Chemistry 221 - Test 2 Review Sheet (Chapters 6-9)
advertisement

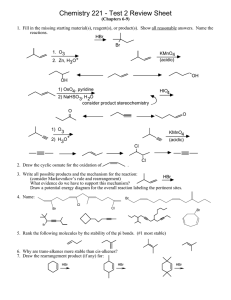
Chemistry 221 - Test 2 Review Sheet (Chapters 6-9) 1. Fill in the missing starting material(s), reagent(s), or product(s). Show all reasonable answers. Name each reaction. Hydrohalogenation HBr or Br Ozonolysis O+ O 1. O3 2. Zn, H3O+ Oxidation H KMnO 4 (acidic) H O OH + CO2 Hydration Oxymercuration/Demercuration 1. Hg(OAc)2, H2O OH Hydroboration/Oxidation 1. BH3, THF 2. H2O2, H2O, OH- 2. NaBH4 OH Hydroxylation OH 1) OsO4 , pyridine (R,R and S,S) 2) NaHSO 3, H 2O HIO4 O + O OH Hydration O Hydroboration/Oxidation 1) BH3, THF 2) H2O2, OH -, H2O HgSO4 HSO 4, H 2O Ozonolysis O Oxidation 1) O3 2) H3O+ Reduction Na, NH 3 OH + KMnO4 (acidic) CO2 O Halogenation Cl 2 Dehydrohalogenation excess Cl KNH 2 Cl O O Os 2. Draw the cyclic osmate for the oxidation of . O O OH O + CO2 3. Write all possible products and the mechanism for the reaction: (consider Markovnikov’s rule and rearrangement) HBr + Br + Br Br HBr Br + + Br Br H H Br + Br + major H H + 1,2-hydride shift (rearrangement) + + minor H Br Br bromide anion bonds to one of the carbocations forming a mixture of 3 products (only 1 shown here) transition states The rearrangement product is consistant with formation intermediate such as a carbocation. The distribution (relative amounts) of products is consistant with carbocation stability. Relatively stable carbocations, analogous to those postulated in the mechanism, have been detected. Draw a potential energy diagram for the overall reaction labeling the pertinent sites. Energy (∆ G) What evidence do we have to support this mechanism? of an intermediate carbocation+Br- products reactants (halide) (alkene+HBr) Reaction Progress 4. Name: cis,cis-11-bromo-2-propyl-1,4,9-undecatriene (5E,8Z,12E)-12-bromo-2,8-dichloro-6-methyl1,5,8,12-tetradecatetraene Br 6-bromo-1,4-cycloheptadiene Br Cl Cl Br Br 3-bromo-2,2,6-trimethyl-4-octyne 6-cyclobutyl-2-hexyne 6-hexyl-11-isopropyl-3,8-tetradecadiyne 5. Rank the following molecules by the relative stability of the pi bonds (#1 most stable). 4 3 6. Why are trans-alkenes more stable than cis-alkenes? Less steric strain 1 2 7. Draw the rearrangement product (if any) for: HBr Br None Br HBr HBr 8. Why do propagation steps occur as many as 10,000 times before termination? Propagation occurs when a radical (which is a very reactive intermediate) reacts with a reactant to form a new radical. This newly formed radical can react with another molecule of reactant forming yet another radical and perpetuating the cycle. Termination of the cycle occurs when two radicals react together. Since there is very little radical present it is much less likely for to radicals to collide than for one radical to collide with a reactant. How does a termination step stop the chain reaction? When two radicals react together a stable product is formed. Since no new unstable radical is formed the reaction stops. Assign the R and S configuration to each of the following stereogenic centers. Which two represent the same molecule. Br Cl S CH CH 3 R 3 H H Rank the relative acidities (1 as highest) of: H Br R CH 3 R Cl CH 3 H R R CH H 3 Cl Br CH 3 CH 3 R S H H CH 3 H Cl Br Water and alcohol have approximately equal acidities H 6 O-H 2 H N Using 1-butyne and 1-iodopropane (and any inorganic reagents) prepare 3-heptyne. NaNH2 I Na 4 H 3 H 5 1 H2 O