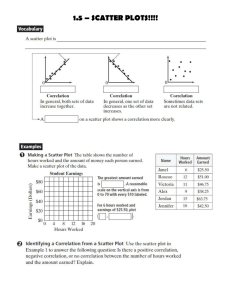
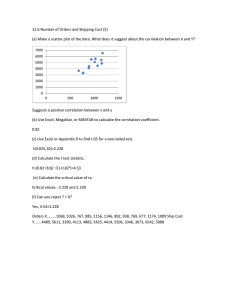
Scatter plots & Association Statistics is about … variation. explain variation.
advertisement

Scatter plots & Association Statistics is about … variation. Recognize, quantify and try to explain variation. –Variation in contents of cola cans can be explained, in part, by the type of cola in the cans. 1 Scatter plots & Association variable – variable of primary interest. Explanatory variable – variable used to try to explain variation in the response. Response 2 Scatter plots & Association When both the response and the explanatory variables are quantitative, display them both in a scatter plot. Look for a general pattern of association. 3 Scatter plots & Association Example: Tar (mg) and carbon monoxide (mg) in cigarettes. –y, Response: CO (mg). –x, Explanatory: Tar (mg). –Cases: 25 brands of cigarettes. 4 Scatter plot 5 Positive Association Above average values of CO are associated with above average values of Tar. Below average values of CO are associated with below average values of Tar. 6 Scatter plots & Association Example: Outside temperature and amount of natural gas used. – Response: Natural gas (1000 ft3). – Explanatory: Outside temperature (o C). – Cases: 26 days. 7 Negative Association Gas 10 5 0 -5.0 .0 5.0 Temp 10.0 15.0 8 Negative Association Above average values of gas are associated with below average temperatures. Below average values of gas are associated with above average temperatures. 9 Correlation Linear Association – How closely do the points on the scatter plot represent a straight line? – The correlation coefficient gives the direction of the linear association and quantifies the strength of the linear association between two quantitative variables. 10 Correlation Standardize y y y zy sy Standardize x xx zx sx 11 ZxZy > 0 ZxZy > 0 12 Correlation Coefficient z r z x y n 1 x x y y r s x s y n 1 13 Correlation Conditions Correlation applies only to quantitative variables. Correlation measures the strength of linear association. Outliers can distort the value of the correlation coefficient. 14 Correlation Coefficient Tar and CO z z r 22.9796 n 1 24 x r y = 0.9575 15 Correlation Coefficient There is a strong positive correlation, linear association, between the tar content and carbon monoxide content of the various cigarette brands. 16 JMP – Multivariate methods – Multivariate Y, Columns Analyze – – Tar (mg) CO (mg) 17 18 Correlation Properties sign of r indicates the direction of the association. The value of r is always between –1 and +1 Correlation has no units. Correlation is not affected by changes of center or scale. The 19 Correlation Cautions “Correlation” and “Association” are different. –Correlation – specific (linear). –Association – vague (trend). Don’t correlate categorical variables. 20 Correlation Cautions Don’t confuse correlation with causation. – There is a strong positive correlation between the number of crimes committed in communities and the number of 2nd graders in those communities. Beware of lurking variables. 21