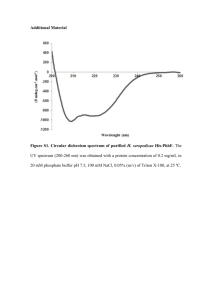
Proteom analysis of Blue Mussel tissue by two
advertisement
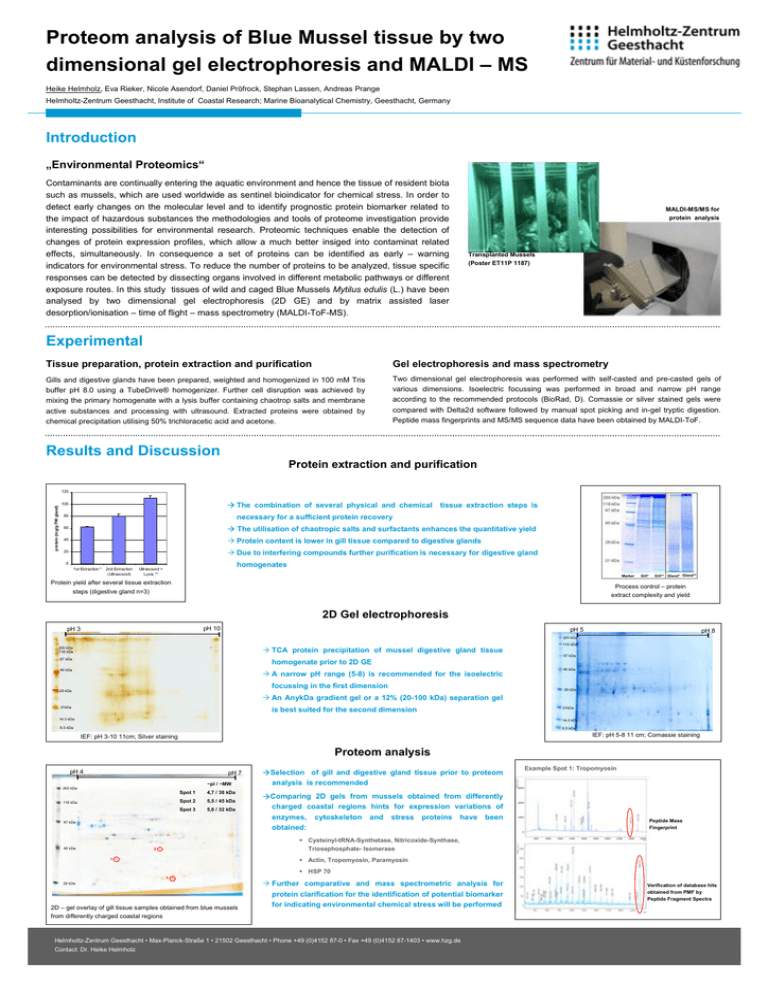
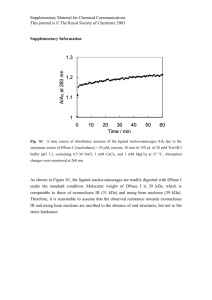
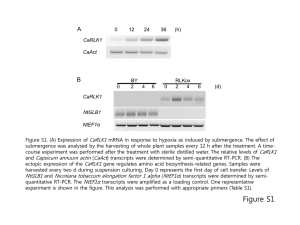
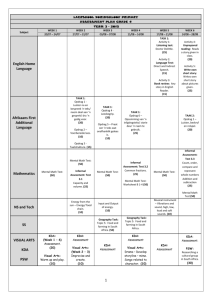
Proteom analysis of Blue Mussel tissue by two dimensional gel electrophoresis and MALDI – MS Heike Helmholz, Eva Rieker, Nicole Asendorf, Daniel Pröfrock, Stephan Lassen, Andreas Prange Helmholtz-Zentrum Geesthacht, Institute of Coastal Research; Marine Bioanalytical Chemistry, Geesthacht, Germany Introduction „Environmental Proteomics“ Contaminants are continually entering the aquatic environment and hence the tissue of resident biota such as mussels, which are used worldwide as sentinel bioindicator for chemical stress. In order to detect early changes on the molecular level and to identify prognostic protein biomarker related to the impact of hazardous substances the methodologies and tools of proteome investigation provide interesting possibilities for environmental research. Proteomic techniques enable the detection of changes of protein expression profiles, which allow a much better insiged into contaminat related effects, simultaneously. In consequence a set of proteins can be identified as early – warning indicators for environmental stress. To reduce the number of proteins to be analyzed, tissue specific responses can be detected by dissecting organs involved in different metabolic pathways or different exposure routes. In this study tissues of wild and caged Blue Mussels Mytilus edulis (L.) have been analysed by two dimensional gel electrophoresis (2D GE) and by matrix assisted laser desorption/ionisation – time of flight – mass spectrometry (MALDI-ToF-MS). MALDI-MS/MS for protein analysis Transplanted Mussels (Poster ET11P 1187) Experimental Tissue preparation, protein extraction and purification Gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry Gills and digestive glands have been prepared, weighted and homogenized in 100 mM Tris buffer pH 8.0 using a TubeDrive® homogenizer. Further cell disruption was achieved by mixing the primary homogenate with a lysis buffer containing chaotrop salts and membrane active substances and processing with ultrasound. Extracted proteins were obtained by chemical precipitation utilising 50% trichloracetic acid and acetone. Two dimensional gel electrophoresis was performed with self-casted and pre-casted gels of various dimensions. Isoelectric focussing was performed in broad and narrow pH range according to the recommended protocols (BioRad, D). Comassie or silver stained gels were compared with Delta2d software followed by manual spot picking and in-gel tryptic digestion. Peptide mass fingerprints and MS/MS sequence data have been obtained by MALDI-ToF. Results and Discussion Protein extraction and purification protein (mg/g FW gland) 120 The combination of several physical and chemical 100 tissue extraction steps is necessary for a sufficient protein recovery 80 60 The utilisation of chaotropic salts and surfactants enhances the quantitative yield 40 Protein content is lower in gill tissue compared to digestive glands Due to interfering compounds further purification is necessary for digestive gland 20 0 1st Extraction * 2nd Extraction (Ultrasound) homogenates Ultrasound + Lysis ** Marker Protein yield after several tissue extraction steps (digestive gland n=3) Gill* Gill** Gland* Gland** Process control – protein extract complexity and yield 2D Gel electrophoresis pH 10 pH 3 pH 5 pH 8 200 kDa TCA protein precipitation of mussel digestive gland tissue 200 kDa 116 kDa 116 kDa 67 kDa 67 kDa homogenate prior to 2D GE 45 kDa A narrow pH range (5-8) is recommended for the isoelectric focussing in the first dimension 29 kDa 45 kDa 29 kDa An AnykDa gradient gel or a 12% (20-100 kDa) separation gel 21kDa is best suited for the second dimension 14.3 kDa 21kDa 14.3 kDa 6.5 kDa 6.5 kDa IEF: pH 5-8 11 cm; Comassie staining IEF: pH 3-10 11cm; Silver staining Proteom analysis pH 4 pH 7 ~pI / ~MW Selection of gill and digestive gland tissue prior to proteom analysis is recommended Example Spot 1: Tropomyosin 200 kDa 116 kDa Spot 1 4,7 / 38 kDa Spot 2 5,5 / 45 kDa Spot 3 5,6 / 32 kDa 67 kDa 45 kDa Comparing 2D gels from mussels obtained from differently charged coastal regions hints for expression variations of enzymes, cytoskeleton and stress proteins have been obtained: Peptide Mass Fingerprint Cysteinyl-tRNA-Synthetase, Nitricoxide-Synthase, Triosephosphate- Isomerase 2 Actin, Tropomyosin, Paramyosin 1 HSP 70 3 29 kDa 2D – gel overlay of gill tissue samples obtained from blue mussels from differently charged coastal regions Further comparative and mass spectrometric analysis for protein clarification for the identification of potential biomarker for indicating environmental chemical stress will be performed Helmholtz-Zentrum Geesthacht • Max-Planck-Straße 1 • 21502 Geesthacht • Phone +49 (0)4152 87-0 • Fax +49 (0)4152 87-1403 • www.hzg.de Contact: Dr. Heike Helmholz Verification of database hits obtained from PMF by Peptide Fragment Spectra