1.2 GHz Clock Fanout Buffer with Output Dividers and Delay AD9508-EP Enhanced Product
advertisement

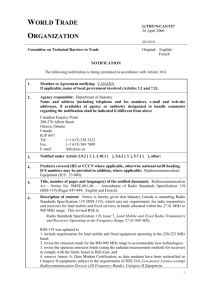
1.2 GHz Clock Fanout Buffer with Output Dividers and Delay AD9508-EP Enhanced Product FEATURES GENERAL DESCRIPTION 1.2 GHz differential clock inputs/outputs 10-bit programmable dividers, 1 to 1024, all integers Up to 4 differential outputs or 8 CMOS outputs Pin strapping mode for hardwired programming at power-up <115 fs rms broadband random jitter (see Figure 25) Additive output jitter: 41 fs rms typical (12 kHz to 20 MHz) Excellent output-to-output isolation Automatic synchronization of all outputs Single 2.5 V power supply Internal low dropout (LDO) voltage regulator for enhanced power supply immunity Phase offset select for output-to-output coarse delay adjust 3 programmable output logic levels: LVDS, HSTL, and CMOS Serial control port (SPI/I2C) or pin programmable mode Space-saving 24-lead LFCSP The AD9508-EP provides clock fanout capability in a design that emphasizes low jitter to maximize system performance. The AD9508-EP benefits applications such as clocking data converters with demanding phase noise and low jitter requirements. ENHANCED PRODUCT FEATURES The device can also be pin programmed for various fixed configurations at power-up without the need for SPI or I²C programming. The AD9508-EP has four independent differential clock outputs, each with various types of logic levels available. Available logic types are LVDS (1.2 GHz), HSTL (1.2 GHz), and 1.8 V CMOS (250 MHz). In 1.8 V CMOS output mode, the differential output becomes two CMOS single-ended signals. The CMOS outputs are 1.8 V logic levels. Each output has a programmable divider that can be bypassed or set to divide by any integer up to 1024. In addition, the AD9508-EP supports coarse output phase adjustment between the outputs. Supports defense and aerospace applications (AQEC standard) Extended temperature range: −55°C to +105°C Controlled manufacturing baseline One assembly/test site One fabrication site Enhanced product change notification Qualification data available on request The AD9508-EP is available in a 24-lead LFCSP and operates from a single 2.5 V power supply. The temperature range is −55°C to +105°C. Additional application and technical information can be found in the AD9508 data sheet. APPLICATIONS Low jitter, low phase noise clock distribution Clocking high speed ADCs, DACs, DDSs, DDCs, DUCs, MxFEs High performance wireless transceivers High performance instrumentation Broadband infrastructure FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM DIV/Φ CLK DIV/Φ CLK DIV/Φ SCLK/SCL/S0 SDIO/SDA/S1 SDO/S3 CS/S2 DIV/Φ CONTROL INTERFACE SPI/I2C/PINS PIN CONTROL RESET SYNC OUT0 OUT0 OUT1 OUT1 OUT2 OUT2 OUT3 OUT3 11367-001 AD9508-EP Figure 1. Rev. B Document Feedback Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners. One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A. Tel: 781.329.4700 ©2013–2014 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Technical Support www.analog.com AD9508-EP Enhanced Product TABLE OF CONTENTS Features .............................................................................................. 1 Serial Port Specifications—I2C Mode .........................................7 Enhanced Product Features ............................................................ 1 External Resistor Values for Pin Strapping Mode .....................7 Applications ....................................................................................... 1 Clock Output Additive Phase Noise ...........................................8 General Description ......................................................................... 1 Clock Output Additive Time Jitter..............................................9 Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1 Absolute Maximum Ratings ......................................................... 10 Revision History ............................................................................... 2 Thermal Characteristics ............................................................ 10 Specifications..................................................................................... 3 ESD Caution................................................................................ 10 Power Supply Current and Temperature Conditions .............. 3 Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions........................... 11 Clock Input and Output DC Specifications .............................. 3 Typical Performance Characteristics ........................................... 13 Output Driver Timing Characteristics ...................................... 5 Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 19 Logic Inputs ................................................................................... 5 Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 19 Serial Port Specifications—SPI Mode ........................................ 6 REVISION HISTORY 10/14—Rev. A to Rev. B Changed Input Resistance (Differential) to Input Resistance (Single-Ended), Table 2 .................................................................... 3 10/13—Rev. 0 to Rev. A Changes to Ordering Guide .......................................................... 19 7/13—Revision 0: Initial Version Rev. B | Page 2 of 19 Enhanced Product AD9508-EP SPECIFICATIONS Typical values are given for VS = 2.5 V and TA = 25°C; minimum and maximum values are given over the full supply voltage range (VDD = 2.5 V ± 5%) and temperature range (TA = −55°C to +105°C); input slew rate > 1 V/ns, unless otherwise noted. POWER SUPPLY CURRENT AND TEMPERATURE CONDITIONS Table 1. Parameter SUPPLY VOLTAGE CURRENT CONSUMPTION LVDS Configuration Min 2.375 HSTL Configuration CMOS Configuration Full Power-Down TEMPERATURE Ambient Temperature Range, TA Junction Temperature, TJ −55 Typ 2.5 Max 2.625 Unit V Test Conditions/Comments 132 148 mA 96 108 mA 156 175 mA 121 136 mA 86 96 mA 142 159 mA 118 132 mA 76 85 mA Input clock at 1200 MHz, differential mode; all LVDS output drivers at 1200 MHz Input clock at 800 MHz, differential mode; all LVDS output drivers at 200 MHz Input clock at 1200 MHz, differential mode; all HSTL output drivers at 1200 MHz Input clock at 491.52 MHz, differential mode; all HSTL output drivers at 491.52 MHz Input clock at 122.88 MHz, differential mode; all HSTL output drivers at 122.88 MHz Input clock at 1200 MHz, differential mode; all CMOS output drivers at 200 MHz, CLOAD = 10 pF Input clock at 800 MHz, differential mode; all CMOS output drivers at 200 MHz, CLOAD = 10 pF Input clock at 100 MHz, differential mode; all CMOS output drivers at 100 MHz, CLOAD = 10 pF 4.6 8 mA +25 +105 135 °C °C Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments 1200 2200 MHz mV p-p 1.15 V Differential input As measured with a differential probe; jitter performance improves with higher slew rates (greater voltage swing) Input pins are internally self biased, which enables ac coupling 1.67 mV V Junction temperatures above 115°C can degrade performance, but no damage should occur unless the absolute temperature is exceeded CLOCK INPUT AND OUTPUT DC SPECIFICATIONS Table 2. Parameter CLOCK INPUTS (DIFFERENTIAL MODE) Input Frequency Input Sensitivity Input Common-Mode Voltage Input Voltage Offset DC-Coupled Input Common-Mode Range Pulse Width Low Pulse Width High Input Resistance (Single-Ended) Input Capacitance Input Bias Current (Each Pin) Symbol Min 0 360 VICM 0.95 VCMR 0.58 1.05 30 417 417 5.0 CIN 100 7 2 9 400 Rev. B | Page 3 of 19 ps ps kΩ pF µA Allowable common-mode voltage range when dc-coupled Full input swing AD9508-EP Parameter CMOS CLOCK MODE (SINGLE-ENDED) Input Frequency Input Voltage High Input Voltage Low Input Current High Input Current Low Input Capacitance LVDS CLOCK OUTPUTS Output Frequency Differential Output Voltage Enhanced Product Symbol Min Typ VIH VIL IINH IINL CIN VDD − 0.4 Max Unit 250 MHz V V µA µA pF 0.4 1 −142 2 Termination = 100 Ω differential (OUTx, OUTx) VOD Delta VOD ΔVOD Offset Voltage Delta VOS VOS ΔVOS Short-Circuit Current LVDS Duty Cycle ISA, ISB 247 1.125 1200 454 MHz mV 50 mV 1.18 1.375 50 V mV 13.6 24 55 61 mA % % 1200 978 971 55 60 MHz mV mV % % 250 MHz 0.1 V V 0.6 V V 0.35 55 V V % 375 45 39 HSTL CLOCK OUTPUTS Output Frequency Differential Output Voltage Common-Mode Output Voltage HSTL Duty Cycle VO VOCM 859 905 45 40 925 940 CMOS CLOCK OUTPUTS Output Frequency Output Voltage 1 mA Load High Low 10 mA Load High Low 10 mA Load (2 × CMOS Mode) High Low CMOS Duty Cycle Test Conditions/Comments VOH VOL 1.7 VOH VOL 1.2 VOH VOL 1.45 45 Rev. B | Page 4 of 19 VOH − VOL measurement across a differential pair at the default amplitude setting with output driver not toggling; see Figure 6 for variation over frequency Absolute value of the difference between VOD when the normal output is high vs. when the complementary output is high (VOH + VOL)/2 across a differential pair Absolute value of the difference between VOS when the normal output is high vs. when the complementary output is high Each pin (output shorted to GND) Up to 750 MHz input 750 MHz to 1200 MHz input Termination = 100 Ω differential; default amplitude setting VOH − VOL with output driver static (VOH + VOL)/2 with output driver static Up to 750 MHz input 750 MHz to 1200 MHz input Single-ended; termination = open; OUTx and OUTx in phase 10 pF load per output; see Figure 14 for output swing vs. frequency Up to 250 MHz Enhanced Product AD9508-EP OUTPUT DRIVER TIMING CHARACTERISTICS Table 3. Parameter LVDS OUTPUTS Output Rise/Fall Time Propagation Delay, Clock to LVDS Output Temperature Coefficient Output Skew, All LVDS Outputs1 On the Same Part Across Multiple Parts Symbol Min Typ Max Unit tR , tF tPD 1.52 152 2.01 2.8 192 2.49 ps ns ps/°C 48 781 ps ps 154 2.56 ps ns ps/°C 59 825 ps ps 1.47 3.14 ns ns ps/°C 112 965 ps ps 77 119 ps LVDS Outputs and CMOS Outputs 497 708 ps HSTL Outputs and CMOS Outputs 424 628 ps HSTL OUTPUTS Output Rise/Fall Time Propagation Delay, Clock to HSTL Output Temperature Coefficient Output Skew, All HSTL Outputs1 On the Same Part Across Multiple Parts CMOS OUTPUTS Output Rise/Fall Time Propagation Delay, Clock to CMOS Output Temperature Coefficient Output Skew, All CMOS Outputs1 On the Same Part Across Multiple Parts tR , tF tPD tR , tF tPD 118 2.05 2.9 1.55 1.18 2.56 3.3 1.98 OUTPUT LOGIC SKEW1 LVDS Outputs and HSTL Outputs 1 Test Conditions/Comments Termination = 100 Ω differential, 1 × LVDS 20% to 80% measured differentially Assumes same temperature and supply; takes into account worst-case propagation delay delta due to worst-case process variation Termination = 100 Ω differential, 1 × HSTL 20% to 80% measured differentially Assumes same temperature and supply; takes into account worst-case propagation delay delta due to worst-case process variation 20% to 80%; CLOAD = 10 pF 10 pF load Assumes same temperature and supply; takes into account worst-case propagation delay delta due to worst-case process variation CMOS load = 10 pF and LVDS load = 100 Ω Outputs on the same device; assumes worst-case output combination Outputs on the same device; assumes worst-case output combination Outputs on the same device; assumes worst-case output combination Output skew is the difference between any two similar delay paths while operating at the same voltage and temperature. LOGIC INPUTS Table 4. Parameter LOGIC INPUTS (RESET, SYNC, IN_SEL) Input Voltage High Input Voltage Low Input Current Input Capacitance Symbol Min VIH VIL IINH, IINL CIN 1.7 Typ −300 Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments 0.7 +100 V V µA pF 2.5 V supply voltage operation 2.5 V supply voltage operation 2 Rev. B | Page 5 of 19 AD9508-EP Enhanced Product SERIAL PORT SPECIFICATIONS—SPI MODE Table 5. Parameter CS Input Voltage Logic 1 Logic 0 Input Current Logic 1 Logic 0 Input Capacitance SCLK Input Voltage Logic 1 Logic 0 Input Current Logic 1 Logic 0 Input Capacitance SDIO (INPUT) Input Voltage Logic 1 Logic 0 Input Current Logic 1 Logic 0 Input Capacitance SDIO (OUTPUT) Output Voltage Logic 1 Logic 0 SDO Output Voltage Logic 1 Logic 0 TIMING SCLK Clock Rate, 1/tCLK Pulse Width High, tHIGH Pulse Width Low, tLOW SDIO to SCLK Setup, tDS SCLK to SDIO Hold, tDH SCLK to Valid SDIO and SDO, tDV CS to SCLK Setup (tS) CS to SCLK Hold (tC) CS Minimum Pulse Width High Min Typ Max Unit 0.4 V V VDD − 0.4 −4 −85 2 Test Conditions/Comments CS has an internal 35 kΩ pull-up resistor µA µA pF SCLK has an internal 35 kΩ pull-down resistor VDD − 0.4 0.4 70 13 2 V V µA µA pF VDD − 0.4 0.4 −1 −1 2 V V µA µA pF 1 mA load current VDD − 0.4 0.4 V V 0.4 V V 1 mA load current VDD − 0.4 30 4.6 3.5 2.9 0 15 3.4 0 3.4 Rev. B | Page 6 of 19 MHz ns ns ns ns ns ns ns ns Enhanced Product AD9508-EP SERIAL PORT SPECIFICATIONS—I2C MODE Table 6. Parameter SDA, SCL (INPUTS) Min Input Voltage Logic 1 Logic 0 Input Current Hysteresis of Schmitt Trigger Inputs SDA (OUTPUT) Output Logic 0 Voltage Output Fall Time from VIH (MIN) to VIL (MAX) TIMING SCL Clock Rate Bus-Free Time Between a Stop and Start Condition, tBUF Repeated Start Condition Setup Time, tSU; STA Repeated Start Condition Hold Time, tHD; STA Stop Condition Setup Time, tSU; STO Low Period of the SCL Clock, tLOW High Period of the SCL Clock, tHIGH Data Setup Time, tSU; DAT Data Hold Time, tHD; DAT Typ Max Unit 0.4 0 V V µA mV 0.4 250 V ns 400 kHz µs 0.6 0.6 µs µs 0.6 1.3 0.6 100 0 µs µs µs ns µs VDD − 0.4 −40 150 1.3 0.9 Test Conditions/Comments SDA and SCL have internal 80 kΩ pull-up resistors VIN = 10% to 90% IO = 3 mA 10 pF ≤ Cb ≤ 400 pF After this period, the first clock pulse is generated EXTERNAL RESISTOR VALUES FOR PIN STRAPPING MODE Table 7. Parameter EXTERNAL RESISTORS Voltage Level 0 Voltage Level 1 Voltage Level 2 Voltage Level 3 Voltage Level 4 Voltage Level 5 Voltage Level 6 Voltage Level 7 Resistor Polarity Pull down to ground Pull down to ground Pull down to ground Pull down to ground Pull up to VDD Pull up to VDD Pull up to VDD Pull up to VDD Min Typ 820 1.8 3.9 8.2 820 1.8 3.9 8.2 Rev. B | Page 7 of 19 Max Unit Ω kΩ kΩ kΩ Ω kΩ kΩ kΩ Test Conditions/Comments Using 10% tolerance resistor AD9508-EP Enhanced Product CLOCK OUTPUT ADDITIVE PHASE NOISE Table 8. Parameter ADDITIVE PHASE NOISE, CLOCK TO HSTL OR LVDS CLK = 1200 MHz, OUTx = 1200 MHz Divide Ratio = 1 10 Hz Offset 100 Hz Offset 1 kHz Offset 10 kHz Offset 100 kHz Offset 1 MHz Offset 10 MHz Offset 100 MHz Offset ADDITIVE PHASE NOISE, CLOCK TO HSTL, LVDS, OR CMOS CLK = 625 MHz, OUTx = 125 MHz Divide Ratio = 5 10 Hz Offset 100 Hz Offset 1 kHz Offset 10 kHz Offset 100 kHz Offset 1 MHz Offset 10 MHz Offset 20 MHz Offset ADDITIVE PHASE NOISE, CLOCK TO HSTL OR LVDS CLK = 491.52 MHz, OUTx = 491.52 MHz Divide Ratio = 1 10 Hz Offset 100 Hz Offset 1 kHz Offset 10 kHz Offset 100 kHz Offset 1 MHz Offset 10 MHz Offset 20 MHz Offset Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments Input slew rate > 1 V/ns −90 −101 −110 −117 −135 −144 −149 −150 dBc/Hz dBc/Hz dBc/Hz dBc/Hz dBc/Hz dBc/Hz dBc/Hz dBc/Hz Input slew rate > 1 V/ns −114 −125 −133 −141 −159 −162 −163 −163 dBc/Hz dBc/Hz dBc/Hz dBc/Hz dBc/Hz dBc/Hz dBc/Hz dBc/Hz Input slew rate > 1 V/ns −100 −111 −120 −127 −146 −153 −153 −153 Rev. B | Page 8 of 19 dBc/Hz dBc/Hz dBc/Hz dBc/Hz dBc/Hz dBc/Hz dBc/Hz dBc/Hz Enhanced Product AD9508-EP CLOCK OUTPUT ADDITIVE TIME JITTER Table 9. Parameter LVDS OUTPUT ADDITIVE TIME JITTER CLK = 622.08 MHz, Outputs = 622.08 MHz CLK = 622.08 MHz, Outputs = 155.52 MHz CLK = 125 MHz, Outputs = 125 MHz CLK = 400 MHz, Outputs = 50 MHz HSTL OUTPUT ADDITIVE TIME JITTER CLK = 622.08 MHz, Outputs = 622.08 MHz CLK = 622.08 MHz, Outputs = 155.52 MHz CMOS OUTPUT ADDITIVE TIME JITTER CLK = 100 MHz, Outputs = 100 MHz Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments 41 70 69 93 144 142 fs rms fs rms fs rms fs rms fs rms fs rms BW = 12 kHz to 20 MHz BW = 20 kHz to 80 MHz BW = 50 kHz to 80 MHz BW = 12 kHz to 20 MHz BW = 20 kHz to 80 MHz BW = 50 kHz to 80 MHz 105 209 206 184 fs rms fs rms fs rms fs rms BW = 12 kHz to 20 MHz BW = 20 kHz to 80 MHz BW = 50 kHz to 80 MHz BW = 12 kHz to 20 MHz 41 56 72 70 76 87 158 156 fs rms fs rms fs rms fs rms fs rms fs rms fs rms fs rms BW = 12 kHz to 20 MHz BW = 100 Hz to 20 MHz BW = 20 kHz to 80 MHz BW = 50 kHz to 80 MHz BW = 12 kHz to 20 MHz BW = 100 Hz to 20 MHz BW = 20 kHz to 80 MHz BW = 50 kHz to 80 MHz 91 fs rms BW = 12 kHz to 20 MHz Rev. B | Page 9 of 19 AD9508-EP Enhanced Product ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS Table 10. Parameter Supply Voltage (VDD) Maximum Digital Input Voltage CLK and CLK Maximum Digital Output Voltage Storage Temperature Range Operating Temperature Range Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10 sec) Junction Temperature Rating 3.6 V −0.5 V to VDD + 0.5 V −0.5 V to VDD + 0.5 V −0.5 V to VDD + 0.5 V −65°C to +150°C −55°C to +105°C 300°C 150°C Thermal characteristics are established using JEDEC JESD51-7 and JEDEC JESD51-5 2S2P test boards. Table 11. Thermal Characteristics, 24-Lead LFCSP Symbol θJA θJMA Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability. θJMA The following equation determines the junction temperature on the application PCB: ΨJT TJ = TCASE + (ΨJT × PD) θJB θJC Thermal Characteristic1 Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance per JEDEC JESD51-2 (still air) Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance, 1.0 m/sec airflow per JEDEC JESD51-6 (moving air) Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance, 2.5 m/sec airflow per JEDEC JESD51-6 (moving air) Junction-to-board thermal resistance per JEDEC JESD51-8 (still air) Junction-to-case thermal resistance (die-to-heat sink) per MIL-STD-883, Method 1012.1 Junction-to-top-of-package characterization parameter per JEDEC JESD51-2 (still air) Unit °C/W 40 °C/W 38.5 °C/W 16.2 °C/W 7.1 °C/W 0.33 °C/W The exposed pad on the bottom of the package must be soldered to ground (VSS) to achieve the specified thermal performance. 2 Results are from simulations. The PCB is a JEDEC multilayer type. Thermal performance for actual applications requires careful inspection of the conditions in the application to determine whether they are similar to those assumed in these calculations. 1 where: TJ is the junction temperature (°C). TCASE is the case temperature (°C) measured by the customer at the top center of the package. ΨJT is the value indicated in Table 11. PD is the power dissipation. Value2 43.5 ESD CAUTION Values of θJA are provided for package comparison and PCB design considerations. θJA can be used for a first-order approximation of TJ by the following equation: TJ = TA + (θJA × PD) where TA is the ambient temperature (°C). Values of θJC are provided for package comparison and PCB design considerations when an external heat sink is required. Values of θJB are provided for package comparison and PCB design considerations. Rev. B | Page 10 of 19 Enhanced Product AD9508-EP 19 SCLK/SCL/S0 21 CLK 20 SYNC 22 CLK 24 SDIO/SDA/S1 23 IN_SEL PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS 18 RESET CS/S2 1 OUT0 2 17 OUT3 16 OUT3 AD9508-EP TOP VIEW SDO/S3 4 15 PROG_SEL EXT_CAP0 5 14 EXT_CAP1 VDD 6 OUT2 12 OUT2 11 S5 10 S4 9 OUT1 7 OUT1 8 13 VDD NOTES 1. THE EXPOSED DIE PAD MUST BE CONNECTED TO GROUND (VSS). 11367-002 OUT0 3 Figure 2. Pin Configuration Table 12. Pin Function Descriptions Pin No. 1 Mnemonic CS/S2 2 3 4 OUT0 OUT0 SDO/S3 5 6 7 8 9 EXT_CAP0 VDD OUT1 OUT1 S4 10 S5 11 12 13 14 15 OUT2 OUT2 VDD EXT_CAP1 PROG_SEL 16 17 18 OUT3 OUT3 RESET Description Chip Select (CS)/Pin Programming (S2). This dual-purpose pin is controlled by the PROG_SEL pin. In SPI mode, CS is an active low CMOS input. When programming the device in SPI mode, CS must be held low. In systems with two or more AD9508-EP devices, CS enables individual programming of each device. In pin programming mode, S2 is hardwired with a resistor to either VDD or ground. The resistor value and resistor biasing determine the channel divider value for the outputs on Pin 11 and Pin 12. LVDS/HSTL Differential Output or Single-Ended CMOS Output. Complementary LVDS/HSTL Differential Output or Single-Ended CMOS Output. SPI Serial Data Output (SDO)/Pin Programming (S3). This dual-purpose pin is controlled by the PROG_SEL pin. In SPI mode, SDO can be configured as an output to read back the internal register settings. In pin programming mode, S3 is hardwired with a resistor to either VDD or ground. The resistor value and resistor biasing determine the channel divider value for the outputs on Pin 16 and Pin 17. Node for External Decoupling Capacitor for LDO Regulator. Tie this pin with a 0.47 µF capacitor to ground. Power Supply (2.5 V Operation). LVDS/HSTL Differential Output or Single-Ended CMOS Output. Complementary LVDS/HSTL Differential Output or Single-Ended CMOS Output. The S4 pin is used in pin programming mode only. (The PROG_SEL pin determines which programming mode is used.) S4 is hardwired with a resistor to either VDD or ground. The resistor value and resistor biasing determine the output logic levels used for the outputs on Pin 2, Pin 3, Pin 7, and Pin 8. The S5 pin is used in pin programming mode only. (The PROG_SEL pin determines which programming mode is used.) S5 is hardwired with a resistor to either VDD or ground. The resistor value and resistor biasing determine the output logic levels used for the outputs on Pin 11, Pin 12, Pin 16, and Pin 17. LVDS/HSTL Differential Output or Single-Ended CMOS Output. Complementary LVDS/HSTL Differential Output or Single-Ended CMOS Output. Power Supply (2.5 V Operation). Node for External Decoupling Capacitor for LDO Regulator. Tie this pin with a 0.47 µF capacitor to ground. Three-State CMOS Input. Pin 15 selects the device programming interface used by the AD9508-EP: SPI, I2C, or pin programming. LVDS/HSTL Differential Output or Single-Ended CMOS Output. Complementary LVDS/HSTL Differential Output or Single-Ended CMOS Output. Device Reset (CMOS Input, Active Low). When this pin is asserted, the internal register settings revert to their default state after the RESET pin is released. RESET also powers down the device when an active low signal is applied to the pin. The RESET pin has an internal 24 kΩ pull-up resistor. Rev. B | Page 11 of 19 AD9508-EP Pin No. 19 Mnemonic SCLK/SCL/S0 20 SYNC 21 CLK 22 23 CLK IN_SEL 24 SDIO/SDA/S1 EP Enhanced Product Description SPI Serial Clock (SCLK)/I2C Serial Clock (SCL)/Pin Programming (S0). This multipurpose pin is controlled by the PROG_SEL pin. In SPI mode, SCLK is the serial clock. In I2C mode, SCL is the serial clock. In pin programming mode, S0 is hardwired with a resistor to either VDD or ground. The resistor value and resistor biasing determine the channel divider value for the outputs on Pin 2 and Pin 3. Clock Synchronization (Active Low). When this pin is asserted, the output drivers are held static and then synchronized on a low-to-high transition of this pin. The SYNC pin has an internal 24 kΩ pull-up resistor. Differential Clock Input or Single-Ended CMOS Input. This pin serves as a differential clock input or as a singleended CMOS input, depending on the logic state of the IN_SEL pin. Complementary Differential Clock Input. Input Select (CMOS Input). A logic high on this pin configures the CLK and CLK inputs for a differential input signal. A logic low configures the CLK input for single-ended CMOS; ac-couple the unused CLK pin to ground with a 0.1 μF capacitor. SPI Serial Data Input and Output (SDIO)/I2C Serial Data (SDA)/Pin Programming (S1). This multipurpose pin is controlled by the PROG_SEL pin. In SPI mode, SDIO is the serial input/output pin. In 4-wire SPI mode, data writes occur on this pin; in 3-wire SPI mode, both data reads and writes occur on this pin. This pin has no internal pull-up/pull-down resistor. In I2C mode, SDA is the serial data pin. In pin programming mode, S1 is hardwired with a resistor to either VDD or ground. The resistor value and resistor biasing determine the channel divider values for the outputs on Pin 7 and Pin 8. Exposed Pad. The exposed die pad must be connected to ground (VSS). Rev. B | Page 12 of 19 Enhanced Product AD9508-EP TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS TIME (250ps/DIV) 700 600 500 400 100 300 500 700 900 1100 1300 1500 FREQUENCY (MHz) 11367-006 11367-003 VOLTAGE (100mV/DIV) DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT SWING (mV p-p) 800 Figure 6. LVDS Differential Output Swing vs. Frequency Figure 3. LVDS Differential Output Waveform at 800 MHz TIME (1.5ns/DIV) 780 760 740 720 700 2.3 2.5 2.7 2.9 3.1 3.3 3.5 POWER SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V) Figure 4. LVDS Differential Output Waveform at 156.25 MHz 200 Figure 7. LVDS Differential Output Swing vs. Power Supply Voltage 2.4 ONE OUTPUT TWO OUTPUTS THREE OUTPUTS FOUR OUTPUTS 2.3 PROPAGATION DELAY (ns) 150 CURRENT (mA) 11367-008 11367-004 VOLTAGE (100mV/DIV) DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT SWING (mV p-p) 800 100 50 2.2 2.1 2.0 1.9 0 400 800 FREQUENCY (MHz) 1200 1600 Figure 5. Power Supply Current vs. Frequency and Number of Outputs Used, LVDS Mode Rev. B | Page 13 of 19 1.7 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0 INPUT DIFFERENTIAL VOLTAGE (V p-p) Figure 8. LVDS Propagation Delay vs. Input Differential Voltage 11367-009 0 11367-005 1.8 AD9508-EP Enhanced Product 2.6 VOLTAGE (300mV/DIV) PROPAGATION DELAY (ns) 2.4 2.2 2.0 1.8 700 500 900 1100 1300 1500 COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE (mV) TIME (5ns/DIV) 11367-010 1.4 300 Figure 12. CMOS Output Waveform at 50 MHz with 10 pF Load Figure 9. LVDS Propagation Delay vs. Input Common-Mode Voltage 60 125 DIVIDER 1 DIVIDER 2 (FREQUENCY RANGE NORMALIZED FROM 0Hz TO 800MHz) DIVIDER 3 (FREQUENCY RANGE NORMALIZED FROM 0Hz TO 500MHz) 55 ONE OUTPUT TWO OUTPUTS THREE OUTPUTS FOUR OUTPUTS FIVE OUTPUTS SIX OUTPUTS SEVEN OUTPUTS EIGHT OUTPUTS CURRENT (mA) 100 50 45 75 0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 FREQUENCY (MHz) 25 25 11367-011 40 50 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250 FREQUENCY (MHz) 11367-014 50 Figure 13. Power Supply Current vs. Frequency and Number of Outputs Used, CMOS Mode Figure 10. LVDS Output Duty Cycle vs. Output Frequency 1.9 300Ω LOAD 500Ω LOAD 750Ω LOAD 1kΩ LOAD 1.8 OUTPUT SWING (V p-p) VOLTAGE (300mV/DIV) 1.7 1.6 TIME (1.25ns/DIV) 1.4 0 50 100 150 200 250 FREQUENCY (MHz) Figure 14. CMOS Output Swing vs. Frequency and Resistive Load Figure 11. CMOS Output Waveform at 200 MHz with 10 pF Load Rev. B | Page 14 of 19 11367-015 1.5 11367-012 DUTY CYCLE (%) 11367-013 1.6 Enhanced Product AD9508-EP 2.0 –55°C +25°C +105°C VOLTAGE (300mV/DIV) OUTPUT SWING (V p-p) 1.8 1.6 1.4 50 100 150 200 250 FREQUENCY (MHz) TIME (1.5ns/DIV) Figure 18. HSTL Differential Output Waveform at 156.25 MHz 200 1.7 150 CURRENT (mA) 1.9 2pF LOAD 5pF LOAD 10pF LOAD 20pF LOAD 0 50 100 150 200 250 100 FREQUENCY (MHz) Figure 16. CMOS Output Swing vs. Frequency and Capacitive Load 0 11367-017 1.1 ONE OUTPUT TWO OUTPUTS THREE OUTPUTS FOUR OUTPUTS 50 1.3 0 400 800 1200 1600 FREQUENCY (MHz) Figure 19. Power Supply Current vs. Frequency and Number of Outputs Used, HSTL Mode 11367-018 TIME (250ps/DIV) 1.9 1.8 1.7 1.6 1.5 1.4 1.3 1.2 100 300 500 700 900 1100 1300 1500 FREQUENCY (MHz) Figure 20. HSTL Differential Output Swing vs. Frequency Figure 17. HSTL Differential Output Waveform at 800 MHz Rev. B | Page 15 of 19 11367-007 DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT SWING (V p-p) 2.0 VOLTAGE (300mV/DIV) OUTPUT SWING (V p-p) Figure 15. CMOS Output Swing vs. Frequency and Temperature (10 pF Load) 1.5 11367-019 0 11367-020 1.0 11367-115 1.2 AD9508-EP Enhanced Product 60 DUTY CYCLE (%) 55 1.8 1.7 50 45 2.7 2.9 3.1 3.5 3.3 POWER SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V) 40 0 2.3 140 2.2 130 JITTER (fs rms) 150 2.1 2.0 1.8 90 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0 INPUT DIFFERENTIAL VOLTAGE (V p-p) 80 11367-022 1.0 1400 1600 110 100 0.8 1200 120 1.9 0.6 1000 Figure 24. HSTL Output Duty Cycle vs. Output Frequency 2.4 0.4 800 600 400 FREQUENCY (MHz) Figure 21. HSTL Differential Output Swing vs. Power Supply Voltage 1.7 0.2 200 0 2 4 8 6 10 SLEW RATE (V/ns) Figure 22. HSTL Propagation Delay vs. Input Differential Voltage Figure 25. Additive Broadband Jitter vs. Input Slew Rate, LVDS and HSTL Modes (Calculated from SNR of ADC Method) 2.6 –80 11367-227 2.5 11367-024 1.6 1.5 2.3 PROPAGATION DELAY (ns) DIVIDER 1 DIVIDER 2 (FREQUENCY RANGE NORMALIZED FROM 0Hz TO 800MHz) DIVIDER 3 (FREQUENCY RANGE NORMALIZED FROM 0Hz TO 500MHz) 1.9 11367-021 DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT SWING (V p-p) 2.0 HSTL 155.52MHz HSTL 311.04MHz HSTL 622.08MHz –90 –100 PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz) PROPAGATION DELAY (ns) 2.4 2.2 2.0 1.8 –110 –120 –130 –140 –150 1.6 500 700 900 1100 COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE (mV) 1300 1500 –170 10 11367-023 1.4 300 Figure 23. HSTL Propagation Delay vs. Input Common-Mode Voltage 100 1k 10k 100k 1M FREQUENCY OFFSET (Hz) 10M 100M 11367-228 –160 Figure 26. Absolute Phase Noise in HSTL Mode with Clock Input at 622.08 MHz and Outputs = 622.08 MHz, 311.04 MHz, and 155.52 MHz Rev. B | Page 16 of 19 Enhanced Product AD9508-EP –80 –90 –90 –100 –100 PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz) –110 –120 –130 –140 –110 1 –120 MARKER FREQUENCY AMPLITUDE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. –116.04dBc/Hz –126.68dBc/Hz –135.27dBc/Hz –142.56dBc/Hz –159.42dBc/Hz –161.97dBc/Hz –164.55dBc/Hz 10Hz 100Hz 1kHz 10kHz 100.5kHz 1MHz 10MHz 2 –130 3 4 –140 –150 5 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M FREQUENCY OFFSET (Hz) –170 10 –90 –90 –100 –100 PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz) –80 –120 –130 –140 1k 10k 100k 1M 1 –110 2 –120 MARKER FREQUENCY AMPLITUDE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. –112.35dBc/Hz –118.81dBc/Hz –127.84dBc/Hz –135.97dBc/Hz –151.91dBc/Hz –157.87dBc/Hz –159.78dBc/Hz –157.88dBc/Hz 10Hz 100Hz 1kHz 10kHz 100.5kHz 1MHz 10MHz 20MHz 4 –140 –150 –160 –160 5 6 1k 10k 1M 100k 10M 100M FREQUENCY OFFSET (Hz) –170 10 11367-230 100 100M 3 –130 –150 –170 10 10M Figure 30. Additive Phase Noise with Clock Input = 1200 MHz and HSTL Outputs = 100 MHz –80 –110 100 FREQUENCY (Hz) Figure 27. Absolute Phase Noise in LVDS Mode with Clock Input at 622.08 MHz and Outputs = 622.08 MHz, 311.04 MHz, and 155.52 MHz 100 1k 10k 100k 1M 7 8 10M 100M FREQUENCY (Hz) Figure 28. Absolute Phase Noise of Clock Source at 622.08 MHz Figure 31. Additive Phase Noise with Clock Input = 622.08 MHz and HSTL Outputs = 155.52 MHz –80 –80 –90 2 –100 3 –110 4 –120 –130 MARKER FREQUENCY AMPLITUDE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. –89.57dBc/Hz –100.45dBc/Hz –109.97dBc/Hz –116.93dBc/Hz –135.33dBc/Hz –144.39dBc/Hz –148.66dBc/Hz –149.78dBc/Hz 10Hz 100Hz 1kHz 10kHz 100kHz 1MHz 10MHz 100MHz –90 1 –100 PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz) 1 5 –140 6 7 8 2 –110 –140 –160 –160 100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M FREQUENCY (Hz) 4 MARKER FREQUENCY AMPLITUDE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. –100.17dBc/Hz –109.18dBc/Hz –117.67dBc/Hz –124.94dBc/Hz –143.83dBc/Hz –151.64dBc/Hz –153.81dBc/Hz –152.87dBc/Hz 10Hz 100Hz 1kHz 10kHz 100.5kHz 1MHz 10MHz 20MHz –130 –150 –170 10 3 –120 –150 11367-329 PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz) 7 –170 10 5 100 1k 10k 100k 6 7 1M 10M 8 100M FREQUENCY (Hz) Figure 32. Additive Phase Noise with Clock Input = 622.08 MHz and LVDS Outputs = 622.08 MHz Figure 29. Additive Phase Noise with Clock Input = 1200 MHz and HSTL Outputs = 1200 MHz Rev. B | Page 17 of 19 11367-129 100 11367-229 –160 10 PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz) 6 –160 11367-330 –150 11367-130 PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz) –80 LVDS 155.52MHz LVDS 311.04MHz LVDS 622.08MHz AD9508-EP Enhanced Product –80 –90 –110 1 –120 AMPLITUDE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. –114.15dBc/Hz –127.18dBc/Hz –134.13dBc/Hz –141.63dBc/Hz –154.66dBc/Hz –155.37dBc/Hz –152.86dBc/Hz –153.09dBc/Hz 10Hz 100Hz 1kHz 10kHz 100.5kHz 1MHz 10MHz 20MHz 2 –130 3 4 –140 –150 5 6 100k 1M 7 8 –160 –170 10 100 1k 10k 10M 100M FREQUENCY (Hz) 11367-131 PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz) –100 MARKER FREQUENCY Figure 33. Additive Phase Noise with Clock Input = 100 MHz and CMOS Outputs = 100 MHz Rev. B | Page 18 of 19 Enhanced Product AD9508-EP OUTLINE DIMENSIONS 0.30 0.25 0.18 0.50 BSC PIN 1 INDICATOR 24 19 18 1 EXPOSED PAD 0.50 0.40 0.30 TOP VIEW 0.80 0.75 0.70 13 12 2.65 2.50 SQ 2.45 6 7 0.25 MIN BOTTOM VIEW 0.05 MAX 0.02 NOM FOR PROPER CONNECTION OF THE EXPOSED PAD, REFER TO THE PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS SECTION OF THIS DATA SHEET. COPLANARITY 0.08 0.20 REF SEATING PLANE COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-220-WGGD. 04-12-2012-A PIN 1 INDICATOR 4.10 4.00 SQ 3.90 Figure 34. 24-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_WQ] 4 mm × 4 mm Body, Very Very Thin Quad (CP-24-7) Dimensions shown in millimeters ORDERING GUIDE Model1 AD9508SCPZ-EP AD9508SCPZ-EP-R7 AD9508/PCBZ 1 Temperature Range −55°C to +105°C −55°C to +105°C Package Description 24-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package (LFCSP_WQ) 24-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package (LFCSP_WQ) Evaluation Board Z = RoHS Compliant Part. I2C refers to a communications protocol originally developed by Philips Semiconductors (now NXP Semiconductors). ©2013–2014 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners. D11367-0-10/14(B) Rev. B | Page 19 of 19 Package Option CP-24-7 CP-24-7