Regional Cultures & Health Outcomes: Implications for Consumer Engagement. Jackson Williams
advertisement
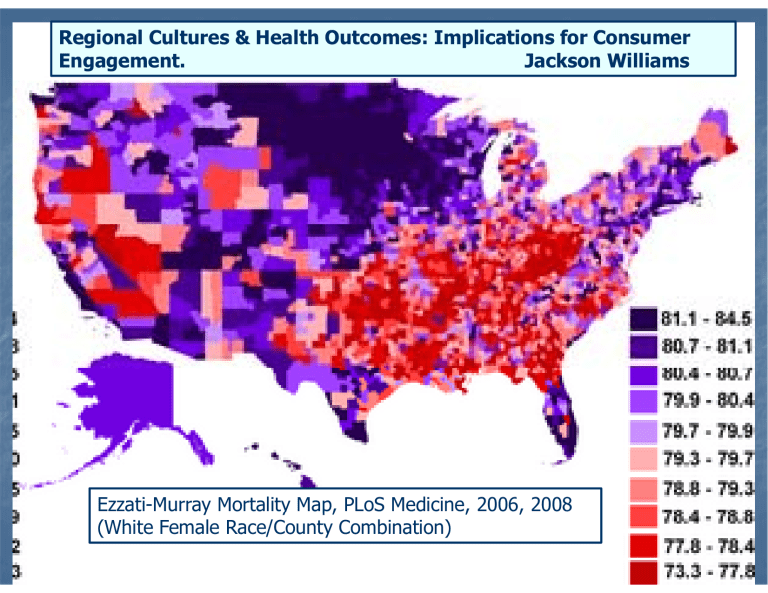
Regional Cultures & Health Outcomes: Implications for Consumer Engagement. Jackson Williams Ezzati-Murrayy Mortalityy Map, p, PLoS Medicine,, 2006,, 2008 (White Female Race/County Combination) Academy Health June 2010 Lieske, 1993 Culture and Health “Culture refers to the shared and learned aspects t off h human cognition iti and d behavior b h i that th t underlie our ability to interpret the world around us and d to t ttake k meaningful i f l action.” ti ” (Edb (Edberg, 2007) Diet Behaviors ((e.g., g , smoking, g, exercise)) Intangibles (e.g., social supports, timetimepreference) Academy Health June 2010 T Two Methods M th d off Analyzing A l i Culture C lt Unit Analysis (e.g., (e g country, country region) Seven Countries Study (Keys) Japanese--Americans study (Marmot & Syme) Japanese Syme) C lt l Dimensions Cultural Di i Analysis A l i Social Capital (Putnam) Traditional/Secular (Inglehart (Inglehart)) Long--Term Orientation (Hofstede Long (Hofstede)) Academy Health June 2010 Matching Obesity Rates: Homelands to Counterpart US States Japan/Hawaii Italy/New Jersey Germany/Wisconsin England/Indiana Scotland/Tennessee Dimensional Analysis: Social Capital Academy Health June 2010 Dimensional Analysis: Traditional/Secular Academy Health June 2010 Dimensional Analysis: Traditional/Secular Academy Health June 2010 Dimensional Analysis: Long Long--Term Orientation Academy Health June 2010 There’s There s Something Going On… On But: Limitations… Culture is a soft concept, and analysis relies heavily on authors in humanities ((Fischer,, Webb)) not sciences Social science bias (vs., e.g., biology) U i comparison Unit i is i not quantitative i i Regional medication adherence data would help tease out consumer engagement Academy Health June 2010 Policy Implications: Three Thought g Paradigms g Public Health Positivism: Publish rankings and demand improvements P t d i Postmodernism: Take T k cultures lt and d associated values as a given; celebrate diversity Di Disparities: ii Is I there h a “Scottish “S i h Effect” Eff ” at work in the U.S.? Academy Health June 2010 Conclusions S Scorecards d and d rankings ki may unfairly f il stigmatize providers, public health officials, and populations. Given diversity of regional subcultures subcultures, best to formulate consumer engagement policies at state le level. el If p provider payment p y is tied to consumer engagement, will providers be deterred from serving certain populations? Academy Health June 2010


