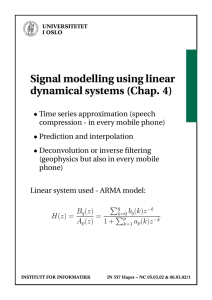
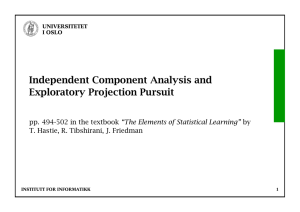
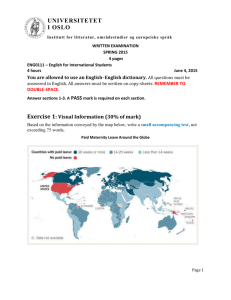
Some graphs to accompany the dynamic analysis of the closed economy RNy
advertisement

UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Some graphs to accompany the dynamic analysis of the closed economy AD-AS model. Ch 19 and 20 in IAM. RNy © ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Inflation AD With high b With high b, π need not fall so much in order to increase the real interest rate. AD With low b y © ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Inflation AD With low h With low h, an increase in π leads to only a small increase in the real interest rate. Therefore a small reduction in y AD With high h y © ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Inflation SRAS Position in t=0 πo AD Position in t=0 yo The short-run equilibrium © ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT y UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Inflation LRAS Π* AD y- The long-run equilibrium © ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT y UNIVERSITETET I OSLO SRAS Position in t=0 Inflation π o Π* AD Position in t=0 yo Y_ Dynamic adjustment from initial situation to long-run equilibirum (no shocks during the process) © ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT y UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Inflation SRAS, t=2 LRAS SRAS, t=0, t=1. C πo=π* B A AD, t=1 AD, t=0, t=2, t=3………. Yo=y_ The response to a temporary demand shock © ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT y UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Inflation LRAS SRAS, t=2 SRAS, t=0, t=1 C B πo=π* A AD, t=1, AD, t=0, Yo=y_ y The response to a permanent temporary demand shock. Without the i-target, the new equilibrium would be at C. However, the real interst rate increased. © ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Inflation AD ( b >0) With b=0 there is no interest rate reduction initially. B A b > 0 reduces the effect on both output and inflation. Policy is countercyclical. B AD, b=0 y Effects of negative demand shock. h>0 in both AD curves. © ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT UNIVERSITETET I OSLO AD ( b >0) and h low Inflation B With b=0 there is no interest rate reduction initially. B A b > 0 reduces the effect on both output and inflation. Policy is countercyclical. AD, b=0 and h high y Effects of negative supply shock: A trade-off between inflation and y stabilization. © ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT