Health Insurance Coverage and Access to Technologies: the Treatment of Infertility
advertisement

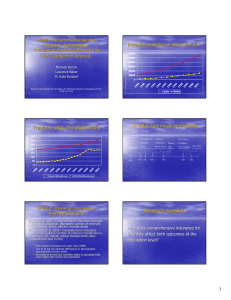
Health Insurance Coverage and Access to Technologies: The Case of Insurance Mandates for the Treatment of Infertility Melinda Henne Laurence Baker M. Kate Bundorf Supported by funding from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the Iris M. Litt Fund Increasing utilization of ART in the U.S. 120000 100000 80000 60000 40000 20000 Cycles Births 01 20 00 20 99 19 98 19 97 19 96 19 95 19 94 19 92 19 91 19 90 19 19 89 0 Trends in rates of multiple births 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 19 80 19 82 19 84 19 86 19 88 19 90 19 92 19 94 19 96 19 98 20 00 20 02 0 Twins/10,000 deliveries HOM/100,000 deliveries 15 States have insurance mandates Arkansas Hawaii Massachusetts California Maryland 1980 New Jersey Montana Connecticut Illinois Louisiana Texas Rhode Island Ohio West Virginia 1985 1987 1989 1991 2001 New York 2002 Effect of insurance coverage on treatment patterns • Jain et al, 2002—Comprehensive insurance coverage increases utilization, decreases number of embryos transferred, births, percent multiple births • Reynolds et al, 2003—Comprehensive insurance coverage reduces number of embryos transferred in women <35, maybe reduce multiple birth rates (significant only in MA) – Both studies evaluated one year only (1998) – Jain et al did not address differences in demographic characteristics across states – Reynolds et al matched mandate states to geographically close states with similar size population Research question How does comprehensive insurance for infertility affect birth outcomes at the population level? Data Sources – Birth Certificates • National Vital Statistics System from the NCHS 1980-1997 – Information abstracted from birth certificates – 100% of births for most states for most years – Total number of births, multiple births (twins or higher order), triplets+ (triplets or higher order – Transform births to deliveries for calculation of multiples Data Sources – Insurance Mandates • RESOLVE and state legislation • Categorized based on likely effectiveness in changing treatment patterns: – Comprehensive (3 states)– requirement that insurance companies (including HMOs) provide coverage for the cost of diagnosis and treatment of infertility, including ART of at least 4 oocyte retrievals. – “Soft” (5 states) – limited coverage – “Offer only” (3 states) – mandates insurance companies to offer coverage, but no mandate to purchase coverage – No Mandate Data Sources - Other • U.S. Census Bureau • Bureau of Economic Analysis • Bureau of Labor Statistics • Current Population Survey Data Analysis – Birth Data yi ,t 1Ci ,t 2 Si ,t 3Oi ,t Gi Yt i ,t where i indexes states and t indexes years y is a birth outcome including deliveries, multiple deliveries, and triplet+ deliveries per 1,000 women, multiples and triplets+ per 1,000 deliveries C, S, and O are time-varying indicators of mandates Y is a year fixed effect G is a state fixed effect Effect on Deliveries per Capita Deliveries per 1000 Women Age 20-49 20-29 30-34 Offer Mandate 3.252 6.782+ 2.139 [2.535] [3.519] [2.049] Soft Mandate -0.309 -0.183 -0.724 [1.482] [1.609] [1.613] Comprehensive Mandate 2.657* 1.079 4.018* [1.066] [2.204] [1.551] Constant 57.868** 111.417** 45.098** [0.989] [1.099] [1.092] Observations 918 918 918 R-squared 0.86 0.92 0.94 Robust standard errors in brackets + significant at 10%; * significant at 5%; ** significant at 1% 35-39 2.218 [1.830] -0.172 [1.353] 2.982 [1.783] 11.191** [0.798] 918 0.94 40-44 1.055 [0.782] -0.18 [0.446] 0.501 [0.541] 2.126** [0.240] 918 0.91 45-49 0.065 [0.065] -0.019 [0.021] 0.004 [0.037] 0.120** [0.020] 918 0.77 Effect on Multiple Deliveries per Capita Multiple Deliveries per 1000 Women Age 20-49 20-29 30-34 Offer Mandate 0.017 0.003 -0.016 [0.042] [0.041] [0.051] Soft Mandate 0 0.027 -0.019 [0.026] [0.018] [0.046] Comprehensive Mandate 0.071* -0.004 0.193** [0.027] [0.032] [0.046] Constant 0.613** 1.168** 0.558** [0.014] [0.013] [0.023] Observations 918 918 918 R-squared 0.74 0.81 0.86 Robust standard errors in brackets + significant at 10%; * significant at 5%; ** significant at 1% 35-39 0.024 [0.047] -0.009 [0.043] 0.124+ [0.071] 0.112** [0.021] 918 0.85 40-44 0.032 [0.019] -0.001 [0.009] 0.032 [0.025] 0.023** [0.006] 918 0.73 45-49 0.011 [0.007] -0.002 [0.002] 0.002 [0.004] -0.004** [0.001] 918 0.59 Effect on Multiples per 1000 Deliveries Multiples per Delivery Age 20-49 20-29 30-34 Offer Mandate -0.619* -0.643** -0.668* [0.267] [0.114] [0.301] Soft Mandate 0.17 0.279 0.061 [0.281] [0.200] [0.288] Comprehensive Mandate 0.743+ -0.043 1.174** [0.428] [0.101] [0.267] Constant 10.760** 10.504** 13.080** [0.116] [0.089] [0.178] Observations 918 918 918 R-squared 0.86 0.77 0.75 Robust standard errors in brackets + significant at 10%; * significant at 5%; ** significant at 1% 35-39 -0.926* [0.450] 0.112 [0.809] 1.19 [1.089] 12.951** [0.347] 918 0.68 40-44 1.18 [1.142] 1.770* [0.676] 3.6 [2.477] 13.074** [0.888] 918 0.38 45-49 11.528 [8.104] 6.159+ [3.120] 7.248 [8.209] -9.279** [3.013] 918 0.48 Effect on Triplet+ Deliveries per Capita Triplet Deliveries per 1000 Women Age 20-49 20-29 30-34 Offer Mandate -0.002 -0.005** -0.010* [0.002] [0.002] [0.005] Soft Mandate 0.001 0.001 0.001 [0.002] [0.001] [0.006] Comprehensive Mandate 0.009** 0.002 0.031** [0.001] [0.003] [0.003] Constant 0.006** 0.016** 0.002 [0.001] [0.001] [0.002] Observations 918 918 918 R-squared 0.75 0.51 0.72 Robust standard errors in brackets + significant at 10%; * significant at 5%; ** significant at 1% 35-39 0.002 [0.003] 0.004 [0.003] 0.013** [0.003] -0.005** [0.002] 918 0.65 40-44 0.001 [0.001] -0.001 [0.001] 0.001 [0.002] -0.001** [0.000] 918 0.41 45-49 0.001* [0.001] 0 [0.000] 0 [0.000] 0 [0.000] 918 0.31 Effect on Triplets+ per 1000 Deliveries Triplets per Delivery Age 20-49 20-29 30-34 Offer Mandate -0.077* -0.059** -0.147* [0.030] [0.016] [0.055] Soft Mandate 0.025 0.008 0.022 [0.039] [0.014] [0.082] Comprehensive Mandate 0.155** 0.028* 0.284** [0.025] [0.011] [0.024] Constant 0.114** 0.143** 0.169** [0.010] [0.007] [0.022] Observations 918 918 918 R-squared 0.78 0.53 0.68 Robust standard errors in brackets + significant at 10%; * significant at 5%; ** significant at 1% 35-39 -0.019 [0.071] 0.173 [0.104] 0.245** [0.045] 0 [0.047] 918 0.53 40-44 -0.029 [0.051] -0.05 [0.159] 0.07 [0.238] 0.01 [0.058] 918 0.28 45-49 1.238+ [0.647] 1.216 [1.566] -0.571 [0.678] 2.502** [0.350] 918 0.22 Summary of Results • In states with comprehensive insurance mandates… – At the population level, delivery rates are higher, although the effect is concentrated among 30-34 year olds. – At the population level, the proportion of multiple deliveries, particularly triplets or higher order, is higher for women 20-29, 30-34, 35-39. • Effects are restricted to mandates providing comprehensive coverage. Conclusions • Generous insurance coverage of ART induces • those for whom the expected benefits of therapy are lower to pursue treatment. The result is that many women undergoing ART when insurance coverage is generous are those for whom the therapy did not increase the probability of a baby but did increase the probability of multiples. Implications Broad insurance coverage for the treatment of infertility should have mechanisms to distinguish between those for whom the benefits of treatment are high and those for whom the benefits are lower. Questions?