Document 12071495
advertisement

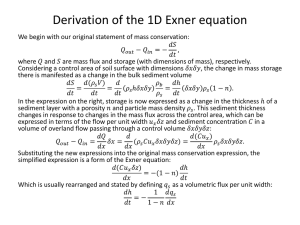
Assessment of Toxicity of Upper Danube River Sediments Using a Combination of Chemical Fractionation, the Danio rerio Embryo Assay and the Ames Fluctuation Test Eric Higley1, Stefanie Grund3, Thomas B.-Seiler2, Urte Lubcke-von Varel6 ,Werner Brack6, Tobias Schulz6, Jan Wölz2, Hanno Zielke2, John Giesy1,5, Henner Hollert2, Markus Hecker4 1. University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, 2 RWTH, Aachen, Germany, 3 University of Heidelberg, Heidelberg, Germany, 4 ENTRIX, Inc., Saskatoon, SK, 5 City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China, 6 UFZ Leipzig, Germany. Sediment Sampling Sites Introduction Objectives Severely contaminated sediments from many rivers and lakes have been shown to be acutely and chronically toxic to fish and benthic invertebrate species. For example, sediment samples from the Upper Danube River that were analyzed in six separate assays were found to have considerable geno-toxic, cytotoxic, mutagenic, embryo-toxic and estrogenic effects. It has been hypothesized that decline in fish stocks in the Upper Danube River since the early 1990s may be associated with this pollution. Here, we report on the results of a study conducted as a part of a larger study to characterize toxicity of extracts from sediments of the Danube River by means of Effect Direct Analysis. In this study, embryo-toxic effects were analyze using the Danio rerio embryo assay, and by assessing lethal and sub lethal endpoints. In addition, mutagenicity was assessed using the Ames fluctuation assay. For the sediment samples that revealed toxicity, fractionation of each sample was performed by separating compounds according to their polarity, planarity, and the size of the aromatic ring system. 18 fractions for each sediment sample were tested separately in the Ames fluctuation assay and Danio rerio embryo assay to assess which group of chemicals within the sediment sample caused the original toxicity. 1. Assess the toxicity of raw sediment extracts from four locations along the Upper Danube River using the Zebrafish Embryo Assay and Ames Fluctuation Assay 2. Evaluate which groups of chemicals caused the measured toxicities using new chemical fractionation techniques that separate the raw sediment extracts into 18 different chemical fractions. Results Mutagenic Effect (# of revertant) TA98 Bacteria Strain +S9 Lauchert reference Öpfingen 16.0 14.0 12.0 10.0 8.0 6.0 4.0 2.0 0.0 Danio rerio Embryo Assay 16.0 14.0 12.0 10.0 8.0 6.0 4.0 2.0 0.0 Lauchert reference Lauchert Öpfingen Sigmaringen Incubate for 90 minutes with histidine Viable eggs less than 1 hour old are collected Zebrafish are breed overnight Add pH indicator media without histidine Place histidine deficient bacteria into 384 well plate without histidine + Zebra fish egg + ISO water Incubate for 48 hours in 96 well plate Incubate at 37 ° C for 48 hours After 48 hours, any bacteria that have back mutated and can produce histidine will live and grow and turn the media from purple to yellow Count # of wells that are yellow Record lethal effects after 48 hours * * * 12.5 25.0 50.0 100.0 200.0 400.0 Augsburg Augsburg 2 1 3 Opfingen (3) (Opf2006) Lech Lauchert (tributary), 3 = Opfingen. according to LFW (2005)) = Sewage treatment plants (> 10,000 residents *** *** * 50.0 100.0 200.0 400.0 PC PC Lauchert reference Lauchert Öpfingen Sigmaringen ** 15.0 * * 10.0 5.0 0.0 SC 12.5 25.0 50.0 100.0 200.0 400.0 PC Sediment Equivalent Concentrations (mg/ml) Figure 2. Dose response of four whole sediment extracts ran in the Ames Fluctuation Assay with and without the liver enzyme S9 mix and on two different bacteria strains. TA98 bacteria measures frameshift mutations and TA100 bacteria measures base pair mutations. * indicates significant difference from control. Figure 4. Mutagenic response of the 18 fractions as measured by the Ames Fluctuation assay (TA98 and TA100 bacteria with and without S9 bioactivation enzymes). * indicates significant difference from control Danio rerio embryo assay on whole extracts Öpfingen Sigmaringen Lauchert Lauchert Reference Sediment sample in DMSO Danube River TA100 Bacteria Strain -S9 * Sediment Equivalent Concentration (mg/ml) Bacteria culture 25.0 TA100 Bacteria Strain +S9 SC Sediment sample in DMSO Lauchert (2) (Lau2006 and 2004) Figure 1: Sampling sites along the Upper Danube River; 1 = Sigmaringen, 2 = *** *** ** 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Results and Conclusions • Mortality of Danio rerio embryos increased in a dose-dependent manner when exposed to whole sediments collected at Öpfingen and Sigmaringen (Figure 3), but none of the fractionated samples were toxic. These results indicate that the observed toxicity was likely due to the combination of groups of chemicals in the whole sediment samples. • Toxicity was observed for whole sediments from Sigmaringen, Öpfingen and Lauchert in the Ames Fluctuation Assay only when TA98 bacteria with S9 were tested (Figure 2). Toxicity was also found in the fractionated samples in both bacterial strains, although the pattern was inconsistent. • Fraction 10, which contains PAH’s with five aromatic rings, produced a significant SC 12.5 25 50 100 mutagenic response in all sediment samples measured only in S9 bio-activated Sediment equivalents concentration (mg/ml) samples (Figure 4) Figure 3. Dose response of four sediment extracts analyzed with the Danio rerio embryo assay • Fraction 15 which contains hydroxyl PAHs produced a significant mutagenic response in all sediment samples measured only in non bio-activated samples (Figure 4) Mortality % Ames Fluctuation Assay Lauchert Sigmaringen *** Mutagenic Effect (# of revertants) •Crude sediment extracts and all 18 fractions were analyzed for their toxicity using the Ames fluctuation assay and Danio rerio egg assay Stuttgart SWITZERLAND *** 12.5 Ingolstadt Sediment Equivalent Concentrations (mg/ml) Mutagenic Effect (# of revertants) •Samples were extracted and fractionated into different chemical groups using a new technique by Varel et al., 2008 that uses 3 HPLC columns and separates the sample into 18 fractions according to their polarity, planarity and the size of their aromatic system Danube Sigmaringen (1) (Sig2006) SC •Sediments were sampled (top 5cm) at four locations along the Upper Danube River using a Van Veenen grabber in January 2006 (Figure 1) deficient Weser Main 3. Analyze all 18 chemical fractions using the Danio rerio Embryo Assay and Ames Fluctuation Assay. Sampling and extraction + Elbe Rhine Methods Histidine Germany