Alabama A&M University Benchmark Comparisons August 2010
advertisement

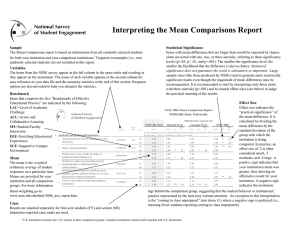
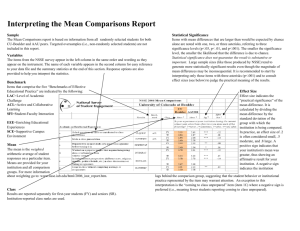
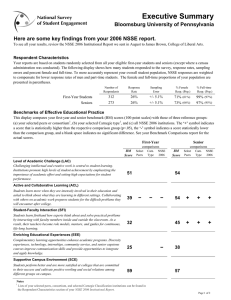
Alabama A&M University Benchmark Comparisons August 2010 NSSE 2010 Benchmark Comparisons Interpreting the Benchmark Comparisons Report To focus discussions about the importance of student engagement and to guide institutional improvement efforts, NSSE created five Benchmarks of Effective Educational Practice: Level of Academic Challenge, Active and Collaborative Learning, StudentFaculty Interaction, Enriching Educational Experiences, and Supportive Campus Environment. This Benchmark Comparisons Report compares the performance of your institution with your selected peers or consortium. In addition, page 9 provides two other comparisons between your school and (a) above-average institutions with benchmarks in the top 50% of all NSSE institutions and (b) high-performing institutions with benchmarks in the top 10% of all NSSE institutions. These displays allow you to determine if the engagement of your typical student differs in a statistically significant, meaningful way from the average student in these comparison groups. Additional details regarding how benchmarks are created can be found on the NSSE Web site. nsse.iub.edu/links/institutional_reporting Statistical Significance Benchmarks with mean differences that are larger than would be expected by chance alone are noted with one, two, or three asterisks, denoting one of three significance levels (p<.05, p< .01, and p<.001). The smaller the significance level, the smaller the likelihood that the difference is due to chance. Please note that statistical significance does not guarantee that the result is substantive or important. Large sample sizes (as with the NSSE project) tend to produce more statistically significant results even though the magnitude of mean differences may be inconsequential. Consult effect sizes to judge the practical meaning of the results. Class and Sample Means are reported for first-year students and seniors. Institutionreported class levels are used. All randomly selected students are included in these analyses. Students in targeted or locally administered oversamples are not included. Level of Academic Challenge (LAC) Mean Comparisons NSSEville State University compared with: NSSEville State C las s M ean First-Year Senior a b c a Mid East Public M ean 52.8 57.2 a S ig 53.8 56.6 b Ef f ect S iz e c -.07 .05 Carnegie Class M ean a a S ig b Ef f ect S iz e c 53.7 57.0 -.06 .01 Senior 100 100 75 75 52.8 53.8 53.1 53.7 50 50 25 25 57.2 56.6 56.9 57.0 NSSE ville State Mid East Public Carnegie Class NSSE 2010 0 NSSEville State a -.02 .02 M ean We ighte d by ge nde r a nd e nro llm e nt s ta tus (plus ins titutio na l s ize fo r c o m pa ris o ns ). * p<.05 ** p<.01 ***p<.001 (2-ta ile d). M e a n diffe re nc e divide d by the po o le d s ta nda rd de via t io n. 0 Benchmark Description & Survey Items A description of the benchmark and the individual items used in its creation is provided. NSSE 2010 Ef f ect S iz e c b 53.1 56.9 First-Year Mean The mean is the weighted arithmetic average of the student level benchmark scores. S ig Effect Sizea Effect size indicates the practical significance of the mean difference. It is calculated by dividing the mean difference by the pooled standard deviation. In practice, an effect size of .2 is often considered small, .5 moderate, and .8 large. A positive sign indicates that your institution’s mean was greater, thus showing an affirmative result for the institution. A negative sign indicates the institution lags behind the comparison group, suggesting that the student behavior or institutional practice represented by the item may warrant attention. Mid East Public Carnegie Class NSSE 2010 Level of Academic Challenge (LAC) Items Challenging intellectual and creative work is central to student learning and collegiate quality. Colleges and universities p romote high levels of student achievement by emp hasizing the imp ortance of academic effort and setting high exp ectations for student p erformance. ● Preparing for class (studying, read ing, writing, doing homework or lab work, etc. related to academic progr am) ● Number of assigned textbooks, books, or book-length p acks of course read ings ● Number of written papers or reports of 20 pag es or more; nu mber of written pap ers or reports of between 5 and 19 pages; and number of written papers or reports of fewer than 5 pages ● Coursework emphasizes: Analysis of the basic elements of an id ea, exp erien ce or theory ● Coursework emphasizes: Synthesis and organizing of ideas, information, or experiences into new, more complex interpretations and relationships ● Coursework emphasizes: Making of judgments about the value of information, argumen ts, or methods ● Coursework emphasizes: Applying theories or con cepts to practical prob lems or in n ew situations ● Working hard er than you thought you cou ld to meet an instructor's standards or expectations ● Campus environ ment emphasizes: Spending significant amount of time studying and on academic work. See Contextualizing NSSE Effect Sizes at nsse.iub.edu/html/effect_size_guide.cfm for additional information. Bar Charts A visual display of first-year and senior mean benchmark scores for your institution and your selected comparison or consortium groups. -2- NSSE 2010 Benchmark Comparisons Alabama A&M University Level of Academic Challenge (LAC) Mean Comparisons Alabama A&M University compared with: Alabama A&M Southeast Public Carnegie Class Effect Class Mean a Mean 51.3 58.6 First-Year Senior a Sig b Size 52.8 56.5 -.12 .15 a Weighted by gender and enrollment status (and by institution size for comparison groups). b * p<.05 ** p<.01 ***p<.001 (2-tailed). Mean difference divided by the pooled standard deviation. c c Mean a 100 75 75 58.6 54.1 53.3 50 50 25 25 0 Alabama A&M Southeast Public b Size c -.15 .12 Effect Mean a Sig b 54.1 57.5 Size Carnegie Class 56.5 56.9 57.5 Southeast Public Carnegie Class NSSE 2010 0 NSSE 2010 Alabama A&M Level of Academic Challenge (LAC) Items Challenging intellectual and creative work is central to student learning and collegiate quality. Colleges and universities promote high levels of student achievement by emphasizing the importance of academic effort and setting high expectations for student performance. ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Hours spent preparing for class (studying, reading, writing, doing homework or lab work, etc. related to academic program) Number of assigned textbooks, books, or book-length packs of course readings Number of written papers or reports of 20 pages or more, between 5 and 19 pages, and fewer than 5 pages Coursework emphasizes: Analysis of the basic elements of an idea, experience or theory Coursework emphasizes: Synthesis and organizing of ideas, information, or experiences into new, more complex interpretations and relationships Coursework emphasizes: Making of judgments about the value of information, arguments, or methods Coursework emphasizes: Applying theories or concepts to practical problems or in new situations Working harder than you thought you could to meet an instructor's standards or expectations Campus environment emphasizes: Spending significant amount of time studying and on academic work -3- c -.21 .08 Senior 100 52.8 Sig 53.3 56.9 First-Year 51.3 NSSE 2010 Effect NSSE 2010 Benchmark Comparisons Alabama A&M University Active and Collaborative Learning (ACL) Mean Comparisons Alabama A&M University compared with: Alabama A&M Southeast Public Carnegie Class Effect Class Mean a Mean 46.6 60.4 First-Year Senior a 42.8 50.8 Sig b Size .22 .51 ** a Weighted by gender and enrollment status (and by institution size for comparison groups). b * p<.05 ** p<.01 ***p<.001 (2-tailed). Mean difference divided by the pooled standard deviation. c c NSSE 2010 Effect Mean a 43.3 51.8 First-Year Sig b Size c .19 .48 * Effect Mean a 43.7 51.4 Sig b ** Senior 100 100 75 75 60.4 50 46.6 42.8 43.3 50.8 51.8 51.4 Southeast Public Carnegie Class NSSE 2010 50 43.7 25 25 0 Alabama A&M Southeast Public Carnegie Class 0 NSSE 2010 Alabama A&M Active and Collaborative Learning (ACL) Items Students learn more when they are intensely involved in their education and asked to think about what they are learning in different settings. Collaborating with others in solving problems or mastering difficult material prepares students for the messy, unscripted problems they will encounter daily during and after college. ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Asked questions in class or contributed to class discussions Made a class presentation Worked with other students on projects during class Worked with classmates outside of class to prepare class assignments Tutored or taught other students (paid or voluntary) Participated in a community-based project (e.g., service learning) as part of a regular course Discussed ideas from your readings or classes with others outside of class (students, family members, co-workers, etc.) -4- Size c .17 .51 NSSE 2010 Benchmark Comparisons Alabama A&M University Student-Faculty Interaction (SFI) Mean Comparisons Alabama A&M University compared with: Alabama A&M Southeast Public Carnegie Class Effect Class Mean a Mean 40.9 44.7 First-Year Senior a Sig b Size 35.3 42.3 .30 .11 a Weighted by gender and enrollment status (and by institution size for comparison groups). b * p<.05 ** p<.01 ***p<.001 (2-tailed). Mean difference divided by the pooled standard deviation. c c Mean a Sig b Size 35.4 41.8 First-Year c .29 .14 Effect Mean a Sig b 35.2 42.4 100 75 75 50 50 44 7 44.7 40.9 35.4 42.3 41.8 42.4 Southeast Public Carnegie Class NSSE 2010 35.2 25 25 0 Alabama A&M Southeast Public Carnegie Class 0 NSSE 2010 Alabama A&M Student-Faculty Interaction (SFI) Items Students learn firsthand how experts think about and solve practical problems by interacting with faculty members inside and outside the classroom. As a result, their teachers become role models, mentors, and guides for continuous, life-long learning. ● ● ● ● ● ● Discussed grades or assignments with an instructor Talked about career plans with a faculty member or advisor Discussed ideas from your readings or classes with faculty members outside of class Worked with faculty members on activities other than coursework (committees, orientation, student-life activities, etc.) Received prompt written or oral feedback from faculty on your academic performance Worked on a research project with a faculty member outside of course or program requirements -5- Size c .31 .11 Senior 100 35.3 NSSE 2010 Effect NSSE 2010 Benchmark Comparisons Alabama A&M University Enriching Educational Experiences (EEE) Mean Comparisons Alabama A&M University compared with: Alabama A&M Southeast Public Carnegie Class Effect Class Mean a Mean 26.3 39.2 First-Year Senior a Sig b Size 27.5 39.3 -.09 -.01 a Weighted by gender and enrollment status (and by institution size for comparison groups). b * p<.05 ** p<.01 ***p<.001 (2-tailed). Mean difference divided by the pooled standard deviation. c c Mean a b Size c -.03 .05 Effect Mean a Sig b 27.9 40.5 Size 100 75 75 50 50 26.7 39.2 39.3 38.2 Alabama A&M Southeast Public Carnegie Class 40.5 27.9 25 25 0 Alabama A&M Southeast Public Carnegie Class 0 NSSE 2010 NSSE 2010 Enriching Educational Experiences (EEE) Items Complementary learning opportunities enhance academic programs. Diversity experiences teach students valuable things about themselves and others. Technology facilitates collaboration between peers and instructors. Internships, community service, and senior capstone courses provide opportunities to integrate and apply knowledge. ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Hours spent participating in co-curricular activities (organizations, campus publications, student gov., social fraternity or sorority, etc.) Practicum, internship, field experience, co-op experience, or clinical assignment Community service or volunteer work Foreign language coursework and study abroad Independent study or self-designed major Culminating senior experience (capstone course, senior project or thesis, comprehensive exam, etc.) Serious conversations with students of different religious beliefs, political opinions, or personal values Serious conversations with students of a different race or ethnicity than your own Using electronic medium (e.g., listserv, chat group, Internet, instant messaging, etc.) to discuss or complete an assignment Campus environment encouraging contact among students from different economic, social, and racial or ethnic backgrounds Participate in a learning community or some other formal program where groups of students take two or more classes together -6- c -.12 -.07 Senior 100 27.5 Sig 26.7 38.2 First-Year 26.3 NSSE 2010 Effect NSSE 2010 Benchmark Comparisons Alabama A&M University Supportive Campus Environment (SCE) Mean Comparisons Alabama A&M University compared with: Alabama A&M Southeast Public Carnegie Class Effect Class Mean a Mean 56.0 61.1 First-Year Senior a Sig b Size 62.2 59.0 -.33 .10 a Weighted by gender and enrollment status (and by institution size for comparison groups). b * p<.05 ** p<.01 ***p<.001 (2-tailed). Mean difference divided by the pooled standard deviation. c c Mean a Sig b 100 75 75 62.3 62.5 61.1 56.0 50 50 25 25 0 Southeast Public c -.34 .09 Effect Mean a Sig b 62.5 59.6 Size Carnegie Class 59.0 59.3 59.6 Southeast Public Carnegie Class NSSE 2010 0 NSSE 2010 Alabama A&M Supportive Campus Environment (SCE) Items Students perform better and are more satisfied at colleges that are committed to their success and cultivate positive working and social relations among different groups on campus. ● ● ● ● ● ● Campus environment provides the support you need to help you succeed academically Campus environment helps you cope with your non-academic responsibilities (work, family, etc.) Campus environment provides the support you need to thrive socially Quality of relationships with other students Quality of relationships with faculty members Quality of relationships with administrative personnel and offices -7- c -.35 .08 Senior 100 Alabama A&M Size 62.3 59.3 First-Year 62.2 NSSE 2010 Effect NSSE 2010 Benchmark Comparisons With Highly Engaging Institutions Interpreting the Top 10% and Top 50% Comparisons This section of the NSSE Benchmark Comparisons report allows you to estimate the performance of your average student in relation to the average student attending two different institutional peer groups identified by NSSE for their high levels of student engagement: (a) institutions with benchmark scores placing them in the top 50% of all NSSE schools in 2010 and (b) institutions with benchmark scores in the top 10% for 2010.a These comparisons allow an institution to determine if the engagement of their students differs in significant, meaningful ways from students in these high performing peer groups. Example First-Year NSSEville State compared with LAC ACL SFI EEE SCE NSSEville State Mean 57.1 50.3 37.3 21.8 60.9 Mean 55.8 45.8 37.2 30.0 64.7 NSSE 2010 Top 50% Sig Effect size * .10 *** .28 .01 *** -.63 *** -.21 NSSE 2010 Top 10% Mean Sig Effect size 60.5 *** -0.28 50.7 -0.02 42.0 *** -0.24 34.4 *** -0.98 69.7 *** -0.49 Based on the example above NSSEville State CAN conclude... The average score for NSSEville State first-year students is slightly above (i.e., small positive effect size) that of the average student attending NSSE 2010 schools that scored in the top 50% on Level of Academic Challenge (LAC). The average NSSEville State first-year student is as engaged (i.e., not significantly different) as the average student attending NSSE 2010 schools that scored in the top 10% on Active and Collaborative Learning (ACL). It is likely that NSSEville State is in the top 50% of all NSSE 2010 schools for first-year students on Level of Academic Challenge (LAC) and Active and Collaborative Learning (ACL).a Based on the example above NSSEville State CANNOT concludea... NSSEville State is in the top half of all schools on the Student-Faculty Interaction (SFI) benchmark for first-year students. NSSEville State is a "top ten percent" institution on Active and Collaborative Learning (ACL) for first-year students. Additional information regarding the Top 50% and Top 10% section of the benchmark report can be found on the NSSE Web site. nsse.iub.edu/links/institutional_reporting a Precision-weighted means (produced by Hierarchical Linear Modeling) were used to determine the top 50% and top 10% institutions for each benchmark, separately for first-year and senior students. Using this method, benchmark scores of institutions with relatively large standard errors are adjusted substantially toward the grand mean of all students, while those with smaller standard errors receive smaller corrections. Thus, schools with less stable data, though they may have high scores, may not be identified among the top scorers. NSSE does not publish the names of the top 50% and top 10% institutions because of our commitment not to release individual school results and our policy against the ranking of institutions. -8- NSSE 2010 Benchmark Comparisons With Highly Engaging Institutions Alabama A&M University First-Year Alabama A&M compared with Alabama A&M Senior First-Year Mean LAC ACL SFI EEE SCE LAC ACL SFI EEE SCE a 51.3 46.6 40.9 26.3 56.0 58.6 60.4 44.7 39.2 61.1 NSSE 2010 Top 50% Mean a Sig 57.2 48.1 39.9 31.1 67.2 60.9 56.6 49.2 47.7 64.7 b NSSE 2010 Top 10% Effect size c -.45 -.09 .05 -.35 -.62 -.17 .22 -.21 -.47 -.19 * * ** Mean a 60.5 52.2 44.2 33.6 70.8 63.8 60.3 55.3 55.8 68.6 Sig b Effect size c -.71 -.32 -.15 -.52 -.81 -.38 .00 -.48 -.97 -.40 *** ** ** * * *** 100 Level of Academic Challenge (LAC) 75 51.3 57.2 60.5 63.8 58.6 60.9 50 25 0 First-Year Active and Collaborative Learning (ACL) 100 60 4 60.4 Student-Faculty Interaction (SFI) 100 46.6 50 48.1 52.2 56.6 60 3 60.3 55.3 50 40.9 Alabama A&M Top 50% Senior 75 75 Legend Senior 39.9 44.2 44.7 49.2 25 25 Top 10% 0 0 This display compares your students with those attending schools that scored in the top 50% and top 10% of all NSSE 2010 institutions on a particular benchmark. First-Year 100 First-Year Senior Enriching Educational Experiences (EEE) 100 47.7 50 26.3 31.1 33.6 39.2 0 Senior Weighted by gender and enrollment status (and by inst. size for comp. groups). * p<.05 ** p<.01 ***p<.001 (2-tailed). Mean diff. divided by the pooled standard dev. 61.1 64.7 50 0 First-Year c 70.8 25 25 b 67.2 56.0 55.8 a Supportive Campus Environment (SCE) 75 75 Senior -9- First-Year Senior 68.6 NSSE 2010 Benchmark Comparisons Detailed Statistics and Effect Sizes a Alabama A&M University First-Year Students Mean Statistics Reference Group Comparison Statistics Distribution Statistics Deg. of Sig. f 2,611 -1.6 .541 -.12 3,381 -2.1 .415 -.15 76 12,628 -2.8 .267 -.21 78 4,866 -6.0 .016 -.45 70 80 981 -9.3 .000 -.71 51.3 13.8 2.6 22 42 51 62 74 Southeast Public 52.8 13.7 .3 30 44 53 62 75 Carnegie Class 53.3 13.6 .2 31 44 53 63 75 NSSE 2010 54.1 13.6 .1 32 45 54 64 Top 50% 57.2 13.1 .2 35 48 57 66 Top 10% 60.5 12.9 .4 38 52 61 SD 5th Effect Mean Diff. SEM Mean c Percentiles d 25th 50th 75th b 95th Freedom e size g LEVEL OF ACADEMIC CHALLENGE (LAC) Alabama A&M (N = 28) ACTIVE AND COLLABORATIVE LEARNING (ACL) Alabama A&M (N = 32) 46.6 16.2 2.9 24 33 48 62 71 Southeast Public 42.8 17.3 .3 19 29 43 52 73 2,838 3.7 .225 .22 Carnegie Class 43.3 16.9 .3 19 33 43 52 72 3,666 3.3 .276 .19 NSSE 2010 43.7 16.8 .1 19 33 43 52 72 13,675 2.9 .328 .17 Top 50% 48.1 17.0 .3 24 38 48 57 76 4,328 -1.5 .621 -.09 Top 10% 52.2 17.8 .6 24 38 52 62 83 805 -5.7 .077 -.32 40.9 23.2 4.2 11 22 33 61 78 Southeast Public 35.3 18.8 .4 11 22 33 44 72 31 5.6 .187 .30 Carnegie Class 35.4 18.7 .3 11 22 33 44 72 31 5.5 .195 .29 NSSE 2010 35.2 18.6 .2 11 22 33 44 72 30 5.8 .177 .31 Top 50% 39.9 19.6 .3 11 28 39 50 78 31 1.0 .807 .05 Top 10% 44.2 21.4 .9 11 28 44 56 83 662 -3.3 .402 -.15 STUDENT-FACULTY INTERACTION (SFI) Alabama A&M (N = 31) ENRICHING EDUCATIONAL EXPERIENCES (EEE) Alabama A&M (N = 30) 26.3 17.3 3.2 3 11 25 35 58 Southeast Public 27.5 13.7 .3 8 18 26 36 51 29 -1.2 .707 -.09 Carnegie Class 26.7 13.5 .2 8 17 25 35 50 29 -.4 .904 -.03 NSSE 2010 27.9 13.5 .1 8 18 26 36 51 29 -1.6 .617 -.12 Top 50% 31.1 13.6 .2 11 22 30 40 54 29 -4.8 .141 -.35 Top 10% 33.6 14.0 .4 12 23 33 42 57 1,281 -7.4 .005 -.52 56.0 23.9 4.5 19 33 61 78 94 Southeast Public 62.2 19.0 .4 31 50 63 75 94 27 -6.2 .184 -.33 Carnegie Class 62.3 18.9 .3 31 50 64 75 94 27 -6.4 .173 -.34 NSSE 2010 62.5 18.8 .2 31 50 64 75 94 27 -6.5 .162 -.35 Top 50% 67.2 18.0 .3 36 56 67 81 97 27 -11.3 .020 -.62 Top 10% 70.8 17.9 .7 39 58 72 83 100 28 -14.8 .003 -.81 SUPPORTIVE CAMPUS ENVIRONMENT (SCE) Alabama A&M (N = 28) a All statistics are weighted by gender and enrollment status. Comparison group statistics are also weighted by institutional size. b Standard deviation is a measure of the amount the individual scores deviate from the mean of all the scores in the distribution. c Standard Error of the Mean: Use SEM to compute a confidence interval (CI) around the sample mean. For example, the 95% CI is the range of values that is 95% likely to contain the true population mean, equal to the sample mean +/- 1.96 * SEM. d A percentile is the point in the distribution of student-level benchmark scores at or below which a given percentage of benchmark scores fall. e Degrees of freedom used to compute the t-tests. Values vary for the total Ns due to weighting and the equal variance assumption. f Statistical significance represents the probability that the difference between the mean of your institution and that of the comparison group occurred by chance. g Effect size is calculated by subtracting the comparison group mean from the school mean, and dividing the result by the pooled standard deviation. IPEDS: 100654 - 10 - NSSE 2010 Benchmark Comparisons Detailed Statistics and Effect Sizes a Alabama A&M University Seniors Mean Statistics Reference Group Comparison Statistics Distribution Statistics Deg. of SEM 58.6 12.4 2.3 39 52 59 65 86 Southeast Public 56.5 14.5 .2 32 47 57 67 80 Carnegie Class 56.9 14.4 .2 32 47 57 67 80 NSSE 2010 57.5 14.4 .1 33 48 58 68 80 Top 50% 60.9 13.7 .2 38 52 61 71 82 Top 10% 63.8 13.6 .4 41 55 65 73 85 Mean SD c Percentiles d 25th 50th 75th b 5th 95th Effect Mean Diff. Sig. f 4,006 2.2 .431 .15 5,162 1.7 .534 .12 18,424 1.1 .689 .08 5,574 -2.3 .380 -.17 1,265 -5.2 .046 -.38 Freedom e size g LEVEL OF ACADEMIC CHALLENGE (LAC) Alabama A&M (N = 28) ACTIVE AND COLLABORATIVE LEARNING (ACL) Alabama A&M (N = 28) 60.4 18.0 3.4 29 48 62 76 90 Southeast Public 50.8 18.5 .3 24 38 50 62 83 4,193 9.5 .007 .51 Carnegie Class 51.8 17.8 .2 24 38 52 62 81 5,400 8.6 .011 .48 NSSE 2010 51.4 17.7 .1 24 38 52 62 81 19,322 9.0 .007 .51 Top 50% 56.6 17.2 .3 29 43 57 67 86 4,707 3.8 .249 .22 Top 10% 60.3 18.0 .6 33 48 61 71 90 1,041 .0 .997 .00 44.7 21.6 4.1 11 31 44 50 83 Southeast Public 42.3 21.2 .3 11 28 39 56 83 4,035 2.3 .565 .11 Carnegie Class 41.8 20.8 .3 11 28 39 56 83 5,205 2.8 .473 .14 NSSE 2010 42.4 21.0 .2 11 28 39 56 83 18,573 2.2 .577 .11 Top 50% 49.2 21.5 .3 17 33 47 61 89 4,109 -4.6 .263 -.21 Top 10% 55.3 22.3 .9 22 39 56 72 94 664 -10.7 .013 -.48 2.7 14 33 37 47 61 -.01 STUDENT-FACULTY INTERACTION (SFI) Alabama A&M (N = 28) ENRICHING EDUCATIONAL EXPERIENCES (EEE) Alabama A&M (N = 27) 39.2 14.0 Southeast Public 39.3 18.0 .3 11 25 39 51 71 27 -.2 .954 Carnegie Class 38.2 17.9 .3 11 25 37 50 69 27 1.0 .724 .05 NSSE 2010 40.5 18.3 .1 12 27 40 53 72 26 -1.4 .616 -.07 Top 50% 47.7 18.0 .2 18 35 48 60 77 27 -8.5 .004 -.47 Top 10% 55.8 17.3 .6 25 44 57 68 83 867 -16.7 .000 -.97 61.1 24.7 4.7 19 42 58 81 100 Southeast Public 59.0 19.6 .3 25 44 58 72 92 26 2.0 .670 .10 Carnegie Class 59.3 19.3 .3 28 47 58 72 92 26 1.8 .713 .09 NSSE 2010 59.6 19.3 .1 28 47 61 72 92 26 1.5 .756 .08 Top 50% 64.7 18.9 .3 33 53 67 78 94 26 -3.6 .452 -.19 Top 10% 68.6 18.6 .7 36 56 69 83 100 28 -7.5 .128 -.40 SUPPORTIVE CAMPUS ENVIRONMENT (SCE) Alabama A&M (N = 27) a All statistics are weighted by gender and enrollment status. Comparison group statistics are also weighted by institutional size. b Standard deviation is a measure of the amount the individual scores deviate from the mean of all the scores in the distribution. c Standard Error of the Mean: Use SEM to compute a confidence interval (CI) around the sample mean. For example, the 95% CI is the range of values that is 95% likely to contain the true population mean, equal to the sample mean +/- 1.96 * SEM. d A percentile is the point in the distribution of student-level benchmark scores at or below which a given percentage of benchmark scores fall. e Degrees of freedom used to compute the t-tests. Values vary for the total Ns due to weighting and the equal variance assumption. f Statistical significance represents the probability that the difference between the mean of your institution and that of the comparison group occurred by chance. g Effect size is calculated by subtracting the comparison group mean from the school mean, and dividing the result by the pooled standard deviation. IPEDS: 100654 - 11 -