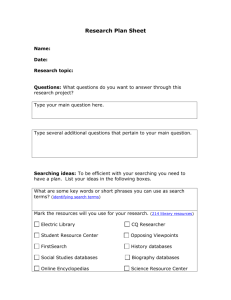
Catalog Displays, Retrieval, and FAST May 31, 2005

Catalog Displays,
Retrieval, and
FAST
May 31, 2005
1
Overview
Online Catalog Interfaces and
Subject Searching
FAST: Faceted Application of Subject
Terminology
2
Subject Searching in
OPACs: Problem Statement
Subject access can be provided via:
Controlled vocabulary
• But users must discover the authoritative terms themselves
• Interfaces that assist users are more effective than those that do not
Natural language
• User must consider word forms, synonyms and homographs in constructing searches
3
Subject Searching in
OPACs: Solutions
Authority control of subject terms
Free text searching conventions
(truncation, Boolean logic, proximity searching)
Browsing
Search facilitation
4
Authority control of subject terms
UF (4xx) or SA, NT, BT (5xx) references direct users to authoritative or related headings
Scope notes may also be displayed
Authority control works!
Wilkes & Nelson (1995): 75% of failed searches in catalog without authority control would have been successful with authority control
5
Authority control of subject terms (cont.)
Should catalogs direct users to the correct form of headings?
Or
Should catalogs display the appropriate entries directly?
6
Authority control of subject terms (cont.)
Problem: Users may not use the terms in the controlled vocabulary
1.
2.
Solutions:
Provide bibliographic instruction in subject searching
Make LCSH (or other thesaurus) available in paper or electronically
7
Free Text Searching
Truncation
User must consider all possible completions to a partial word entry
Example 1: librari? will retrieve
librarians and librarianship, but miss library
Example 2: cat? will retrieve both cat and cats (desired result), but also
catapult and caterpillar
8
Free Text Searching (cont.)
Boolean logic
Use of Boolean operators AND, OR, NOT
Users need to understand how to use operators
Users need to know what is in the database
Example: Castles AND movies might retrieve works on
Irene and Vern Castle (American dancers)
Research demonstrates that most users have difficulty constructing effective Boolean searches
Also, some catalogs do not explicitly inform users about default operators
Works best with instruction (online or training sessions)
9
Free Text Searching (cont.)
Proximity searching
Can specify word order, words next to each other, words within a prescribed number of words of each other
Problems with free-text searching even with these techniques
Lack of context
Cannot account easily for foreign languages
10
Browsing
Definition: Browsing is an exploration of a database with the idea that something interesting or useful might be encountered following connections.
(Olson and Boll)
Browsers can sometimes identify a specific purpose
Some area(s) of interest begin(s) the search
11
Browsing
Or
Pre-automation: browse in the shelflist
find one or two items of interest in the catalog, then continue the search at the shelf
Post-automation: browse an online shelflist
Surfing the web is a type of browsing activity!
12
Search Facilitation
Sophisticated search capabilities (such as
Boolean searching) are not used
Help screens and screens with lists of commands are also not heavily used
Require the user to go to the help screens or interpret the information
13
Search Facilitation (cont.)
Spell checkers
Allow users to browse the classification scheme if captions are included with class numbers
Tree structures based on subject headings
14
FAST: Faceted Application of
Subject Terminology
LCSH is widely used and has been basis of numerous other thesauri around the world
Its application (constructing headings) requires significant training
FAST is an attempt to simplify the process of assigning subject headings, but still use LCSH ’ s rich vocabulary
FAST is compatible with LCSH – can convert from LCSH to FAST
15
FAST Design
Be usable by people with minimal training and experience,
Enable a broad range of users to assign subject terminology to Web resources,
Be amenable to automated authority control,
Be compatible with use as embedded metadata,
Focus on making use of LCSH as a
post-coordinate system in an online environment.
16
FAST Facets
Six facets:
Topical
Geographic
Form
Period
Personal names
Corporate names
17
Examples
Each facet is assigned in its own
MARC field:
Blacksmithing $x Equipment and supplies
California $z Los Angeles $z Hollywood
$v Controversial literature $v Early works to 1800
1900-1999
18
Conversion of existing headings
650 0 Authority files (Information retrieval) $z Italy $z Florence $v
Congresses.
Converts to:
Authority files (Information retrieval)
§ Italy $z Florence
Congresses
19
Additional Simplification
Characteristics
Authority file permanently retains all authority records
Authority records are designated
“ obsolete ” rather than removed from the database
Supports the linked structure of the file
All FAST records will be linked back to the
LC authority record from which it was derived using 7xx linking fields.
Ongoing OCLC project: will hear more in the future
20