KUTZTOWN UNIVERSITY KUTZTOWN, PENNSYLVANIA SPU 328 Positive Behavioral Intervention and Supports
advertisement
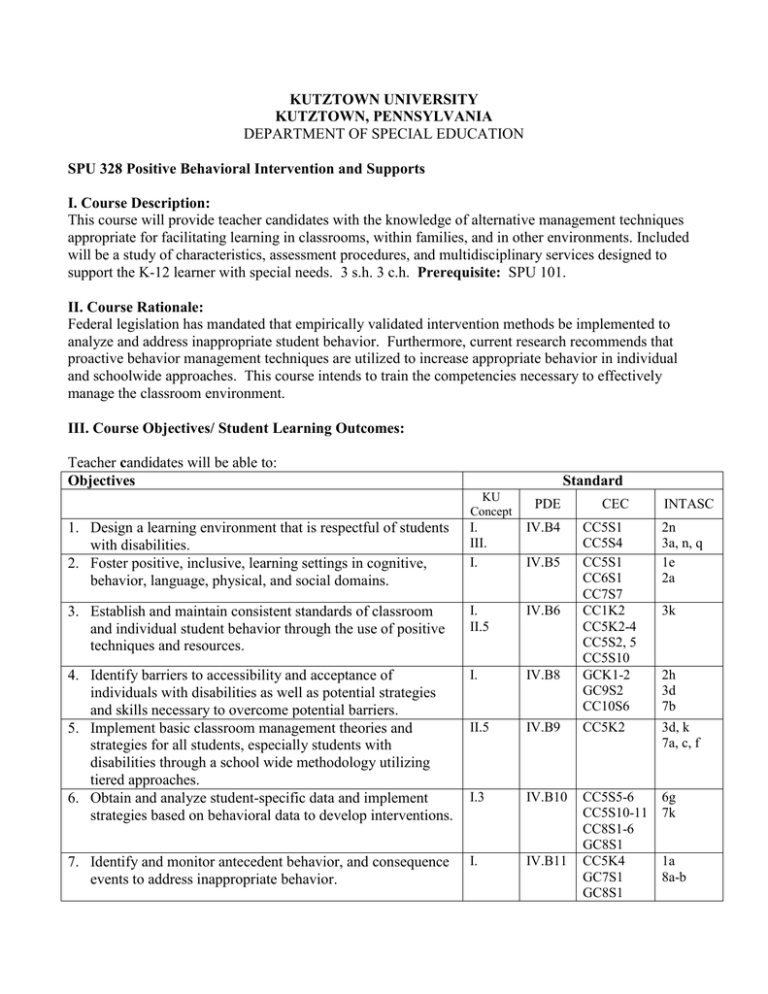
KUTZTOWN UNIVERSITY KUTZTOWN, PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF SPECIAL EDUCATION SPU 328 Positive Behavioral Intervention and Supports I. Course Description: This course will provide teacher candidates with the knowledge of alternative management techniques appropriate for facilitating learning in classrooms, within families, and in other environments. Included will be a study of characteristics, assessment procedures, and multidisciplinary services designed to support the K-12 learner with special needs. 3 s.h. 3 c.h. Prerequisite: SPU 101. II. Course Rationale: Federal legislation has mandated that empirically validated intervention methods be implemented to analyze and address inappropriate student behavior. Furthermore, current research recommends that proactive behavior management techniques are utilized to increase appropriate behavior in individual and schoolwide approaches. This course intends to train the competencies necessary to effectively manage the classroom environment. III. Course Objectives/ Student Learning Outcomes: Teacher candidates will be able to: Objectives Standard KU Concept PDE 1. Design a learning environment that is respectful of students with disabilities. 2. Foster positive, inclusive, learning settings in cognitive, behavior, language, physical, and social domains. I. III. I. IV.B4 3. Establish and maintain consistent standards of classroom and individual student behavior through the use of positive techniques and resources. I. II.5 IV.B6 4. Identify barriers to accessibility and acceptance of individuals with disabilities as well as potential strategies and skills necessary to overcome potential barriers. 5. Implement basic classroom management theories and strategies for all students, especially students with disabilities through a school wide methodology utilizing tiered approaches. 6. Obtain and analyze student-specific data and implement strategies based on behavioral data to develop interventions. I. IV.B8 II.5 IV.B9 I.3 IV.B10 7. Identify and monitor antecedent behavior, and consequence events to address inappropriate behavior. I. IV.B11 IV.B5 CEC INTASC CC5S1 CC5S4 CC5S1 CC6S1 CC7S7 CC1K2 CC5K2-4 CC5S2, 5 CC5S10 GCK1-2 GC9S2 CC10S6 CC5K2 2n 3a, n, q 1e 2a CC5S5-6 CC5S10-11 CC8S1-6 GC8S1 CC5K4 GC7S1 GC8S1 6g 7k 3k 2h 3d 7b 3d, k 7a, c, f 1a 8a-b 8. Recognize the contribution of family and students in identifying causes and preventions of inappropriate behaviors. I. IV.B12 9. Identify and explicitly teach social skills needed for all educational settings. I. IV.B13 10. Identify and implement crisis prevention and intervention techniques indicated in a student’s behavior plan. I. IV.B14 11. Participate and contribute in the development of positive behavioral support plans. I. IV.B15 12. Develop, support and demonstrate positive, inclusive learning environments for all students by promoting the engagement and independence of students with disabilities in classroom environments. 13. Adapt physical environments to provide optimal learning opportunities for students with disabilities. 14. Identify and implement methods for ensuring individual academic success in one-to-one, small-group, and largegroup settings. 15. Provide instruction in community-based settings to students with disabilities. 16. Use and maintain assistive technologies that support student participation. I. II.5 III. IV.B16 I. II.5 I. 17. Plan instruction in a variety of educational settings. 18. Teach students with disabilities to give and receive meaningful feedback from peers and adults. 19. Use skills in problem solving and conflict resolution for educational plans. 20. Establish consistent and appropriate classroom routines for students with disabilities. 21. Demonstrate the ability to integrate the IEP within the classroom routine. 22. Apply appropriate reinforcement techniques in serving individuals with disabilities. IV. CC1K7 CC2K4 CC7S3 CC10S2, 4 CC5K5 CC5S2 CC6S1-2 CC1K2 GC1K2 CC5K6 CC1K2 CC5S5,10, 11 CC10K2 GC4K5 CC5S1,4,9 1k 10d, m, q IV.B17 GC5K2 IV.B18 GC5K3 3d 7b 3b,j,o,p I. IV.B19 GC5S1 I. IV.B20 GC5S2 CC7S9 I. II.4 I.2 IV.B21 GC5S3 IV.B22 GC5S4 I.1,2 IV.B23 I. II.5 I. II.5 IV.B24 GC5S5 CC10S7 CC5S12 GC5S6 GC5S6 CC7S1 I. II.5 IV.B26 IV.B25 CC5S11 GC7S1 1a, e 3h,l, q 8m, q 3d, o 7a 10b 3a-b. f, k 3n, p, q, r 7b-c 8c 4g 6i 7k 8n, r 7b-c 8c 3h,o 6q 10a-b,n,r 3d,k 2a-b, h 3a,k 7a 7b 9o ASSESSMENT Assessment of each teacher candidate’s level of accomplishment with reference to the course objectives will be based upon a subset of the following: 1. Written and oral assignments that articulate understanding of terminology relevant to the population of students with behavior disorders. 2. Create a positive learning atmosphere for students with behavior disorders. 3. Synthesize research findings regarding etiology and best teaching practices for students with behavior disorders. 4. Modify the psychosocial and academic environment for students with behavior disorders. 5. Create, implement, and evaluate a functional analysis of behavior. 6. Reflective journal V. Course Outline I. Overview A. Historical Perspective B. Definition, Terminology, Legal Mandates C. Prevalence D. Classification, Educational Characteristics E. Family variables II. Special Services A. History and Philosophy of Human Services B. Community-Based Services C. Service Delivery Systems D. Integration of Services E. Mental Health, Social Welfare, and Legal Correctional Systems III. Educational Services A. Assessment, Referrals, Intervention B. School Placement C. Multidisciplinary Services D. Response to Intervention E. Prevention of behavior problems IV. Applied Behavior Analysis fundamentals A. Data collection B. Progress monitoring C. Behavioral objectives D. Experimental designs E. Functional analysis of behavior F. Linking assessment information to specially designed instruction V. Intervention strategies A. Reinforcement B. Punishment C. Replacement behaviors D. Differential reinforcement methods E. Extinction F. Social skills instruction G. Developing and implementing individual behavior support plans VI. Positive supports in classroom environments A. Generalization of behaviors B. Adaptations in the physical and psychosocial environment C. Conflict resolution D. Teaching social skills E. Creating instructional classroom rules F. Schoolwide positive behavior support X. Current Educational Research Issues, Trends, Implications for the Future A. Collaboration with school personnel B. Conferencing with parents C. Autistic spectrum disorder D. Synthesizing current best practices VII. Instructional Resources Alberto, P.A. & Troutman, A.C. (2007). Applied Behavior Analysis for Teachers (7th ed.). Upper Saddle River, N.J.: Prentice Hall. Batshaw, M.L., Pellegrina, L, and Roizen, N.J. (2007). Children with disabilities. Cooper, J.O., Heron, T.E., & Heward, W.L. (2007). Applied behavior analysis (2nd ed.). Upper Saddle River, N.J.: Prentice Hall. Faltis, C. (2000). Join fostering: Teaching and learning in multilingual classrooms (3rd Columbus, OH: Merrill. ed.). Heward, W.L., Heron, T.E., Neef, N.A., Peterson, S.M., Sainato, D.M., Cartledge, G., Gardner, R., Peterson, L.D., Hersh, S,B., & Dardig, J.C. (2005). Focus on behavior analysis in education: Achievements, challenges, and opportunities. Upper Saddle River, N.J.: Prentice Hall. Kauffman, J.M. & Landrum, T.J. (2009). Characteristics of emotional and behavioral disorders of children and youth (9th ed.). Upper Saddle River, N.J.: Prentice Hall. Page, R. M. (2000). Fostering emotional well-being in the classroom (2nd ed.). Austin, TX: Ed. Pro- Pennsylvania Department of Education, Bureau of Special Education. (2001a). Evaluation Report [(ER) format]. Retrieved April 13, 2003, from www.pde.state.pa.us/special_edu/site Pennsylvania Department of Education, Bureau of Special Education. (2001b). Education Program [(IEP) format]. Retrieved April 13, 2003, from www.pde.state.pa.us/special_edu/site Individualized Polloway, E. A. (2000). Strategies for teaching learners with special needs (7th ed.). OH: Merrill Columbus, Salend, S. J. (2000). Creating inclusive classrooms: Effective and reflective practices. Columbus, OH: Merrill. Schloss J.P. & Smith, M. (1998). Applied behavior analysis in the classroom (2nd ed.). Needham Heights, MA.: Allyn and Bacon. Yell, M.L., Meadows, N.B., Drasgow, E., Shriner, J.G. (2009). Evidence-based practices for educating students with emotional and behavioral disorders. Upper Saddle River, N.J.: Prentice Hall. Revised 6/2012





