Correlation between Non-Insulin Diabetic Patients and A1C Hemoglobin Levels • Literature Review
advertisement
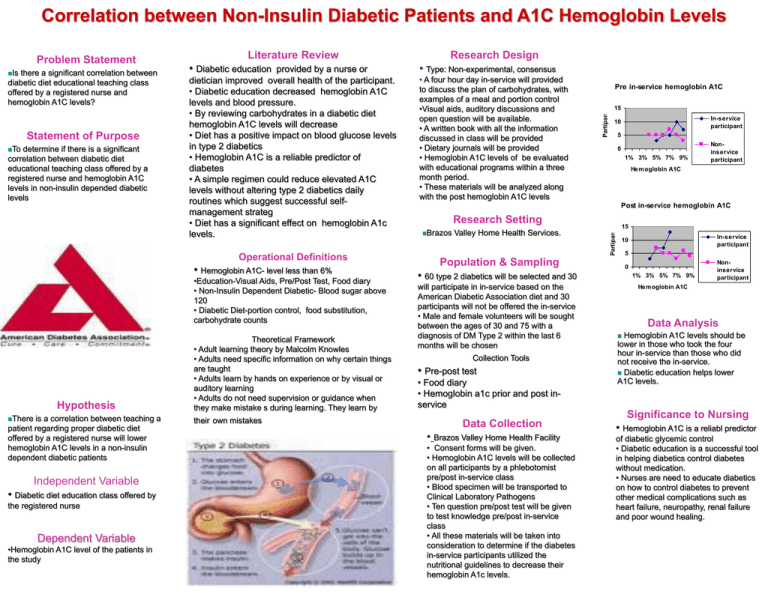
Correlation between Non-Insulin Diabetic Patients and A1C Hemoglobin Levels there a significant correlation between diabetic diet educational teaching class offered by a registered nurse and hemoglobin A1C levels? Statement of Purpose To determine if there is a significant correlation between diabetic diet educational teaching class offered by a registered nurse and hemoglobin A1C levels in non-insulin depended diabetic levels • Diabetic education provided by a nurse or • Type: Non-experimental, consensus dietician improved overall health of the participant. • Diabetic education decreased hemoglobin A1C levels and blood pressure. • By reviewing carbohydrates in a diabetic diet hemoglobin A1C levels will decrease • Diet has a positive impact on blood glucose levels in type 2 diabetics • Hemoglobin A1C is a reliable predictor of diabetes • A simple regimen could reduce elevated A1C levels without altering type 2 diabetics daily routines which suggest successful selfmanagement strateg • Diet has a significant effect on hemoglobin A1c levels. • A four hour day in-service will provided to discuss the plan of carbohydrates, with examples of a meal and portion control •Visual aids, auditory discussions and open question will be available. • A written book with all the information discussed in class will be provided • Dietary journals will be provided • Hemoglobin A1C levels of be evaluated with educational programs within a three month period. • These materials will be analyzed along with the post hemoglobin A1C levels Operational Definitions • Hemoglobin A1C- level less than 6% •Education-Visual Aids, Pre/Post Test, Food diary • Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetic- Blood sugar above 120 • Diabetic Diet-portion control, food substitution, carbohydrate counts Hypothesis There is a correlation between teaching a patient regarding proper diabetic diet offered by a registered nurse will lower hemoglobin A1C levels in a non-insulin dependent diabetic patients Independent Variable • Diabetic diet education class offered by the registered nurse Dependent Variable •Hemoglobin A1C level of the patients in the study Theoretical Framework • Adult learning theory by Malcolm Knowles • Adults need specific information on why certain things are taught • Adults learn by hands on experience or by visual or auditory learning • Adults do not need supervision or guidance when they make mistake s during learning. They learn by their own mistakes Pre in-service hemoglobin A1C 15 In-service participant 10 5 0 1% 3% 5% 7% 9% Noninservice participant Hem oglobin A1C Post in-service hemoglobin A1C Research Setting Brazos Valley Home Health Services. 15 Partipant Is Research Design Partipant Problem Statement Literature Review 5 Population & Sampling 0 • 60 type 2 diabetics will be selected and 30 will participate in in-service based on the American Diabetic Association diet and 30 participants will not be offered the in-service • Male and female volunteers will be sought between the ages of 30 and 75 with a diagnosis of DM Type 2 within the last 6 months will be chosen Collection Tools • Pre-post test • Food diary • Hemoglobin a1c prior and post inservice Data Collection • Brazos Valley Home Health Facility • Consent forms will be given. • Hemoglobin A1C levels will be collected on all participants by a phlebotomist pre/post in-service class • Blood specimen will be transported to Clinical Laboratory Pathogens • Ten question pre/post test will be given to test knowledge pre/post in-service class • All these materials will be taken into consideration to determine if the diabetes in-service participants utilized the nutritional guidelines to decrease their hemoglobin A1c levels. In-service participant 10 1% 3% 5% 7% 9% Noninservice participant Hem oglobin A1C Data Analysis Hemoglobin A1C levels should be lower in those who took the four hour in-service than those who did not receive the in-service. Diabetic education helps lower A1C levels. Significance to Nursing • Hemoglobin A1C is a reliabl predictor of diabetic glycemic control • Diabetic education is a successful tool in helping diabetics control diabetes without medication. • Nurses are need to educate diabetics on how to control diabetes to prevent other medical complications such as heart failure, neuropathy, renal failure and poor wound healing.