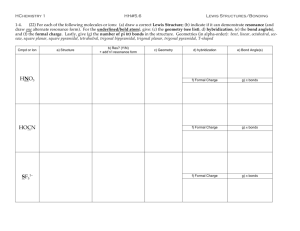
Chemistry 111 Study Sheet Answers Ionic Solid
advertisement
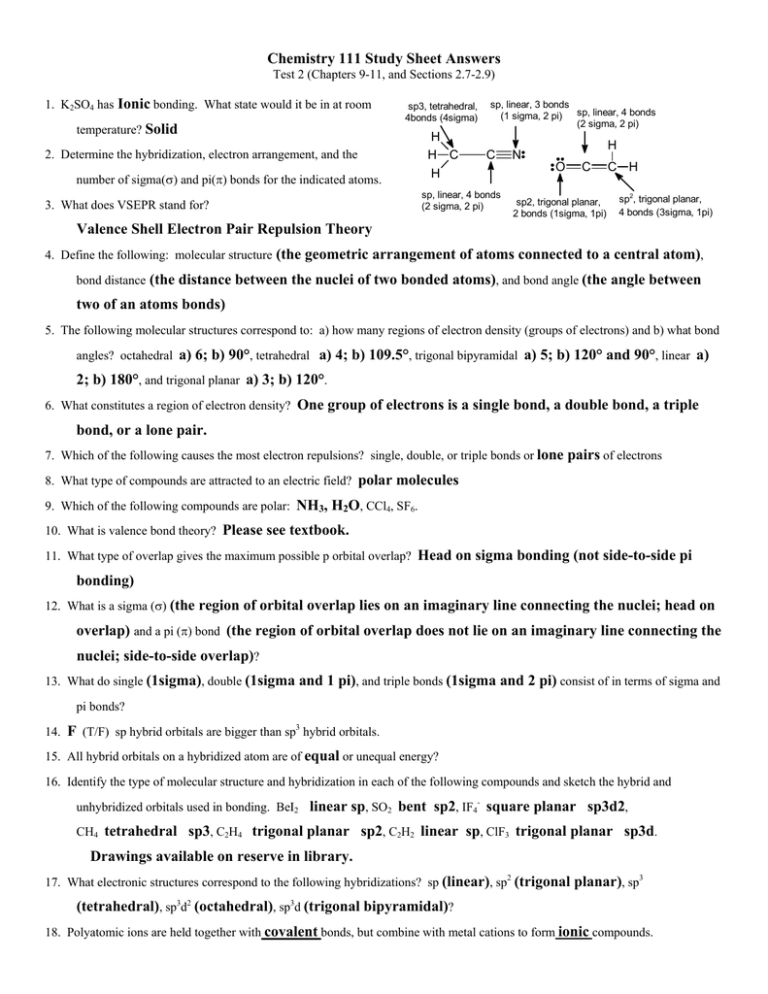
Chemistry 111 Study Sheet Answers Test 2 (Chapters 9-11, and Sections 2.7-2.9) 1. K2SO4 has Ionic bonding. What state would it be in at room sp3, tetrahedral, 4bonds (4sigma) temperature? Solid 2. Determine the hybridization, electron arrangement, and the number of sigma(σ) and pi(π) bonds for the indicated atoms. 3. What does VSEPR stand for? H H C H sp, linear, 3 bonds (1 sigma, 2 pi) sp, linear, 4 bonds (2 sigma, 2 pi) C sp, linear, 4 bonds (2 sigma, 2 pi) H N O C sp2, trigonal planar, 2 bonds (1sigma, 1pi) C H sp2, trigonal planar, 4 bonds (3sigma, 1pi) Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory 4. Define the following: molecular structure (the geometric arrangement of atoms connected to a central atom), bond distance (the distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms), and bond angle (the angle between two of an atoms bonds) 5. The following molecular structures correspond to: a) how many regions of electron density (groups of electrons) and b) what bond angles? octahedral a) 6; b) 90°, tetrahedral a) 4; b) 109.5°, trigonal bipyramidal a) 5; b) 120° and 90°, linear a) 2; b) 180°, and trigonal planar a) 3; b) 120°. 6. What constitutes a region of electron density? One group of electrons is a single bond, a double bond, a triple bond, or a lone pair. 7. Which of the following causes the most electron repulsions? single, double, or triple bonds or lone pairs of electrons 8. What type of compounds are attracted to an electric field? polar molecules 9. Which of the following compounds are polar: NH3, H2O, CCl4, SF6. 10. What is valence bond theory? Please see textbook. 11. What type of overlap gives the maximum possible p orbital overlap? Head on sigma bonding (not side-to-side pi bonding) 12. What is a sigma (σ) (the region of orbital overlap lies on an imaginary line connecting the nuclei; head on overlap) and a pi (π) bond (the region of orbital overlap does not lie on an imaginary line connecting the nuclei; side-to-side overlap)? 13. What do single (1sigma), double (1sigma and 1 pi), and triple bonds (1sigma and 2 pi) consist of in terms of sigma and pi bonds? 14. F (T/F) sp hybrid orbitals are bigger than sp3 hybrid orbitals. 15. All hybrid orbitals on a hybridized atom are of equal or unequal energy? 16. Identify the type of molecular structure and hybridization in each of the following compounds and sketch the hybrid and unhybridized orbitals used in bonding. BeI2 linear sp, SO2 bent sp2, IF4- square planar sp3d2, CH4 tetrahedral sp3, C2H4 trigonal planar sp2, C2H2 linear sp, ClF3 trigonal planar sp3d. Drawings available on reserve in library. 17. What electronic structures correspond to the following hybridizations? sp (linear), sp2 (trigonal planar), sp3 (tetrahedral), sp3d2 (octahedral), sp3d (trigonal bipyramidal)? 18. Polyatomic ions are held together with covalent bonds, but combine with metal cations to form ionic compounds. 19. Predict the charge on the monoatomic ions formed from the following atoms: Te 2-, Cs 1+, Si 4-, F 1-, Na 1+. 20. What did the colorful compounds that we looked at in lab have in common? transition metals ferrous chloride FeCl2, potassium bisulfate KHSO4, 21. Write the formula for: diphosphorus pentoxide P2O5, lead(II) oxide PbO, silicon dioxide SiO2, barium hydride BaH2. 22. Name the following compounds: N2O4 dinitrogen tetroxide, Fe(OH)3 iron(III) hydroxide, K2O potassium oxide, KHSO4 potassium bisulfate, NH4Cl ammonium chloride, KClO2 potassium chlorite, KClO4 potassium perchlorate, KClO potassium hypochlorite, KClO3 potassium chlorate, PbCrO4 lead(II) chromate, Ba3(PO3)2 barium phosphite, KMnO4 potassium permanganate, K2S potassium sulfide, AuPO4 (gold has 2 possible charges but was not on your list). 23. Give the formula for the following compounds: ammonium phosphate (NH4)3PO4, sodium acetate NaC2H3O2, iron(III) bromide FeBr4, sulfur trioxide SO3, copper(II) nitrate Cu(NO3)2, phosphorous pentachloride PCl5, nitrogen dioxide NO2. 24. anions→ cations↓ Na 1 S Cl C2H3O2 SO4 NO2 PO4 Na2S NaCl NaC2H3O2 Na2SO4 NaNO2 Na3PO4 CaCl2 Ca(C2H3O2)2 CaSO4 Ca(NO2)2 Ca3(PO4)2 Ca(OH)2 3 Al(C2H3O2)3 Al2(SO4)3 Al(NO2)3 AlPO4 Al(OH)3 H2SO4 HNO2 H3PO4 H2O CuNO2 Cu3PO4 CuOH Ca CaS Al Al2S3 AlCl3 H H2S HCl HC2H3O2 Cu+1 Cu2S CuCl CuC2H3O2 Cu2SO4 Cu+2 CuS CuCl2 Cu(C2H3O2)2 CuSO4 2 4 5 Cu(NO2)2 6 Cu3(PO4)2 1. sodium sulfide; 2. calcium chloride; 3. aluminum acetate; 4. sulfuric acid; 5. copper(I) nitrite; 6. copper(II) phosphate; 7. sodium hydroxide 25. Identify the cation and anion and their charge for each of the following compounds. NH41+ Cl– ; Co2+ S2- ; Ba2+ O22– (peroxide) ; Cs1+ CN1– ; Sn2+ SO32– OH 7 NaOH Cu(OH)2