Moderate and Severe Obesity Have Large Differences in Health Care Costs
advertisement

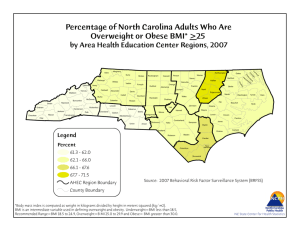
Moderate and Severe Obesity Have Large Differences in Health Care Costs Tatiana Andreyeva, RAND Graduate School Roland Sturm, RAND Jeanne S. Ringel, RAND Why look at health care costs across obesity groups? • Obesity-related health problems are particularly common among severely obese individuals • One would expect commensurate differences in health care costs across obesity groups, yet few data are available • The prevalence of severe obesity is increasing at a much faster rate than the spread of obesity Obesity and Health Status 45 % reporting fair or poor health 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 Normal, 18.5<BMI<25 Obese, 30<BMI<35 Overweight, 25<BMI<30 Males 50-69 Severely obese, BMI>35 Females 50-69 Source: Sturm et al, Health Affairs, March 2004 Obesity and Disability % with any ADL limitation 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 Normal, 18.5<BMI<25 Overweight, 25<BMI<30 Obese, 30<BMI<35 Males 50-69 Severely obese, BMI>35 Females 50-69 Source: Sturm et al, Health Affairs, March 2004 Severe obesity is increasing at a much faster rate than the spread of obesity 500 BMI>=30 BMI>=35 400 BMI>=40 BMI>=45 300 BMI>=50 200 100 19 86 19 87 19 88 19 89 19 90 19 91 19 92 19 93 19 94 19 95 19 96 19 97 19 98 19 99 20 00 Percentage Increase (1986=100) 600 Source: Sturm, Arch Internal Med, Oct 2003 Our Approach • Estimate the association between obesity and health care utilization and expenditures across varying degrees of obesity – Data from Health and Retirement Study, 1996-2000 Methodology • Main dependent variables: – Health care utilization • outpatient visits, hospitalization, inpatient days – Total health care expenditures • Main explanatory variable: BMI weight class – Normal weight (18.5-25), Overweight (25-30), Moderate obesity (30-35), Severe obesity (35-40), and Extreme obesity (40+) • Analyze data cross-sectionally Model Estimation Results • Average predicted health care utilization and costs • Adjusted for sociodemographic characteristics and behavioral risk factors • By weight class Obesity and Health Care Costs 9000 Annual total health care costs in 2002 $s 8000 7000 6000 5000 4000 3000 2000 1000 0 Obese, 30<BMI<35 Severely obese, 35<BMI<40 Males 54-69 Extremely obese, BMI 40+ Females 54-69 Obesity and Health Care Utilization 18 Number of outpatient visits 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 Obese, 30<BMI<35 Severely obese, 35<BMI<40 Males 54-69 Extremely obese, BMI 40+ Females 54-69 Obesity and Health Care Utilization Number of inpatient days 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 Obese, 30<BMI<35 Severely obese, 35<BMI<40 Males 54-69 Extremely obese, BMI 40+ Females 54-69 Limitations • Self-reported height and weight underestimate BMI • Limited age range of HRS data • Excluded institutionalized population • Cross-sectional estimates and cannot be interpreted as causal effects Discussion • Widely cited average effects of obesity on health care costs (36-37%) obscure major differences across obesity groups – BMI of 35-40 is associated with twice the increase in medical expenditures above normal weight (50% increase) than BMI of 30-35 (25% increase) – BMI of 40+ doubles costs (100% above normal weight) • Average estimates will underpredict future health care costs because severe obesity grows at a much faster rate than obesity in general Conclusion An increasing burden of obesity on the health care system grows disproportionally for the most obese segment of the US population As the prevalence of severe obesity increases at a much faster rate than that of obesity, average estimates of obesity effects obscure real consequences for individuals, hospitals and health plans. Back up Model Estimation • Log-linear model for health care expenditure data – Better fit the data than alternative models in cross-validation tests – Homogenous smearing transformation • Linear model for continuous utilization outcomes (number of doctor visits and hospital days) and a probit model for any inpatient stay • Analyze data separately by gender Obesity and Health Care Costs 9000 Annual total health care costs in 2002 $s 8000 7000 6000 5000 4000 3000 2000 1000 0 Obese, 30<BMI<35 Severely obese, 35<BMI<40 Extremely obese, BMI>=40 Individuals ages 54-69 Obesity, BMI>=30 Obesity and Health Care Utilization Number of outpatient visits 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 Obese, 30<BMI<35 Severely obese, 35<BMI<40 Extremely obese, BMI>=40 Individuals ages 54-69 Obesity, BMI>=30 Obesity and Health Care Utilization Number of inpatient days 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 Obese, 30<BMI<35 Severely obese, 35<BMI<40 Extremely obese, BMI>=40 Individuals ages 54-69 Obesity, BMI>=30 Obesity and Health Care Utilization % with any inpatient stay 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 Obese, 30<BMI<35 Severely obese, 35<BMI<40 Males 54-69 Extremely obese, BMI 40+ Females 54-69