MATH 1030-008: FINAL EXAM FORMULAS TO KNOW
advertisement
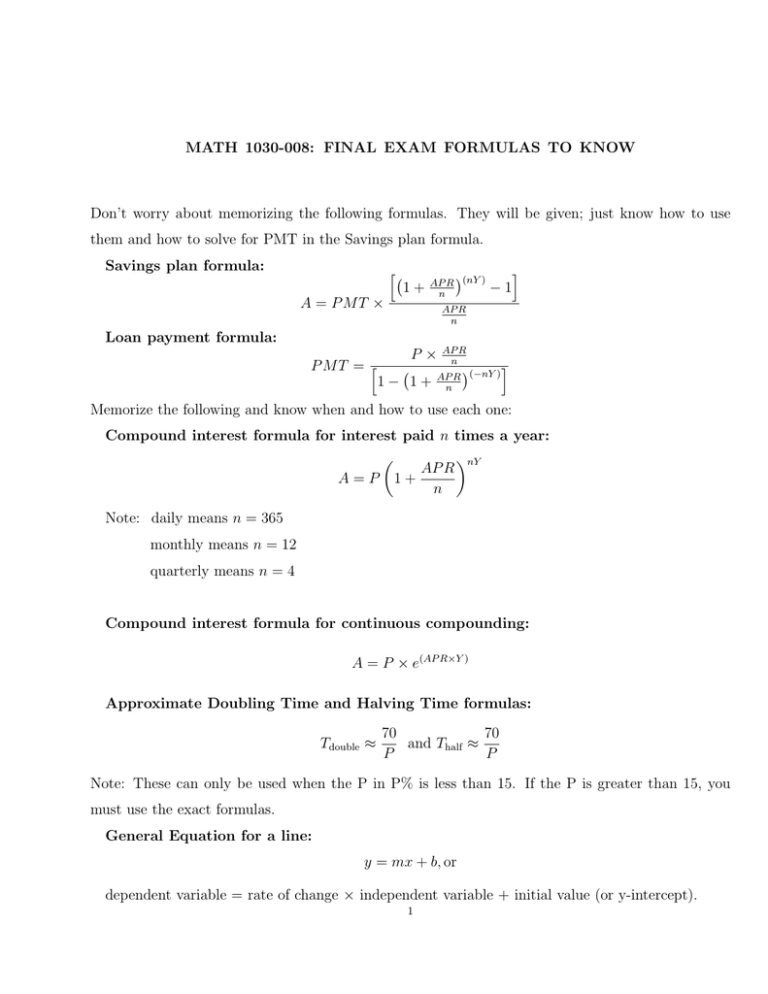
MATH 1030-008: FINAL EXAM FORMULAS TO KNOW Don’t worry about memorizing the following formulas. They will be given; just know how to use them and how to solve for PMT in the Savings plan formula. Savings plan formula: h 1+ A = P MT × AP R (nY ) n i −1 AP R n Loan payment formula: P MT = h P× 1− 1+ AP R n AP R (−nY ) n i Memorize the following and know when and how to use each one: Compound interest formula for interest paid n times a year: nY AP R A=P 1+ n Note: daily means n = 365 monthly means n = 12 quarterly means n = 4 Compound interest formula for continuous compounding: A = P × e(AP R×Y ) Approximate Doubling Time and Halving Time formulas: Tdouble ≈ 70 70 and Thalf ≈ P P Note: These can only be used when the P in P% is less than 15. If the P is greater than 15, you must use the exact formulas. General Equation for a line: y = mx + b, or dependent variable = rate of change × independent variable + initial value (or y-intercept). 1 2 MATH 1030-008: FINAL EXAM FORMULAS TO KNOW Rate of change: rate of change = slope = m = change in dependent variable change in independent variable = rise run = change in y change in x Surface Area and Volume of a Rectangular Box (a.k.a Prism) Surface Area = 2(lw + wh + lh) Volume = lwh Surface Area and Volume of a Cylinder Surface Area = Area of 2 circles + Area of curved curface of cylinder = 2πr2 + Area of a rectangle with length πd and height h = 2πr2 + πdh = 2πr2 + 2πrh Volume = πr2 h Note: The above formulas have the formulas for area of a circle and area for a rectangle in them; this means you will need to know those too. Equations for Exponential functions Q = Q0 × (1 + r)t Q = Q0 × 2t/Tdouble t/Tdouble Q = Q0 × 21



