. No filters required. Removal Efficiency: approx. 99.9% Other: Discharge limit 2.6 ppb (drinking water stnd 5 ppb) 3. Design Tools: Air stripper vendor (used computer model) 4. Remediation Hardware: Hydro Group 5. Capital Cost: (built January 1990) 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: $300/month labor Air Filters: $5,000/yr. Aquimag: $40,000/yr. Electricity: $6500/month Carbon Treatment 1. Design Goals a. Contaminant Types: b. Contaminant Discharge Limits: 2. Design Parameters a. GAC Type: b. GAC Volume: c. Flow Through Rate: d. Contact Time: e. Removal Efficiency: f. Other: Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper V. 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Page 6 TECHNOLOGY PERFORMANCE A. Remediation Technology Choice 1. Other Remediation Technologies Considered for this Site: No B. 2. Why was Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper Chosen over Other Technologies? Too high of flow for GAC. 3. Remediation Technologies used at this Site in addition to Air Stripper: Operation of Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper 1. 2. C. Duration: January 1990 - present Other: Lessons Learned 1. Lessons Learned about the Operation of the Equipment: Learned on-line about precipitation problems (kept plugging with black powdery precipitate, Mn and Fe throughout packing) - use Aquimag now. 2. Why was the Technology Successful? Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper TCE below drinking water standards. 3. VI. Why was the Technology Unsuccessful? CONTRACT TYPE AND COSTS A. B. C. Design of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: Construction of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: Operation of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: Page 7 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Ground Water Pump and Treat with An Air Stripper nav_rem2.doc 3/20/97 Purpose: Concurrent Technologies Corporation (CTC), in conjunction with the Naval Facilities Engineering Command (NAVFAC), is collecting real-life design information on remediation technologies involving Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper. The collected information will be compiled into a technical design guidance document that will indicate if a specific selected remediation technology will be effective at a given site, the design criteria that should be considered for that site, and lessons learned from past users of these technologies. The guidance document will provide the information necessary to effectively design the selected remediation technology. Point of Contact concerning questionnaire Heather Fennessey: Phone number/E-mail: 814-269-6479 fenesse@ctc.com Date entered: 4/23/96 SITE VISIT Date updated: I. GENERAL INFORMATION A. B. Installation Information 1. Type of Installation (e.g., Navy): Commercial 2. Facility Name: Eaton Corporation (makes circuit breakers) 3. Address: Beaver, PA Information Source 1. Name: Jeff Forschner 2. Address: Westinghouse Electric Corporation 11 Stanwix Street Pittsburgh, PA 15222-1384 3. Phone: 412-642-4959 4. Fax: 412-642-3318 5. E-mail Address: Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper II. Page 2 SITE CHARACTERISTICS A. B. Vadose Zone 1. Soil Type: 2. Unified Soil Classification: 3. Moisture Content: 4. Depth to Water Table: Saturated Zone Aquifer 1 C. 1. Soil Type: 2. Unified Soil Classification: 3. Hydraulic Conductivity: 4. Transmissivity: 5. Depth to Water Table: 6. Hydraulic Gradient: 7. Aquifer Type: 8. Capillary Fringe Height: Aquifer 2 90 ft Contaminants Present 1. Source of Contamination (e.g., gasoline spill): 2. Horizontal Extent of Site: 400 ft x 300 ft 3. Vertical Extent of Site: 4. Temperature Range at Site: 5. Contaminant Names and Concentrations in Ground Water (ppm): TCE Solvent Spills 30 ft 0 -90oF Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper III. PILOT OR BENCH SCALE TESTS A. Pump Test 1. Type (e.g., step test, continuous discharge): Step Tests for well placement 2. Test Duration: 3. Pump Test Rate: 4. Pumping Well 5. 6. B. a. Type: b. Screened Interval: c. Packer Depth: Observation Well a. Type: b. Screened Interval: c. Packer Depth: d. Method of Data Collection: Method of Analysis: Pilot Test 1. Goals: 2. Other: Page 3 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper IV. Page 4 TECHNOLOGY DESIGN Typical System Components: Extraction Wells (Section A) Oil Water Separator (Section B) Air Stripper (Section C) Carbon Treatment (Section D) Other A. Extraction Wells 1. Design Goals a. 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. g. 3. A1. Pipe Type: Stainless steel Pipe Diameter: 4 inch Depth: 100 ft. Screen Interval: Lower Aquifer Screen Type: 0.01 slits Number and Spacing: 2 - 50-75 ft apart Other: 4. Cummings Rider - hydrogeologists consultants, based design on pump tests Remediation Hardware: N/A 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Design Tools: $5,000/well UV Lights 1. B. Provide 50 GPM to treatment system (Variable) Note: UV Lights used to prevent plugging of GAC. Oil and Water Separator 1. Design Goals: 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. Flow Rate: Efficiency: Other: No separator needed, because all contaminants are dissolved. Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Page 5 Equalization Tank - 10-12 shut down/day B1. Equalization Tank - 10-12 shut downs/day B2. Filters C. Air Stripper 1. Design Goals: 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. g. D. Stripper Height: Stripper Diameter: Blower Rate: Packing Material: Pretreatment Requirements: Removal Efficiency: Other: 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Carbon Treatment 1. Design Goals a. b. 2. Contaminant Types: TCE Contaminant Discharge Limits: 20 avg-40 max. to Ohio River Design Parameters a. GAC Type: regenerated activated, 18-40 mesh Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper V. Page 6 b. GAC Volume: 2000 lb./vessel x 2 c. Flow Through Rate: 50 GPM d. Contact Time: Empty bed contact time above 12 min.; designed for more than 50 GPM e. Removal Efficiency: 75% 3. Design Tools: Isotherms, contact time, 4. Remediation Hardware: Encotech, Donora, PA 5. Capital Cost: $85,000 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: 7. Other: Operates 10% faster than pumping. TECHNOLOGY PERFORMANCE A. Remediation Technology Choice 1. Other Remediation Technologies Considered for this Site: Soil extraction; air stripping 2. Why was Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper Chosen over Other Technologies? Soil conditions; contaminants in ground water; did not want to heat air stripper exhaust (high electricity costs) -> because would still have to go through GAC. 3. B. Remediation Technologies used at this Site in addition to Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper: None. Operation of Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper 1. 2. Duration: Other: December 1994 - present Checked 2x / month Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper C. Lessons Learned 1. Lessons Learned about the Operation of the Equipment: Manganese (Mn) in groundwater causes carbon to clump (decreases absorption). Inject nitrogen gas; backwash every 2 weeks. UV light - prevents GAC from clogging (approx. 2000 effective) 2. Why was the Technology Successful? Met discharge limits and contaminant standards for aquifer. 3. VI. Why was the Technology Unsuccessful? CONTRACT TYPE AND COSTS A. B. C. Page 7 Design of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: Rolled into purchase price. (See (B)) Construction of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: $170,000 total Operation of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: $35,000 - $40,000/yr. Contracts out labor and analytical. Concurrent Technologies Corporation Ground Water Pump and Treat with An Air Stripper nav_rem2.doc 3/20/97 Purpose: Concurrent Technologies Corporation (CTC), in conjunction with the Naval Facilities Engineering Command (NAVFAC), is collecting real-life design information on remediation technologies involving Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper. The collected information will be compiled into a technical design guidance document that will indicate if a specific selected remediation technology will be effective at a given site, the design criteria that should be considered for that site, and lessons learned from past users of these technologies. The guidance document will provide the information necessary to effectively design the selected remediation technology. Point of Contact concerning questionnaire: Heather Fennessey Phone number/E-mail: 814/269-6479/fennesse@ctc.com Date entered: 4/5/96 Date updated: I. GENERAL INFORMATION A. B. Installation Information 1. Type of Installation (e.g., Navy): Navy 2. Facility Name: Naval Air Warfare Center, Aircraft Division, Trenton 3. Address: 1440 Parkway Ave Trenton, NJ 08628 Information Source 1. Name: EA Engineering, Science, and Technology 2. Address: Two Oak Way Berkley Heights, NJ 07922 3. Phone: 908-665-2440 4. Fax: 908-665-2464 5. E-mail Address: MYT@eaeng.mhs.compuserve.com Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper II. Page 2 SITE CHARACTERISTICS A. Vadose Zone 1. Soil Type: gravel) and fill material. B. Alluvial deposits (glacial melt water deposits of clay, sand, 2. Unified Soil Classification: SM-CL 3. Moisture Content: Approx. 12% 4. Depth to Water Table: 4-20 ft (overburn thickness ranges from 6-22 and ft) Saturated Zone Aquifer 1 1. Soil Type: Fractured bedrock - Interbedded mudstone/slitstone (Lockatong Fm.) and sandstone (Stockton Fm.). 2. Unified Soil Classification: -- 3. Hydraulic Conductivity: 4. Transmissivity: varies across wide range, depending on the fracture system pumped. Based on constant-rate aquifer tests performed on 3 different monitoring wells at the site, average transmissitivity values range from 2,678 gpd/ft - 8,194 gpd/ft. 5. Depth to Water Table: 6. Hydraulic Gradient: 7. Aquifer Type: Fractured bedrock, multi-layered aquifer comprised of layered incomponent and competent beds. Ground water flow is mainly along partings parallel to bedding planes, with some flow along vertical fractures between conductive layers. 8. Capillary Fringe Height: -- Estimated at 10-4 ft/sec from slug tests. 4-20 ft below grade 0.009-0.027 ft/ft Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper C. Page 3 Contaminants Present 1. Source of Contamination (e.g., gasoline spill): TCE spills, minor pipe 2. Horizontal Extent of Site: Approx. 700 ft x 700 ft 3. Vertical Extent of Site: 4. Temperature Range at Site: 5. Contaminant Names and Concentrations in Ground Water (ppm): At least 125 ft below grade. -5 - 100 oF (Maximum Concentration observed in pumping well) Trichloroethene (TCE): 18 ppm 1,2-Dichloroethene (1,2-DCE): 67 ppm Vinyl Chloride: 15 ppm III. PILOT OR BENCH SCALE TESTS A. Pump Test (3 different wells) 1. Type (e.g., step test, continuous discharge): 2. Test Duration: Constant rate (all 3 tests) Aquifer Test 1: 72 hours Aquifer Test 2: 72 hours Aquifer Test 3: 44 hours 3. Pump Test Rate: 25 GPM for all 3 tests 4. Pumping Well (all bedrock wells) a. Type: All 6” diameter single-cased monitoring wells. b. Open-hole Interval: Aquifer Test 1: 26-41 ft BG Aquifer Test 2: 20.5-60 ft BG Aquifer Test 3: 69-84 ft BG c. 5. Packer Depth: N/A Observation Well (all monitoring wells) a. Type: 4” overburden wells and 6” bedrock wells. leaks Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper 6. B. Page 4 b. Screened Interval: Overburden wells 4-25 ft below grade; bedrock wells openhole interval averaged 15-25 ft long, set anywhere between 20-125 ft below grade. c. Packer Depth: d. Method of Data Collection: pressure transducers/data logger. Method of Analysis: (type A early data). N/A Manual electric water level meter and Theis, Cooper-Jacob straight line, Residual Drawdon, Neuman Pilot Test 1. Goals: No pilot test performed. 2. IV. Other: TECHNOLOGY DESIGN Typical System Components: Extraction Wells (Section A) Oil Water Separator (Section B) Air Stripper (Section C) Carbon Treatment (Section D) Other A. Extraction Wells 1. Design Goals a. 2. Provide 60 GPM to treatment system Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. g. (Recovery well) Pipe Type: Steel Casing Pipe Diameter: 6” Depth: 26 ft below grade Screen Interval: Open-hole from 26-41 ft below grade Screen Type: N/A Number and Spacing: N/A Other: N/A Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper B. 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Oil and Water Separator Not applicable 1. Design Goals: 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. C. Page 5 Flow Rate: Efficiency: Other: 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Air Stripper 1. Design Goals: Achieve <100 ppb total VOCs in effluent. Flexibility to achieve a lower target concentration or to treat a higher influent concentration. 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. g. Stripper Height: 7-8 ft (Tray Stripper) Stripper Diameter: Not applicable - 6 trays Blower Rate: 600 or 650 CFM Packing Material: N/A - tray stripper Pretreatment Requirements: Sand/Bag Filters. Clarifier is available. Removal Efficiency: 99.99% Other: Offgas from stripper is treated by a catalytic oxidizer. Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper Design Tools: Shallow Tray Modeler (Northeast Environmental) or STAT (Carbonair Environmental). Page 6 3. D. Modeler 4. Remediation Hardware: Northeast Environmental Shallow Tray units or Carbonair Environmental STAT units (air strippers). Global Technologies VTM Chlorocat (catalytic oxidizer). 5. Capital Cost: Engineer’s estimate: Process Equipment: $140,00 Including ductwork, electrical, concrete: $176,000 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Engineer’s estimate: $50,000 (not including cost to discharge effluent to the sanitary sewer plant). Carbon Treatment 1. Design Goals a. b. 2. Not applicable Contaminant Types: Contaminant Discharge Limits: Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. GAC Type: GAC Volume: Flow Through Rate: Contact Time: Removal Efficiency: Other: 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper V. Page 7 TECHNOLOGY PERFORMANCE A. Remediation Technology Choice 1. Other Remediation Technologies Considered for this Site: A Liquid-phase Carbon Adsorption system was originally installed. However, continued pumping resulted in mobilization of pure-phase DNALP, thereby increasing concentrations in the pumping well. Carbon adsorption was determined to be inefficient and not cost effective for long-term operation of the treatment system. A technology evaluation was performed and looked in detail at air stripping with off-gas treatment and UV oxidation. 2. 3. Why was Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper Chosen over Other Technologies? Air stripping with catalytic oxidation was determined to be more cost effective than UV oxidation or carbon adsorption over the long term. Remediation Technologies used at this Site in addition to Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper: Inorganic Removal System: equalization tank, inclined plate clarifier with pH adjustment and polymer addition, two parallel pressure sand filters, two parallel filter with 50 micron bag filters. B. Operation of Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper 1. 2. C. Duration: Not constructed yet. Construction is expected to begin after April 1996. Other: Lessons Learned Not applicable as system is not in place yet. 1. Lessons Learned about the Operation of the Equipment: 2. Why was the Technology Successful? 3. Why was the Technology Unsuccessful? Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper VI. CONTRACT TYPE AND COSTS A. B. C. Design of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: Navy RAC Contractor - Foster Wheeler/Lump Sum Approx. $20,000 Construction of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: Navy RAC Contractor - Foster Wheeler/Lump Sum Engineer’s Estimate: See IV C.5 Operation of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: Navy RAC Contractor - Foster Wheeler/Lump Sum Engineer’s Estimate: See IV C.6 Page 8 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Ground Water Pump and Treat with An Air Stripper nav_rem2.doc 3/20/97 Purpose: Concurrent Technologies Corporation (CTC), in conjunction with the Naval Facilities Engineering Command (NAVFAC), is collecting real-life design information on remediation technologies involving Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper. The collected information will be compiled into a technical design guidance document that will indicate if a specific selected remediation technology will be effective at a given site, the design criteria that should be considered for that site, and lessons learned from past users of these technologies. The guidance document will provide the information necessary to effectively design the selected remediation technology. Point of Contact concerning questionnaire: Scott W. Cuppett Phone number/E-mail: 814-269-2856/cuppett@ctc.com Date entered: Date updated: I. 2/96 GENERAL INFORMATION A. B. Installation Information 1. Type of Installation (e.g., Navy): USDE 2. Facility Name: US Department of Energy, Kansas City Plant 3. Address: Kansas City, Missouri Information Source 1. Name: Bruno Bodfeld 2. Address: Stone & Weber 3. Phone: 617/589-2767 4. Fax: 5. E-mail Address: 6. Source: EPA-542-R-95-003. March 1995. Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper II. Page 2 SITE CHARACTERISTICS A. B. Vadose Zone 1. Soil Type: Shales (PA Bedrock) 2. Unified Soil Classification: 3. Moisture Content: 4. Depth to Water Table: Saturated Zone Aquifer 1 C. 1. Soil Type: 2. Unified Soil Classification: 3. Hydraulic Conductivity: 4. Transmissivity: 5. Depth to Water Table: 6. Hydraulic Gradient: 7. Aquifer Type: 8. Capillary Fringe Height: 9. Porosity: 10. Groundwater velocity: 1.1-2.3 ft/day (sandstone 0.04-0.005 ft/day) 0.002-0.02 ft/ft 20% 8.4-55 ft/yr. Contaminants Present 1. Source of Contamination (e.g., gasoline spill): Manufacturing Process 2. Horizontal Extent of Site: 4,000 ft. 3. Vertical Extent of Site: 4. Temperature Range at Site: 5. Contaminant Names and Concentrations in Ground Water (ppm): PCE 40 ft. Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper TCE > 10,000 g/L 1,2-DCE Vinyl Chloride 6. III. Annual Precipitation: 34 inches PILOT OR BENCH SCALE TESTS A. Pump Test 1. Type (e.g., step test, continuous discharge): 2. Test Duration: 3. Pump Test Rate: 4. Pumping Well 5. 6. B. a. Type: b. Screened Interval: c. Packer Depth: Observation Well a. Type: b. Screened Interval: c. Packer Depth: d. Method of Data Collection: Method of Analysis: Pilot Test 1. Goals: 2. Other: Page 3 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper IV. Page 4 TECHNOLOGY DESIGN Typical System Components: Extraction Wells (Section A) Oil Water Separator (Section B) Air Stripper (Section C) Carbon Treatment (Section D) This System: Extraction wells, acidification, filtration, UV/Peroxide oxidation; neutralization; pump to miunicipal wastewater plant A. Extraction Wells 1. Design Goals a. 2. GPM to treatment system Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. g. B. Provide 2 Pipe Type: Stainless steel Pipe Diameter: 1-1/4” Depth: Approx. 247 ft Screen Interval: 27-47 ft below surface Screen Type: Stainless steel Number and Spacing: 14 Other: 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Oil and Water Separator 1. Design Goals: 2. Design Parameters 3. a. Flow Rate: b. Efficiency: c. Other: Design Tools: Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper C. 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Air Stripper - UV/Peroxide System 1. Design Goals: 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. g. D. Page 5 Stripper Height: Stripper Diameter: Blower Rate: Packing Material: Pretreatment Requirements: Removal Efficiency: > 99.95% VOCs Other: Maximum effulent permit of 0.16 mg/L total organic halogen; 0.69-100 mg/L metals 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Carbon Treatment 1. Design Goals a. b. 2. Not applicable Contaminant Types: Contaminant Discharge Limits: Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. GAC Type: GAC Volume: Flow Through Rate: Contact Time: Removal Efficiency: Other: Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper V. 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Page 6 TECHNOLOGY PERFORMANCE A. Remediation Technology Choice 1. Other Remediation Technologies Considered for this Site: 2. Why was Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper Chosen over Other Technologies? Although more expensive than air stripping, the UV/Peroxide system was selected because it destroys contaminants rather than transferring contaminants to other media. B. 3. Remediation Technologies used at this Site in addition to Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper: Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) Operation of Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper 1. 2. C. 5/88 - 2/94 + Lessons Learned 1. Duration: Other: Lessons Learned about the Operation of the Equipment: The ability to control flows from the central treatment systems building would be less difficult than manually adjusting individual well heads. Predicting aquifer restoration is complicated due to hydrogeologic variablity. Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper 2. VI. Why was the Technology Successful? The UV/Peroxide system eliminated need for GAC polishing and treatment and reduced operation and maintenance costs. Successful in containing contaminated groundwater. 3. Why was the Technology Unsuccessful? Frequent chemical treatment. Growth of bacterial slime. Inadequate initial design of UV/Ozone/Peroxide treatment system Significant downtime of UV/Peroxide system for cleaning filters, etc. CONTRACT TYPE AND COSTS A. B. Design of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: Construction of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: $1,383,400 (capital cost - equipment, site preparation, construction/engineering, start-up) C. Page 7 Operation of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: $355,200 (inclding maintenence, project management, laboratory analysis, supplies) Concurrent Technologies Corporation Ground Water Pump and Treat with An Air Stripper nav_rem2.doc 3/20/97 Purpose: Concurrent Technologies Corporation (CTC), in conjunction with the Naval Facilities Engineering Command (NAVFAC), is collecting real-life design information on remediation technologies involving Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper. The collected information will be compiled into a technical design guidance document that will indicate if a specific selected remediation technology will be effective at a given site, the design criteria that should be considered for that site, and lessons learned from past users of these technologies. The guidance document will provide the information necessary to effectively design the selected remediation technology. Point of Contact concerning questionnaire: Scott W. Cuppett Phone number/E-mail: 814-269-2856/cuppett@ctc.com Date entered: Date updated: I. 2/96 GENERAL INFORMATION A. B. Installation Information 1. Type of Installation (e.g., Navy): DOE 2. Facility Name: Savannah River Site A/M Area 3. Address: Aiken, South Carolina Information Source 1. Name: Scott McMullin 2. Address: 3. Phone: DOE Savannah River Aiken, SC 803/725-5541 4. Fax: 5. E-mail Address: Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper II. Page 2 SITE CHARACTERISTICS A. B. Vadose Zone 1. Soil Type: 2. Unified Soil Classification: 3. Moisture Content: 4. Depth to Water Table: approx. 100 ft Saturated Zone Aquifer 1 C. 5. 1. Soil Type: 2. Unified Soil Classification: 3. Hydraulic Conductivity: 9-73 ft./day 4. Transmissivity: 175-12,500 gpd/day 5. Depth to Water Table: approx. 100 ft 6. Hydraulic Gradient: 7. Aquifer Type: 8. Capillary Fringe Height: Aquifer 2 sand/clay Contaminants Present 1. Source of Contamination (e.g., gasoline spill): 2. Horizontal Extent of Site: 150 ft 3. Vertical Extent of Site 4. Temperature Range at Site: 1200 acres Contaminant Names and Concentrations in Ground Water (ppm): Chlorinated Aliphatics (TCE, PCE, TCA) VOC in groundwater up to 500 ppm. TCE in groundwater over 48 ppm. Groundwater contains 260,000-450,000 pounds of dissolved organic solvents. Soil TCE concentration > 10 ppm. Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper III. PILOT OR BENCH SCALE TESTS A. Pump Test 1. Type (e.g., step test, continuous discharge): 2. Test Duration: 3. Pump Test Rate: 4. Pumping Well 5. 6. B. a. Type: b. Screened Interval: c. Packer Depth: Observation Well a. Type: b. Screened Interval: c. Packer Depth: d. Method of Data Collection: Method of Analysis: Pilot Test 1. Goals: 2. Other: Page 3 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper IV. Page 4 TECHNOLOGY DESIGN Typical System Components: Extraction Wells (Section A) Oil Water Separator (Section B) Air Stripper (Section C) Carbon Treatment (Section D) Other A. Extraction Wells 1. Design Goals a. 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. g. B. Provide 610 GPM to treatment system Operated at approx. 500 GPM. Pipe Type: Pipe Diameter: Depth: Screen Interval: Screen Type: Number and Spacing: Other: 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Oil and Water Separator 1. Design Goals: 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. Flow Rate: Efficiency: Other: > 200 ft 11 recovery wells Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper C. 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Air Stripper 1. Design Goals: 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. g. D. Stripper Height: 70 ft Stripper Diameter: 4.5 ft Blower Rate: 2,500 CFM Packing Material: Propylene Pretreatment Requirements: Removal Efficiency: Other: 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Carbon Treatment 1. Design Goals a. b. 2. Contaminant Types: Contaminant Discharge Limits: Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. GAC Type: GAC Volume: Flow Through Rate: Contact Time: Removal Efficiency: Other: Page 5 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper V. 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Page 6 TECHNOLOGY PERFORMANCE A. B. Remediation Technology Choice 1. Other Remediation Technologies Considered for this Site: 2. Why was Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper Chosen over Other Technologies? 3. Remediation Technologies used at this Site in addition to Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper: Operation of Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper 1. 2. Duration: Other: 2 years Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper C. VI. Lessons Learned 1. Lessons Learned about the Operation of the Equipment: 2. Why was the Technology Successful? 3. Why was the Technology Unsuccessful? CONTRACT TYPE AND COSTS A. B. C. Design of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: See (B) Construction of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: $4,103,000 (design plus construction) Operation of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: $149,200 Page 7 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Ground Water Pump and Treat with An Air Stripper nav_rem2.doc 3/20/97 Purpose: Concurrent Technologies Corporation (CTC), in conjunction with the Naval Facilities Engineering Command (NAVFAC), is collecting real-life design information on remediation technologies involving Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper. The collected information will be compiled into a technical design guidance document that will indicate if a specific selected remediation technology will be effective at a given site, the design criteria that should be considered for that site, and lessons learned from past users of these technologies. The guidance document will provide the information necessary to effectively design the selected remediation technology. Point of Contact concerning questionnaire: Scott W. Cuppett Phone number/E-mail: 814-269-2856/cuppett@ctc.com Date entered: Date updated: I. 2/96 GENERAL INFORMATION A. B. Installation Information 1. Type of Installation (e.g., Navy): Air Force 2. Facility Name: Langley Air Force Base, IRP Site 4 3. Address: Langley, VA Information Source 1. Name: Bruno Bodfeld 2. Address: Stone & Weber 3. Phone: 617/589-2767 4. Fax: 5. E-mail Address: 6. Source: EPA-542-R-95-003. March 1995. Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper II. Page 2 SITE CHARACTERISTICS A. B. C. Vadose Zone 1. Soil Type: Fine sand, silts, shell beds 2. Unified Soil Classification: 3. Moisture Content: 4. Depth to Water Table: 23.8-36.2% approx. 7 ft Saturated Zone (Note: 3 aquifer systems are present - water table, upper artesian, and principle artesian) 1. Soil Type: 2. Unified Soil Classification: 3. Hydraulic Conductivity: 0.00099-0.002 ft/day 4. Transmissivity: 0.99-2.2 ft2/day 5. Depth to Water Table: artesian 4-6 ft. water table; 400 ft. upper artesian; 700 ft. principle 6. Hydraulic Gradient: 7. Aquifer Type: 8. Capillary Fringe Height: 9. Temperature: 10. pH: 20-24oC 6.4-7.2 Contaminants Present 1. Source of Contamination (e.g., gasoline spill): 2. Horizontal Extent of Site: 1,000 ft x 2,000 ft 3. Vertical Extent of Site: 4. Temperature Range at Site: 5. Contaminant Names and Concentrations in Ground Water (ppm): In water table only Up to 3 ppb BTEX; total petroleum hydrocarbons - 25-4,100 ppb Free product floating on groundwater exceeded 1 foot thickness. PILOT OR BENCH SCALE TESTS III. UST with JP-4 A. Pump Test 1. Type (e.g., step test, continuous discharge): 2. Test Duration: 3. Pump Test Rate: Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper 4. 5. 6. B. IV. Pumping Well a. Type: b. Screened Interval: c. Packer Depth: Observation Well a. Type: b. Screened Interval: c. Packer Depth: d. Method of Data Collection: Method of Analysis: Pilot Test 1. Goals: 2. Other: TECHNOLOGY DESIGN Typical System Components: Extraction Wells (Section A) Oil Water Separator (Section B) Air Stripper (Section C) Carbon Treatment (Section D) A. Extraction Wells 1. Design Goals a. Provide max. 60; avg. 32 GPM to treatment system (2 gpm per well average) Page 3 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. g. B. Pipe Type: Pipe Diameter: 8” Depth: 14 ft. BG Screen Interval: 3” well screen Screen Type: Number and Spacing: 16 Other: Internal 3/4” copper tubing with adjustable depth. 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Oil and Water Separator 1. Design Goals: 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. C. Page 4 Flow Rate: Efficiency: Other: High efficiency coalesce type 6 ft diameter, 24 ft long 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Air Stripper Column #1 1. Design Goals: 2. Design Parameters Column #2 a. Stripper Height: 16 ft 16 ft b. Stripper Diameter: 36” 30” c. Blower Rate: 1440 CFM @ 60 GPM 800 CFM @ 60 GPM d. Packing Material: Polypropylene Polypropylene e. Pretreatment Requirements: oil/water separation f. Removal Efficiency: g. Other: Discharge criteria of BTEX - Benzene (7 ppb), Toluene (50 ppb), Ethylbenzene (4.3 ppb), Total Xylenes (13 ppb), Lead (5.6 ppb), and TPH (1,000 ppb) Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper D. 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Carbon Treatment 1. Design Goals a. b. 2. Contaminant Types: Contaminant Discharge Limits: Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. V. Page 5 GAC Type: GAC Volume: Flow Through Rate: Contact Time: Removal Efficiency: Other: 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: TECHNOLOGY PERFORMANCE A. Remediation Technology Choice 1. Other Remediation Technologies Considered for this Site: 2. Why was Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper Chosen over Other Technologies? 3. Remediation Technologies used at this Site in addition to Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper: Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper B. C. Operation of Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper 1. Duration: 7/92-1/94 + 2. Other: Lessons Learned 1. Lessons Learned about the Operation of the Equipment: Operational difficulties prevented an effective capture zone. Heat tracing was inadequate in original design; oil/water separator experienced icing problems during shut downs. Controls must be readily accessible. Sampling ports must be located at treatment plant to enable quantification of system performance. The exhaust pipe on the oil and water separator must allow gases to release. Roof over treatment plant would have decreased downtime. Significant attention must be payed to prevention of fouling. 2. Why was the Technology Successful? 3. Why was the Technology Unsuccessful? VI. Operational problems prevented long-term operation, so zone of influence was reduced. Could not properly access system performance because of inability to take samples. CONTRACT TYPE AND COSTS A. B. C. Page 6 Design of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: See (B) Construction of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: $569,739 (design plus construction) Operation of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: (includes labor, materials, and equipment) Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper $216,561/yr (1993) $143,047/yr (1994) Page 7 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Ground Water Pump and Treat with An Air Stripper nav_rem2.doc 3/20/97 Purpose: Concurrent Technologies Corporation (CTC), in conjunction with the Naval Facilities Engineering Command (NAVFAC), is collecting real-life design information on remediation technologies involving Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper. The collected information will be compiled into a technical design guidance document that will indicate if a specific selected remediation technology will be effective at a given site, the design criteria that should be considered for that site, and lessons learned from past users of these technologies. The guidance document will provide the information necessary to effectively design the selected remediation technology. Point of Contact concerning questionnaire: Scott W. Cuppett Phone number/E-mail: 814-269-2856/cuppett@ctc.com Date entered: Date updated: I. 2/96 GENERAL INFORMATION A. B. Installation Information 1. Type of Installation (e.g., Navy): Air Force 2. Facility Name: Fort Drum Fuel Dispensing Area 1595 3. Address: Watertown, NY Information Source 1. Name: Bruno Bodfeld 2. Address: Stone & Weber 3. Phone: 617/589-2767 4. Fax: 5. E-mail Address: 6. Source: EPA-542-R-95-003. March 1995. Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper II. Page 2 SITE CHARACTERISTICS A. B. Sand Layer Vadose Zone 1. Soil Type: 2. Unified Soil Classification: 3. Moisture Content: 4. Depth to Water Table: Clay Layer 2.5-26% Saturated Zone Aquifer 1 C. 1. Soil Type: 2. Unified Soil Classification: 3. Hydraulic Conductivity: 0.11-0.0012 cm/sec 4. Transmissivity: 11,787-32,518 (Jacob Method) 5. Depth to Water Table: 6. Hydraulic Gradient: 7. Aquifer Type: 8. Capillary Fringe Height: 9. Groundwater velocity: 0.027 ft/ft 3.7 ft/day Contaminants Present 1. 2. Source of Contamination (e.g., gasoline spill): UST & wastewater from vehicle washing. Horizontal Extent of Site: 3. Vertical Extent of Site: 4. Temperature Range at Site: 5. Contaminant Names and Concentrations in Ground Water (ppm): Benzene, Toluene, 45.1 oF average Ethylbenzene, and Xylenes (BTEX) 6. Annual precipitation: 3.28 inch/month rainfall; 9.51 inch/month snowfall Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper III. PILOT OR BENCH SCALE TESTS A. Pump Test 1. Type (e.g., step test, continuous discharge): 2. Test Duration: 3. Pump Test Rate: 4. Pumping Well 5. 6. B. a. Type: b. Screened Interval: c. Packer Depth: Observation Well a. Type: b. Screened Interval: c. Packer Depth: d. Method of Data Collection: Method of Analysis: Pilot Test 1. Goals: 2. Other: Page 3 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper IV. TECHNOLOGY DESIGN Typical System Components: Extraction Wells (Section A) Oil Water Separator (Section B) Air Stripper (Section C) Carbon Treatment (Section D) Other A. Extraction Wells 1. Design Goals a. 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. g. B. Provide 5-6 GPM to treatment system Pipe Type: Pipe Diameter: Depth: 25 ft BG Screen Interval: 5-20 ft Screen Type: Number and Spacing: 2 Other: 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Oil and Water Separator 1. Design Goals: 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. 3. Flow Rate: Efficiency: Other: Design Tools: 575 gallon capacity Page 4 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper C. 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Air Stripper 1. Design Goals: 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. g. D. 750 CFM Stripper Height: 20 ft Stripper Diameter: 18” Blower Rate: 750 CFM Packing Material: Delta-Pak PVC Film Packing Pretreatment Requirements: Removal Efficiency: Other: 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Carbon Treatment 1. Design Goals a. b. 2. Contaminant Types: BTEX, Gasoline, and #2 Fuel Oil Contaminant Discharge Limits: Benzene: 3 µg/L Xylenes: 190 µg/L Toluene: 35 µg/L Ethylbenzene: 8 µg/L TARGET GAC EFFLUENT total < 0.20 mg/L Design Parameters a. b. c. d. GAC Type: GAC Volume: 200 lb./drum x 4 drums (in series) Flow Through Rate: Contact Time: Page 5 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper e. f. Page 6 Removal Efficiency: Other: 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 4 steel drums at 55 gallons each. GAC per drum / 2 in series. V. 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: TECHNOLOGY PERFORMANCE A. B. Remediation Technology Choice 1. Other Remediation Technologies Considered for this Site: 2. Why was Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper Chosen over Other Technologies? 3. Remediation Technologies used at this Site in addition to Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper: Operation of Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper 1. 2. Duration: ongoing Other: Info reported from time span of March 1992 - mid 1993. Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper C. Page 7 Lessons Learned 1. 2. Lessons Learned about the Operation of the Equipment: Recovery pumps required frequent maintenance. GAC system fouling with biomass and iron (high iron concentration > 17 mg/L). This site is unpaved; infiltrating precipitation affects contaminant mobilization. Why was the Technology Successful? Data not available yet. 3. VI. Why was the Technology Unsuccessful? System downtime due to fouling of oil/water separator and GAC units with inorganics and biomass; Recovery pumps deteriorated; Iron precipitation problem; Lack of trained personnel. CONTRACT TYPE AND COSTS A. B. C. Design of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: $365,720 Construction of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: $593,060 Operation of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: $129,440 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Ground Water Pump and Treat with An Air Stripper nav_rem2.doc 3/20/97 Purpose: Concurrent Technologies Corporation (CTC), in conjunction with the Naval Facilities Engineering Command (NAVFAC), is collecting real-life design information on remediation technologies involving Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper. The collected information will be compiled into a technical design guidance document that will indicate if a specific selected remediation technology will be effective at a given site, the design criteria that should be considered for that site, and lessons learned from past users of these technologies. The guidance document will provide the information necessary to effectively design the selected remediation technology. Point of Contact concerning questionnaire: Scott W. Cuppett Phone number/E-mail: 814-269-2856/cuppett@ctc.com Date entered: Date updated: I. 2/96 GENERAL INFORMATION A. B. Installation Information 1. Type of Installation (e.g., Navy): Air Force 2. Facility Name: McClellan Air Force Base 3. Address: Sacramento, CA Information Source 1. Name: Bruno Bodfeld 2. Address: Stone & Weber 3. Phone: 617/589-2767 4. Fax: 5. E-mail Address: 6. Source: EPA-542-R-95-0203. March 1995. Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper II. Page 2 SITE CHARACTERISTICS A. B. C. Vadose Zone 1. Soil Type: 2. Unified Soil Classification: 3. Moisture Content: 4. Depth to Water Table: 25% Saturated Zone (Note: An estimated 5 aquifers are present.) 1. Soil Type: 2. Unified Soil Classification: 3. Hydraulic Conductivity: 2.8-30.7 ft/day 4. Transmissivity: 100-2,000 ft2/day 5. Depth to Water Table: 6. Hydraulic Gradient: 7. Aquifer Type: 8. Capillary Fringe Height: Contaminants Present 1. Source of Contamination (e.g., gasoline spill): burn area 2. Horizontal Extent of Site: 3. Vertical Extent of Site: 4. Temperature Range at Site: 5. Contaminant Names and Concentrations in Ground Water (ppm): 6. Landfill; UST; disposal pit; open 60 oF average TCE; cis-1,2-DCE; PCE; 1,2-DCA Contaminants in groundwater were in 3 phases: sorbed into soil matrix, solubized in porewater, or free product Annual precipitation: 17 inches Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper III. PILOT OR BENCH SCALE TESTS A. Pump Test 1. Type (e.g., step test, continuous discharge): 2. Test Duration: 3. Pump Test Rate: 4. Pumping Well 5. 6. B. a. Type: b. Screened Interval: c. Packer Depth: Observation Well a. Type: b. Screened Interval: c. Packer Depth: d. Method of Data Collection: Method of Analysis: Pilot Test 1. Goals: 2. Other: Page 3 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper IV. Page 4 TECHNOLOGY DESIGN Typical System Components: Extraction Wells (Section A) Oil Water Separator (Section B) Air Stripper (Section C) Carbon Treatment (Section D) Other A. Extraction Wells 1. Design Goals a. 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. g. B. Provide 100-250 GPM to treatment system Pipe Type: Pipe Diameter: Depth: Screen Interval: 6-5/8” Screen Type: Number and Spacing: Other: 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Oil and Water Separator 1. Design Goals: 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. 3. Flow Rate: Efficiency: Other: Design Tools: PVC 2” 300 ft Slotted screen 7 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper C. 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Air Stripper 1. 2. Design Goals: Design capacity of 1,000 GPM. Average flow rate of 250 Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. g. D. Page 5 Stripper Height: Stripper Diameter: Blower Rate: Packing Material: Pretreatment Requirements: Removal Efficiency: Other: 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Carbon Treatment 1. Design Goals a. b. 2. Contaminant Types: Contaminant Discharge Limits: Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. GAC Type: GAC Volume: Flow Through Rate: Contact Time: Removal Efficiency: Other: GPM. Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper V. 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Page 6 TECHNOLOGY PERFORMANCE A. Remediation Technology Choice 1. Other Remediation Technologies Considered for this Site: 2. Why was Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper Chosen over Other Technologies? 3. Remediation Technologies used at this Site in addition to Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper: Thermal oxidizer and caustic scrubber for offgases; 2 gal units in series to polish liquid phase prior to discharge. B. Operation of Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper 1. 2. C. Duration: Other: Lessons Learned 1. Lessons Learned about the Operation of the Equipment: The plant has excess treatment capacity that requires internal groundwater recycling to sustain efficient treatment; thereby, increasing the operating cost. Precipitate of calcium and magnesium in air stripper were effected by substituting 2” packing for 1”. Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper 2. 3. VI. Why was the Technology Successful? Successful at contaning migration of contaminants. Effectively and consistently reduced VOC levels below discharge criteria. The success of the system makes it a candidate for future remediation efforts. Why was the Technology Unsuccessful? System must be expanded to capture other known contamination areas. Corrosion in hot vapor train due to condensation of acid gas . Changing the construction materials from carbon steel to nickel alloys improved laminar flow and eliminated stagnant regions. Acetone’s insolubility in water. CONTRACT TYPE AND COSTS A. B. C. Page 7 Design of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: Construction of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: Operation of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: $1,240,000 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Ground Water Pump and Treat with An Air Stripper nav_rem2.doc 3/20/97 Purpose: Concurrent Technologies Corporation (CTC), in conjunction with the Naval Facilities Engineering Command (NAVFAC), is collecting real-life design information on remediation technologies involving Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper. The collected information will be compiled into a technical design guidance document that will indicate if a specific selected remediation technology will be effective at a given site, the design criteria that should be considered for that site, and lessons learned from past users of these technologies. The guidance document will provide the information necessary to effectively design the selected remediation technology. Point of Contact concerning questionnaire: Scott W. Cuppett Phone number/E-mail: 814-269-2856/cuppett@ctc.com Date entered: Date updated I. 2/29/96 GENERAL INFORMATION A. B. Installation Information 1. Type of Installation (e.g., Navy): Army 2. Facility Name: Twin Cities Army Ammunition Plant 3. Address: New Brighton, Minnesota Information Source 1. Name: Bruno Bodfeld 2. Address: Stone & Weber Env. Technology & Services 3. Phone: 617/589-2767 4. Fax: 5. E-mail Address: 6. Source: EPA-542-R-95-003. March 1995. Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper II. Page 2 SITE CHARACTERISTICS A. B. C. Vadose Zone 1. Soil Type: Fractured bedrock; sand, clay, till layers 2. Unified Soil Classification: 3. Moisture Content: 4. Depth to Water Table: Saturated Zone Multilayer aquifer system 1. Soil Type: 2. Unified Soil Classification: 3. Hydraulic Conductivity: 0.001-137 ft/day 4. Transmissivity: 3,160-28,725 ft2/day 5. Depth to Water Table: 6. Hydraulic Gradient: 7. Aquifer Type: 8. Capillary Fringe Height: Contaminants Present 1. Source of Contamination (e.g., gasoline spill): (dumping, burning, etc.) Variety of waste disposal practices 2. Horizontal Extent of Site: 6 miles 3. Vertical Extent of Site: 4. Temperature Range at Site: 5. Contaminant Names and Concentrations in Ground Water (ppb): 500 ft NGVD 44 oF average 1,1-DCE 1,1-DCA *1,2-DCE-160ppb Chloroform *1,1,1-TCA *TCE-10,000 ppb *PCE TRCLE-3600 ppb 1,1,1-TCE-950 ppb TCLEE (* Target Constituents) 6. Average precipitation: 25 inches rainfall/yr; 40 inches snow/yr. Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper III. PILOT OR BENCH SCALE TESTS A. Pump Test 1. Type (e.g., step test, continuous discharge): 2. Test Duration: 3. Pump Test Rate: 4. Pumping Well 5. 6. B. a. Type: b. Screened Interval: c. Packer Depth: Observation Well a. Type: b. Screened Interval: c. Packer Depth: d. Method of Data Collection: Method of Analysis: Pilot Test 1. Goals: 2. Other: Page 3 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper IV. TECHNOLOGY DESIGN Typical System Components: Extraction Wells (Section A) Oil Water Separator (Section B) Air Stripper (Section C) Carbon Treatment (Section D) Other A. Extraction Wells 1. Design Goals a. b. 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. g. B. Provide 1450 GPM to treatment system Variable flow rate desired. Pipe Type: Steel Pipe Diameter: 8” Depth: 175 ft Screen Interval: Screen Type: Stainless steel (8”) Number and Spacing: 17 Other: Designed for an operating life of 30 years. 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Oil and Water Separator 1. Design Goals: 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. 3. Flow Rate: Efficiency: Other: Design Tools: Page 4 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper C. 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Air Stripper 1. Design Goals: 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. g. D. Page 5 Stripper Height: 36 ft Stripper Diameter: 2@7 ft; 2@8 ft (4 towers total) Blower Rate: 6,800-8,900 CFM Packing Material: Propylene Pretreatment Requirements: Removal Efficiency: 98% Other: Designed for an operating life of 30 years. Average of 23 lb VOCs removed/day. 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Carbon Treatment 1. $0.12 / 1000 gal $588,599 Not applicable Design Goals a. b. 2. $0.30 / 1000 gal $8,034,454 Contaminant Types: Contaminant Discharge Limits: Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. GAC Type: GAC Volume: Flow Through Rate: Contact Time: Removal Efficiency: Other: Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper V. 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Page 6 TECHNOLOGY PERFORMANCE A. Remediation Technology Choice 1. Other Remediation Technologies Considered for this Site: Bioremediation B. 2. Why was Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper Chosen over Other Technologies? 3. Remediation Technologies used at this Site in addition to Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper: Operation of Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper 1. 2. C. Duration: Other: 10/87 - 9/92+ (30+ years expected) Over 1.4 billion gallons of water pumped between 10/91- 9/92 Lessons Learned 1. 2. Lessons Learned about the Operation of the Equipment: A preventive maintenance program was helpful in increasing operational performance of the treatment facility. Phased design helped to ensure the system’s proper sizing and effectiveness. Efforts to quantifiy and model aquifer properties had limited usefulness because of multilayer aquifer system. Why was the Technology Successful? Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper 3. VI. 92,700 lbs VOCs removed in 6 years. Plume containment successful. Why was the Technology Unsuccessful? Extraction wells experienced both increases and decreases in the concentration of TRCLE. Air stripping transfer contaminants to the air. (Carbon technology may be needed) May have to extend forecasted duration from 30 years to 50-70 years, based on data collected. Little affect on plume size. CONTRACT TYPE AND COSTS A. B. C. Design of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: See (B) Construction of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: $8,034,454 (design plus installation) Operation of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: $588,599/yr. (includes power, labor, maintenence, laboratory charges, and replacement of tower packaging) Page 7 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Ground Water Pump and Treat with An Air Stripper nav_rem2.doc 3/20/97 Purpose: Concurrent Technologies Corporation (CTC), in conjunction with the Naval Facilities Engineering Command (NAVFAC), is collecting real-life design information on remediation technologies involving Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper. The collected information will be compiled into a technical design guidance document that will indicate if a specific selected remediation technology will be effective at a given site, the design criteria that should be considered for that site, and lessons learned from past users of these technologies. The guidance document will provide the information necessary to effectively design the selected remediation technology. Point of Contact concerning questionnaire: Scott W. Cuppett Phone number/E-mail: 814-269-2856/cuppett@ctc.com Date entered: Date updated: I. 4/96 SITE VISIT GENERAL INFORMATION A. B. Installation Information 1. Type of Installation (e.g., Navy): 2. Facility Name: 3. Address: Army Tobyhanna Army Depot Tobyhanna, PA 18466 Information Source 1. Name: Tom Wildoner 2. Address: Tobyhanna Army Depot Tobyhanna, PA 18466 3. Phone: 717-895-6498 4. Fax: 5. E-mail Address: Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper II. Page 2 SITE CHARACTERISTICS A. B. C. Vadose Zone 1. Soil Type: 2. Unified Soil Classification: 3. Moisture Content: 4. Depth to Water Table: Saturated Zone Aquifer 1 Aquifer 2 375-450 ft 1. Soil Type: 2. Unified Soil Classification: 3. Hydraulic Conductivity: 4. Transmissivity: 5. Depth to Water Table: 187 ft 6. Hydraulic Gradient: 0.03 ft/ft 7. Aquifer Type: Bedrock 8. Capillary Fringe Height: Contaminants Present 1. Source of Contamination (e.g., gasoline spill): 2. Horizontal Extent of Site: < 1 mile 3. Vertical Extent of Site: 4. Temperature Range at Site: 5. Contaminant Names and Concentrations in Ground Water (ppm): TCE - 16 ppb Barried drums Normal annual temp is 50oF Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper III. PILOT OR BENCH SCALE TESTS A. Pump Test 1. Type (e.g., step test, continuous discharge): 2. Test Duration: 3. Pump Test Rate: 4. Pumping Well 5. 6. B. a. Type: b. Screened Interval: c. Packer Depth: Observation Well a. Type: b. Screened Interval: c. Packer Depth: d. Method of Data Collection: Method of Analysis: Pilot Test 1. Goals: 2. Other: Page 3 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper IV. TECHNOLOGY DESIGN Typical System Components: Extraction Wells (Section A) Oil Water Separator (Section B) Air Stripper (Section C) Carbon Treatment (Section D) Other A. Extraction Wells 1. Design Goals a. 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. g. B. Provide 100 GPM to treatment system Pipe Type: Steel Pipe Diameter: 8” Depth: 185 ft. Screen Interval screen-depth to bottom 170 ft; diameter-4”: Screen Type: Number and Spacing: Other: Concrete grout; grout bottom-10 ft below surface 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Oil and Water Separator - Not applicable. 1. Design Goals: 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. Flow Rate: Efficiency: Other: Page 4 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper C. 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Air Stripper 1. Design Goals: 2. Reduce TCE concentrations by 72%. Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. g. D. Page 5 Stripper Height: 20 ft. Stripper Diameter: Blower Rate: Packing Material: Pretreatment Requirements: Removal Efficiency: ~90% Other: 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: Stripping tower is FRP Atlac resin with UV protection. Stripping blower motors are 208 volts, 3 phase, and 1 HP. 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Carbon Treatment 1. GAC system was replaced in 1989 with an air stripper. Design Goals a. b. 2. < $7,000/yr (1989 electricity usage) Contaminant Types: Contaminant Discharge Limits: Design Parameters a. b. c. GAC Type: GAC Volume: Flow Through Rate: Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper d. e. f. V. Page 6 Contact Time: Removal Efficiency: Other: 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: TECHNOLOGY PERFORMANCE A. Remediation Technology Choice 1. Other Remediation Technologies Considered for this Site: B. Calgon GAC filter was installed in 1981, but replaced in 1989 with an air stripper. 2. Why was Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper Chosen over Other Technologies? Calgon GAC system not performing well. 3. Remediation Technologies used at this Site in addition to Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper: Operation of Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper 1. 2. Duration: Other: 6 years Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper C. VI. Lessons Learned 1. Lessons Learned about the Operation of the Equipment: 2. Why was the Technology Successful? 3. Why was the Technology Unsuccessful? CONTRACT TYPE AND COSTS A. B. C. Design of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: Construction of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: Operation of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: ERS Page 7 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Ground Water Pump and Treat with An Air Stripper nav_rem2.doc 3/20/97 Purpose: Concurrent Technologies Corporation (CTC), in conjunction with the Naval Facilities Engineering Command (NAVFAC), is collecting real-life design information on remediation technologies involving Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper. The collected information will be compiled into a technical design guidance document that will indicate if a specific selected remediation technology will be effective at a given site, the design criteria that should be considered for that site, and lessons learned from past users of these technologies. The guidance document will provide the information necessary to effectively design the selected remediation technology. Point of Contact concerning questionnaire: Scott Cuppett Phone number/E-mail: 814-269-2856/cuppett@ctc.com Date entered: Date updated: I. 2/15/96 GENERAL INFORMATION A. B. Installation Information 1. Type of Installation (e.g., Navy): 2. Facility Name: 3. Address: Navy Naval Construction Battalion Center Gulfport, MS Information Source 1. Name: Art Conrad 2. Address: South Division NAVAC Eng Com 2155 Eagle Drive P.O. Box 190010 N. Chas, SC 29419-9010 3. Phone: 803-820-5520 4. Fax: 803-820-5563 5. E-mail Address: alconrad@efdsouth,navfac.navy.mil Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper II. Page 2 SITE CHARACTERISTICS A. B. C. Vadose Zone 1. Soil Type: Poorly graded medium-grained sands with some fines. 2. Unified Soil Classification: SP 3. Moisture Content: NA 4. Depth to Water Table: 6 ft Saturated Zone Aquifer 1 Aquifer 2 Silty sand N/A 1. Soil Type: 2. Unified Soil Classification: SP 3. Hydraulic Conductivity: 2.0 x 10-4 cm/sec 4. Transmissivity: 2,000 ft2/day 5. Depth to Water Table: 6 ft 6. Hydraulic Gradient: 0.006 feet/feet 7. Aquifer Type: Unconfined 8. Capillary Fringe Height: N/A Contaminants Present 1. Source of Contamination (e.g., gasoline spill): Solvent burned for fire fighting training. 2. Horizontal Extent of Site: 200 ft 3. Vertical Extent of Site: 4. Temperature Range at Site: 5. Contaminant Names and Concentrations in Ground Water (ppm): 35 ft 20C Volatile (e.g. Vinyl Chloride; 1,1,1-TCE; Toluene) Semi-Volatile (e.g. Naphthalen) Pesticides Dioxines Inorganics (e.g. Cadmium (Cd); Chromium (Cr); Nickel (Ni)) Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper III. Page 3 PILOT OR BENCH SCALE TESTS A. Pump Test 1. Type (e.g., step test, continuous discharge): 2. Test Duration: 3. Pump Test Rate: N/A 4. Pumping Well 5. 6. B. a. Type: b. Screened Interval: c. Packer Depth: N/A N/A Observation Well N/A a. Type: b. Screened Interval: c. Packer Depth: d. Method of Data Collection: Method of Analysis: Pilot Test 1. Goals: 2. Other: N/A Slug Test Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper IV. Page 4 TECHNOLOGY DESIGN Typical System Components: Extraction Wells (Section A) Oil Water Separator (Section B) Air Stripper (Section C) Carbon Treatment (Section D) Other A. Extraction Wells (with recovery trench) 1. Design Goals a. 2. 25 GPM to treatment system Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. g. B. Provide Pipe Type: Pipe Diameter: Depth: Screen Interval: 10 ft Screen Type: Number and Spacing: Other: 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: SS 3 and 70 feet apart Modelling using flowpath N/A N/A Oil and Water Separator 1. Design Goals: 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. SS 4” 20 ft 30 gallons Flow Rate: Efficiency: Other: 25 GPM N/A N/A Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper C. 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: N/A N/A N/A N/A Air Stripper 1. Design Goals: 25 GPM 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. g. D. Page 5 Stripper Height: 96 inches Stripper Diameter: 12 inches (width) Blower Rate: 150 CFM Packing Material: N/A Pretreatment Requirements: None Removal Efficiency: N/A Other: 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Carbon Treatment N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A 1. Design Goals 2. a. Contaminant Types: b. Contaminant Discharge Limits: Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. GAC Type: GAC Volume: Flow Through Rate: Contact Time: Removal Efficiency: Other: Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper V. 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Page 6 TECHNOLOGY PERFORMANCE A. Remediation Technology Choice 1. Other Remediation Technologies Considered for this Site: Bioremediation technology, soil vapor extraction, air sparging. B. 2. Why was Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper Chosen over Other Technologies? Objective is to recover free-phase product 3. Remediation Technologies used at this Site in addition to Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper: None at this time. Operation of Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper 1. 2. C. Duration: Other: 3 months and ongoing Lessons Learned 1. Lessons Learned about the Operation of the Equipment: N/A 2. Why was the Technology Successful? Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper TCE below drinking water standards. In progress 3. VI. Why was the Technology Unsuccessful? CONTRACT TYPE AND COSTS A. B. C. Design of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: Construction of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: Operation of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: Page 7 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Ground Water Pump and Treat with An Air Stripper nav_rem2.doc 3/20/97 Purpose: Concurrent Technologies Corporation (CTC), in conjunction with the Naval Facilities Engineering Command (NAVFAC), is collecting real-life design information on remediation technologies involving Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper. The collected information will be compiled into a technical design guidance document that will indicate if a specific selected remediation technology will be effective at a given site, the design criteria that should be considered for that site, and lessons learned from past users of these technologies. The guidance document will provide the information necessary to effectively design the selected remediation technology. Point of Contact concerning questionnaire: Trueman Seamans Phone number/E-mail: 804-322-4210/seamans@efdlant.navfac.navy.mil Date entered: Date updated: I. 3/20/96 GENERAL INFORMATION A. B. Installation Information 1. Type of Installation (e.g., Navy): 2. Facility Name: 3. Address: Navy Naval Air Warfare Center Lakehurst, New Jersey; Area H Information Source 1. Name: 2. Address: 3. Phone: 4. Fax: 5. E-mail Address: 6. Source: Moretrench Environmental Services. Operations and Maintenence Manual. Area H. Naval Air Warfare Center, New Jersey. October 1992. Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper II. Page 2 SITE CHARACTERISTICS A. B. Vadose Zone 1. Soil Type: 2. Unified Soil Classification: 3. Moisture Content: 4. Depth to Water Table: Saturated Zone Aquifer 1 C. 1. Soil Type: 2. Unified Soil Classification: 3. Hydraulic Conductivity: 4. Transmissivity: 5. Depth to Water Table: 6. Hydraulic Gradient: 7. Aquifer Type: 8. Capillary Fringe Height: Contaminants Present 1. Source of Contamination (e.g., gasoline spill): 2. Horizontal Extent of Site: 3. Vertical Extent of Site: 4. Temperature Range at Site: 5. Contaminant Names and Concentrations in Ground Water (ppm): Aquifer 2 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper III. PILOT OR BENCH SCALE TESTS A. Pump Test 1. Type (e.g., step test, continuous discharge): 2. Test Duration: 3. Pump Test Rate: 4. Pumping Well 5. 6. B. a. Type: b. Screened Interval: c. Packer Depth: Observation Well a. Type: b. Screened Interval: c. Packer Depth: d. Method of Data Collection: Method of Analysis: Pilot Test 1. Goals: 2. Other: Page 3 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper IV. Page 4 TECHNOLOGY DESIGN Typical System Components: Extraction Wells (Section A) Oil Water Separator (Section B) Air Stripper (Section C) Carbon Treatment (Section D) A. Extraction Wells 1. Design Goals a. 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. g. B. Provide ________ GPM to treatment system Pipe Type: Pipe Diameter: Depth: Screen Interval: Screen Type: Number and Spacing: Other: 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Oil and Water Separator 1. Design Goals: 2. Design Parameters a. Flow Rate: Centrifugal 150 GPM pump transfers process water from equalization tank to aerator Unit: 2,000 gal tank Rotary Aerator, Electric Mixer, and Recirculation Pump that is used to precipitate iron vents to air inlet of the strippers. b. Efficiency: c. Other: 3. Design Tools: Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper 4. Page 5 Remediation Hardware: A. Equalization tank: 5,000 gal tank equipped with an oil skimmer. B. Coagulant unit: 500 gal tank, electric mixer, and electric feed pump to add a 50% solution of coagulant to the aerator tank. Coagulant will agglomerate colloidal solids to achieve an effective size and settling rate. C. 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Air Stripper 1. Design Goals: 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. g. D. Two strippers in series Stripper Height: 14 ft packing Stripper Diameter: 3 ft OD Blower Rate: 500 to 1,000 cfm Packing Material: Pretreatment Requirements: Removal Efficiency: 99% Other: 150 GPM process water 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: pH Adjustment Unit is a 500 gal caustic holding tank and electric feed pump to add a 50% caustic solution of NaOH to the equalization tank. This raises the pH to 8.5 to precipitate out metal hydroxides. Carbon Treatment 1. Design Goals a. b. 2. Liquid Phase Vapor Phase Contaminant Types: Contaminant Discharge Limits: Design Parameters a. GAC Type: 3. b. GAC Volume: c. Flow Through Rate: d. Contact Time: e. Removal Efficiency: f. Other: Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: (2) 4,000 lb units in series (2) 2,000 lb units in series 150 GPM 15 min A. Polymer feet unit is a 500 gal tank and electric mixer and pump to feed flocculent to the flocculation tank to aid settling. B. Clarifier tank (8,800 gal) separates by sedimentation the precipitated solids. C. Clarifier sludge tank (2,000 gal) and a plate and frame filter press provide de-watering of the solids. Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper Page 6 D. 4-filter train treats water prior to the air stripper. V. 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: 7. Other: Treated water is discharged to an irrigation system TECHNOLOGY PERFORMANCE A. B. Remediation Technology Choice 1. Other Remediation Technologies Considered for this Site: 2. Why was Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper Chosen over Other Technologies? 3. Remediation Technologies used at this Site in addition to Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper: Operation of Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper 1. 2. C. Duration: Other: Lessons Learned 1. Lessons Learned about the Operation of the Equipment: Heating the air stripper emissions prior to entering the vapor phase carbon unit lowered the relative humidity to about 50% and raised the VOC removal efficiency. Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper VI. 2. Why was the Technology Successful? 3. Why was the Technology Unsuccessful? CONTRACT TYPE AND COSTS A. B. C. Design of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: Construction of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: Operation of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: Page 7 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper Page 8 Purpose: Concurrent Technologies Corporation (CTC), in conjunction with the Naval Facilities Engineering Command (NAVFAC), is collecting real-life design information on remediation technologies involving Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper. The collected information will be compiled into a technical design guidance document that will indicate if a specific selected remediation technology will be effective at a given site, the design criteria that should be considered for that site, and lessons learned from past users of these technologies. The guidance document will provide the information necessary to effectively design the selected remediation technology. Point of Contact concerning questionnaire: Trueman Seamans Phone number/E-mail: 804-322-4210/seamans@efdlant.navfac.navy.mil Date entered: Date updated: I. 3/20/96 GENERAL INFORMATION A. B. Installation Information 1. Type of Installation (e.g., Navy): 2. Facility Name: 3. Address: Navy Naval Air Engineering Center Lakehurst, NJ; Site No. 28, Area E Information Source 1. Name: 2. Address: 3. Phone: 4. Fax: 5. E-mail Address: 6. Source: Moretrench American Corporation, Inc. Design Verification for the Groundwater Treatment System. Site No. 28, Area E. Naval Air Engineering Center. Lakehurst, NJ. December 1991. Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper II. Page 9 SITE CHARACTERISTICS A. B. Vadose Zone 1. Soil Type: 2. Unified Soil Classification: 3. Moisture Content: 4. Depth to Water Table: Saturated Zone Aquifer 1 2 C. 1. Soil Type: 2. Unified Soil Classification: 3. Hydraulic Conductivity: 4. Transmissivity: 5. Depth to Water Table: 6. Hydraulic Gradient: 7. Aquifer Type: 8. Capillary Fringe Height: Contaminants Present 1. Source of Contamination (e.g., gasoline spill): 2. Horizontal Extent of Site: 3. Vertical Extent of Site: 4. Temperature Range at Site: 5. Contaminant Names and Concentrations in Ground Water (ppm): Napthalene 2-Methyl Naphthalene Toluene o-Xylene Ethylbenzene Benzene Aquifer Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper III. PILOT OR BENCH SCALE TESTS A. Pump Test 1. Type (e.g., step test, continuous discharge): 2. Test Duration: 3. Pump Test Rate: 4. Pumping Well 5. 6. B. a. Type: b. Screened Interval: c. Packer Depth: Observation Well a. Type: b. Screened Interval: c. Packer Depth: d. Method of Data Collection: Method of Analysis: Pilot Test 1. Goals: 2. Other: Page 10 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper IV. TECHNOLOGY DESIGN Typical System Components: Extraction Wells (Section A) Oil Water Separator (Section B) Air Stripper (Section C) Carbon Treatment (Section D) Other A. Extraction Wells 1. Design Goals a. 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. g. B. Provide ________ GPM to treatment system Pipe Type: Pipe Diameter: Depth: Screen Interval: Screen Type: Number and Spacing: Other: 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Oil and Water Separator 1. Design Goals: 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. 3. Flow Rate: Efficiency: Other: Design Tools: Page 11 Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper C. 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Air Stripper 1. Design Goals: 2. Design Parameters a. b. c. d. e. f. g. Two air strippers in series Stripper Height: 14 ft packing Stripper Diameter: 36 in OD Blower Rate: Packing Material: Jaeger Tripacks Plastic Pretreatment Requirements: Removal Efficiency: >99% Other: air to water ratio: 75 to 1 3. Design Tools: 4. Remediation Hardware: D. Page 12 Airstrip Version 1.2 Computer Program !" # $! %& 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: Carbon Treatment 1. Phase Design Goals a. b. 2. Treat Liquid Phase Treat Vapor Air Stripper Effluent Air Stripper Emissions Contaminant Types: Contaminant Discharge Limits: Design Parameters a. b. c. GAC Type: GAC Volume: Flow Through Rate: Two 4,00 Units in Series 2,000 lb carbon bed 100 GPM (130 GPM Max) 800 CFM (1100 CFM Max) d. Contact Time: 19.8 min at 100 GPM (15.2 min @ 130 GPM) e. f. Removal Efficiency: Other: 1.3 lb/day @ 100 CFM process flow Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper V. Page 13 3. Design Tools: Carbon capacity based on isotherm data for sorption of aqueous constituents, EPA–600/8-80-023, 1980 4. Remediation Hardware: 5. Capital Cost: 6. Operating and Maintenance Cost: TECHNOLOGY PERFORMANCE A. B. Remediation Technology Choice 1. Other Remediation Technologies Considered for this Site: 2. Why was Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper Chosen over Other Technologies? 3. Remediation Technologies used at this Site in addition to Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper: Operation of Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper 1. 2. C. Duration: Other: Lessons Learned 1. Lessons Learned about the Operation of the Equipment: Concurrent Technologies Corporation Remediation Survey Ground Water Pump and Treat with an Air Stripper VI. 2. Why was the Technology Successful? 3. Why was the Technology Unsuccessful? CONTRACT TYPE AND COSTS A. B. C. Design of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: Construction of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: Operation of System 1. Contract Type: 2. Cost: Page 14