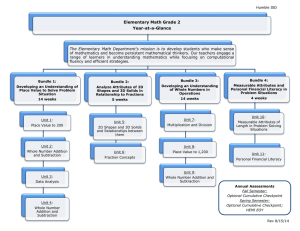
High-Performance Work Practices as Drivers of Quality and Efficiency: An Evidence-Based
advertisement

High-Performance Work Practices as Drivers of Quality and Efficiency: An Evidence-Based Management Review Andrew N. Garman, PsyD, MS Associate Professor, Health Systems Management Rush University Acknowledgments • Sponsored by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ), through the ACTION Network initiative – Health Research and Educational Trust • The Ohio State University • Rush University • Project team: – – – – – Ann Scheck McAlearney - The Ohio State University Andrew N. Garman – Rush University Megan McHugh – Health Research & Educational Trust Paula H. Song - The Ohio State University Michael I. Harrison – Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality – Dina Moss – Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Introduction • High-Performance Work Practices (HPWPs) – Personnel practices associated with improved organizational performance – Mutually reinforcing HR systems (or ‘bundles’) are likely to have greater impact Introduction • Considerable body of ‘more is better’ research from other industries • Much less research available on which practices work best, in which types of organizations, and under what conditions Our Study • A systematic review, to identify the results with the greatest relevance to healthcare organizations • Research questions: – What evidence is there that HPWPs can benefit healthcare organizations? – Which HPWPs / bundles appear to have the greatest potential for benefit? – What are the mechanisms through which HPWPs have positive effects? Method: Literature Scan Sources • Research journals – U.S., Europe, Australia – Other developed countries • Industry/trade associations – SHRM Foundation – research archives – University Healthsystems Consortium – Advisory Board • Government publications – VA system, NHS, Other (e.g., military leadership) Approach to Scan • Two-step process: – Step one: • Identify practices, and practice bundles • Assess relative promise of practices/bundles for influencing outcomes in healthcare settings – Step two: • ‘Vet’ practices and bundles with advisory panel • Identify most promising practices or bundles for further study Results: Logic Model Exogenous Factors Frontline control & freedom to challenge Factors influencing HPWP adoption: •Senior leadership support ' •Lower union density •Higher number of network affiliations Factors influencing HPWP impact & sustainability • Higher quality of the local labor market • Continued leadership support Quality of candidate Pools - Pool size - Applicant quality Rigorous recruiting Selective hiring Career development Employment security Management training linked to organizational needs Reduced status distinctions Performance contingent comp: Manager Teams / decentralized decision-making Succession planning System reliability / resilience Staff resources - Staffing adequacy - Staffing stability Quality of hires (capabilities) -Experience -Capacity to learn -Motivation -Loyalty Staff effectiveness - Quality focus - Communication - Problem-solving Extensive Training Leadership alignment & development Information sharing (organizational) Capacity for continuous system improvement - Motivation to learn - Capacity to learn - Freedom to 'challenge the system' Performancecontingent comp: Employee Organizational engagement Staff acquisition & development Conveying mission & vision Employee involvement in decision-making Labor costs Organizational performance • Fewer "never events" • Lower malpractice costs • Innovation • Lower agency utilization costs • Lower turnover costs Employee Outcomes • Lower turnover •Higher satisfaction / engagement •Lower burnout •Higher general well-being Exogenous Factors Bundle #2: 'Frontline control & freedom to challenge' ' Employment Security Management training linked to organizational needs Reduced status distinctions Performance contingent comp: manager Teams / decentralized decision-making Succession planning Factors influencing HPWP adoption: System reliability / Senior leadership support capacity for selfcorrection Quality of Hires Staff resources Lower union density Quality of (capabilities) - staffing adequacy Candidate Pools - Experience - staffing stability - Pool size number -of Capacity to learn Higher network affiliations - Applicant quality -Motivation Staff effectiveness - quality focus - communication - problem-solving -Loyalty Bundle #4: ‘Management efficiency' Capacity for continuous system improvement - Motivation to learn - Capacity to learn - Freedom to 'challenge the system' Factors influencing HPWP impact & sustainability Higher quality of the local labor market Information PerformanceCareer sharing contingent Continued leadership support Rigorous Selective Extensive Develop(organizational) comp: Employee recruiting hiring ment Training Organizational engagement Bundle #1: ‘Staff talent acquisition & development’ Conveying mission & vision Employee involvement in decision-making Labor costs Organizational Performance • Decreased "never events" • Decreased malpractice costs • More efficient Innovation adoption • Lower agency utilization costs • Lower turnover costs Employee Outcomes -Lower voluntary & involuntary turnover -Higher satisfaction / engagement - Lower burnout -Higher general well-being Exogenous Factors Affecting HPWPs The ‘enabling’ bundle: Organizational Engagement Bundle #2: 'Frontline control & freedom to challenge' Factors influencing HPWP adoption: •Senior leadership support ' •Lower union density Bundle #4: ‘Management efficiency' Employment Security Management training linked to organizational needs Reduced status distinctions Performance contingent comp: manager Teams / decentralized decision-making Succession planning Organizational information sharing Conveying mission & vision Employee involvement in decision-making Performance-contingent compensation Factors influencing HPWP functioning & continued success: • Higher quality of the local labor market • Continued leadership support Quality of Hires (capabilities) - Experience - Capacity to learn -Motivation -Loyalty Quality of Candidate Pools - Pool size - Applicant quality Rigorous recruiting System reliability / capacity for selfcorrection Staff resources - staffing adequacy - staffing stability Selective hiring Career Development Staff effectiveness - quality focus - communication - problem-solving Extensive Training Bundle #1: ‘Staff talent acquisition & development’ Capacity for continuous system improvement - Motivation to learn - Capacity to learn - Freedom to 'challenge the system' Labor costs Organizational Performance • Decreased "never events" • Decreased malpractice costs • More efficient Innovation adoption • Lower agency utilization costs • Lower turnover costs Employee Outcomes -Lower voluntary & involuntary turnover -Higher satisfaction / engagement - Lower burnout -Higher general well-being Exogenous Factors Affecting HPWPs The ‘high leverage’ bundle: Staff Acquisition & Development Factors influencing HPWP adoption: •Senior leadership support ' •Lower union density Factors influencing HPWP functioning & continued success: • Higher quality of the local labor market • Continued leadership support Bundle #2: 'Frontline control & freedom to challenge' Bundle #4: ‘Management efficiency' Employment Security Management training linked to organizational needs Reduced status distinctions Performance contingent comp: manager Teams / decentralized decision-making Succession planning Rigorous recruiting Selective hiring Extensive training Career development / internal labor pools Quality of Candidate Pools - Pool size - Applicant quality Quality of Hires (capabilities) - Experience - Capacity to learn -Motivation -Loyalty System reliability / capacity for selfcorrection Staff resources - staffing adequacy - staffing stability Staff effectiveness - quality focus - communication - problem-solving Information sharing (organizational) Capacity for continuous system improvement - Motivation to learn - Capacity to learn - Freedom to 'challenge the system' Performancecontingent comp: Employee Bundle #3: ‘Organizational Engagement’ Communicating Mission & Vision Employee Involvement in Decision-making Labor costs Organizational Performance • Decreased "never events" • Decreased malpractice costs • More efficient Innovation adoption • Lower agency utilization costs • Lower turnover costs Employee Outcomes -Lower voluntary & involuntary turnover -Higher satisfaction / engagement - Lower burnout -Higher general well-being Exogenous Factors Affecting HPWPs The ‘direct effect’ bundle: Frontline control & freedom to challenge Bundle #4: ‘Management efficiency' Factors influencing HPWP adoption: •Senior leadership support •Lower union density ' •Higher number of network affiliations Management training linked to organizational needs Factors influencing HPWP functioning & continued success: • Higher quality of the local labor market • Continued leadership support Succession planning Employment security Reduced status distinctions Teams / decentralized decision-making Quality of Hires (capabilities) - Experience - Capacity to learn -Motivation -Loyalty Quality of Candidate Pools - Pool size - Applicant quality Rigorous recruiting System reliability / capacity for selfcorrection Staff resources - staffing adequacy - staffing stability Selective hiring Career Development Staff effectiveness - quality focus - communication - problem-solving Extensive Training Information sharing (organizational) Capacity for continuous system improvement - Motivation to learn - Capacity to learn - Freedom to 'challenge the system' Performancecontingent comp: Employee Bundle #3: ‘Organizational Engagement’ Bundle #1: ‘Staff talent acquisition & development’ Communicating Mission & Vision Employee Involvement in Decision-making Labor costs Organizational Performance • Decreased "never events" • Decreased malpractice costs • More efficient Innovation adoption • Lower agency utilization costs • Lower turnover costs Employee Outcomes -Lower voluntary & involuntary turnover -Higher satisfaction / engagement - Lower burnout -Higher general well-being Exogenous Factors Affecting HPWPs The ‘leadership’ bundle: Leadership alignment and development Bundle #2: 'Frontline control & freedom to challenge' Factors influencing HPWP adoption: •Senior leadership support •Lower union density ' •Higher number of network affiliations Employment Security Factors influencing HPWP functioning & continued success: • Higher quality of the local labor market • Continued leadership support Reduced status distinctions Teams / decentralized decision-making Management training linked to organizational needs & goals Performance-contingent compensation for broader goals Succession planning Quality of Hires (capabilities) - Experience - Capacity to learn -Motivation -Loyalty Quality of Candidate Pools - Pool size - Applicant quality Rigorous recruiting System reliability / capacity for selfcorrection Staff resources - staffing adequacy - staffing stability Selective hiring Career Development Staff effectiveness - quality focus - communication - problem-solving Extensive Training Information sharing (organizational) Capacity for continuous system improvement - Motivation to learn - Capacity to learn - Freedom to 'challenge the system' Performancecontingent comp: Employee Bundle #3: ‘Organizational Engagement’ Bundle #1: ‘Staff talent acquisition & development’ Communicating Mission & Vision Employee Involvement in Decision-making Labor costs Organizational Performance • Decreased "never events" • Decreased malpractice costs • More efficient Innovation adoption • Lower agency utilization costs • Lower turnover costs Employee Outcomes -Lower voluntary & involuntary turnover -Higher satisfaction / engagement - Lower burnout -Higher general well-being Significance / Relevance • Identifies evidence-based strategies from other industries • Provides a holistic model for examining personnel practices within healthcare settings • Identifies salient exogenous and organizational factors affecting HPWP outcomes