California minimum staffing law, nurse satisfaction, wages, and
advertisement

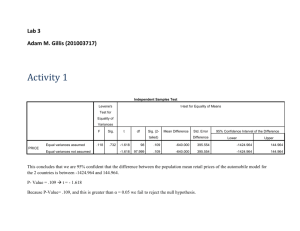
California minimum staffing law, nurse satisfaction, wages, and hours worked: Analyses of 1997, 2004, 2006, and 2008 survey data. Michelle Tellez, RN. MS. PhD. California State University, East Bay michelle.tellez@csueastbay.edu What shortage? • Nurse shortage since 1998 • Estimated to reach 340,000 by 2020 • California is 49th in RN per capita Objectives of the study 1. To describe changes in the California nurse population from 1997 to 2008. 1. 2. 3. 4. 1997 before ratios 2004 immediately after implementation 2006 mid-term effects 2008 long-term effects 2. To examine the relationship between wages, satisfaction, staffing, and year of survey on hours worked per week. Research questions ▫ What are the marginal effects of : Year of survey Staffing: RNs+LVNs+AIDEs hours per patient days Overall satisfaction with job Hourly wages ▫ on the number of hours nurses work ? Sample • California RNs who were able to respond at the margin (incrementally) to the regulatory changes taking place in the state. • Inclusion criteria were: ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ (a) that nurses be female, (b) be between the ages of 20 and 65, (c) reside in the state, (d) be working in nursing at the time of the survey, (e) have completed the California BRN questionnaire in full. Figure 1. Gender of currently working RNs residing in California, by survey year. Why just females? 100% 7.4% 7.4% 10.5% 14.4% 92.6% 92.6% 89.5% 85.7% 1997 2004 2006 2008 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% Male Female Table 2. Employment status of RNs with active California licenses residing in California, by survey year Note: 2006 and 2008 data are weighted to represent all RNs with active licenses Why just working nurses? 1997 Employed in nursing Not employed in nursing Number of respondents 2004 2006 2008 84.2% 87.5% 86.7% 86.9% 15.8% 12.5% 13.3% 13.1% 2,955 4,890 4,280 4,346 Study design • Secondary data analysis of cross-sectional survey data ▫ California Board of Registered Nursing Surveys from 1997, 2004, 2006 and 2008 ▫ California Area Resource Files of 2007 ▫ Office of Statewide Health Planning and Development (OSHPD) hospital data for 1996, 2003, 2005, 2007 Year of the survey: 1997 (proxy for before the ratio implementation), 2004 (immediately after implementation), 2006 (mid-term) and 2008 (long-te Table 1. Frequency of participants that met the inclusion criteria by survey year. Final Sample included in the study 1997 2004 Frequency (%) 2006 2008 Total 1482 2122 2332 2532 8472 (17.5) (25.0) (27.5) (29.9) (100) Model to estimate: Hours worked Demographic s Human Capital Work Characteristics Age & Age sq Level of education Setting Ethnicity Type of position Marital status Satisfaction Children Staffing Other dependents Wages Foreign or US educated Other income Region Region of the state the nurse resides Analysis 1. 2. 3. 4. Computed frequencies and means. Computed OLS regression using the model . Computed OLS with the model + interactions. Computed a 2SLS regression + instrumental variables to account for endogeneity. 5. Tested for non-linear relationships. Objective 1. 1. To describe changes in the California nurse population from 1997 to 2008. Age 25% 1990 20% 1993 1997 2004 15% 2006 2008 10% 5% 0% Under 30 30-34 35-39 40-44 45-49 50-54 55-59 60-64 65 or older Race and Ethnicity Racial/Ethnic backgrounds White, not Hispanic 1997 2004 2006 2008 64.5% 61.5% 62.0% 55.5% Hispanic 4.9% 6.5% 5.7% 8.3% Black/African American 4.8% 3.5% 4.6% 4.1% Asians 22.8% 25.3% 24.5% 28.8% Other 2.9% 3.2% 3.2% 3.4% Number of Cases 2,458 2,948 3,712 4,756 Marital status 1997 2004 2006 2008 Never married 13.5% 12.3% 12.6% 13.9% Married 66.5% 68.2% 66.9% 67.6% Separated or divorced 17.6% 17.0% 16.7% 15.5% Widowed 2.4% 2.6% 3.8% 2.9% Number of Cases 2,463 2,946 3,719 4,046 Children living at home None One or more Number of Cases 1997 38.2% 61.8% 2,297 2004 45.7% 54.3% 2,933 2006 53.1% 46.9% 3,406 2008 49.2% 50.8% 4,153 Other dependents 100% 90% 6.2% 5.3% 6.9% 15.8% 16.2% 14.9% 23.9% 80% 70% 4 or more people 60% 3 people 2 people 50% 1 person 40% 81.2% 76.1% 74.3% 73.8% 73.7% 30% Any None 20% 10% 0% 1997 2004 2006 2008 Level of education 100% 6.8% 8.5% 90% 13.2% 12.2% 80% 38.0% 70% 38.1% 40.9% 41.6% 60% Master's or Doctorate Degree Baccalaureate degree 50% Associate degree 40% 36.7% 30% 39.7% 36.3% 36.7% 9.6% 9.5% 2006 2008 20% 26.6% 10% 18.4% 13.7% 0% 1997 2004 Diploma program Location of education 1997 2004 2006 2008 California 55.1% 58.3% 56.7% 55.1% Other States 24.0% 22.2% 25.6% 21.4% International 20.9% 19.4% 17.8% 23.5% Number of respondents 2,366 2,894 3,732 4,076 Location of employment 1997 2004 2006 2008 57.4% 57.7% 8.0% 7.5% 7.4% 9.0% 10.8% 12.6% 16.0% 6.0% 9.9% 10.5% 7.7% Other 10.9% 10.8% 12.9% 11.9% Number of Cases 2,444 3,661 Acute hospital 60.2% 60.9% Nursing homes/Home care/Skilled nursing Ambulatory care 13.9% Department of Public Health 2,971 4,080 Type of position 1997 2004 2006 2008 Direct patient care provider/staff nurse 62.1% 57.3% 65.1% 63.5% Management 16.3% 19.2% 14.6% 18.3% Advance Practice Nursing 6.7% 6.5% 6.9% 5.9% Other 15.1% 16.9% 13.7% 13.7% Number of cases 2,375 2,925 3,675 4,108 Satisfaction 1997 2004 2006 2008 Physical work environment 3.60 3.45 3.57 3.59 Your job overall 3.95 3.94 4.05 4.14 * 3.83 3.96 The nursing profession overall Annual income from nursing 1997 2004 2006 2008 $20,000 or less 9.5% 4.9% 4.6% 2.4% $20,001 to $40,000 20.9% 12.1% 7.6% 5.3% $40,001 to $60,000 34.5% 34.4% 20.3% 16.0% $60,001 to $80,000 27.1% 28.6% 33.4% 30.8% $80,001 to $100,000 0% 13.0% 20.8% 25.7% $100,001 to $125,000 0% 3.6% 9.1% 13.2% More than $125,000 0% 1.1% 4.1% 6.6% $45,073 $59,937 $73,542 $81,428 2,420 2,885 3,447 3,728 Mean Annual Income Number of Cases Average hourly wages RNs in the survey 1997 2004 2006 2008 Mean in hourly $34.67 wages $38.60 $44.80 $46.97 Number of cases 2,122 2,332 2,536 1,482 Average hours worked per week 1997 2004 2006 2008 Mean in hours 36.3 35.6 35.2 36.5 Standard deviation 11.0 11.9 * * Number of cases 2,470 3,064 3,510 3,984 Objective 2. • To examine the relationship between wages, satisfaction, staffing , year of survey and the number of hours worked. Overall Satisfaction with job Dv: Ave hours worked per week OLS β (Robust Std Er) OLS with Interactions β (Robust Std Er) 2SLS with Interactions and Ivs β (Robust Std Er) All RNs Not sig Not sig Not sig Acute care RNs Not sig Not sig Not sig 0.371* (0.160) Not sig Not sig Acute care in direct pt care positions Note: age, age squared, ethnicity, marital status, children, other dependents, level of education, location of education, location of employment, position held, region of residence, staffing, other income, and wages were included in the first 2 equations. The 3rd equation was conducted in 2 steps. First step omitted. Overall satisfaction DV: Hours worked All RNs Satisfaction Satisfaction squared Satisfaction Categories (2008) Neither vs Dissatisfied Satisfied vs Dissatisfied Very Satisfied vs Disssatis. OLS OLS Not sig -2.528** (0.933) -.246 (0.441) 0.162 (0.162) Note: age, age squared, ethnicity, marital status, children, other dependents, level of education, location of education, location of employment, position held, region of residence, staffing, other income, and wages were included in the equations. Staffing: RNs+LVNs+ Aides hours per pt day group OLS β (Robust Std Er) OLS with Interactions β (Robust Std Er) 2SLS with Interactions and IVs β (Robust Std Er) All RNs Not sig Not sig Not sig Acute care RNs Staffing*2004 Staffing*2006 Staffing*2008 Not sig Not sig -4.405 (2.329) 4.010 (2.216) 4.515 (2.661) 5.099*(2.459 Acute care in direct pt care positions Staffing*2004 Staffing*2006 Staffing*2008 Not sig Not sig -4.088* (2.020) 4.380* (2.021) 5.067* (2.332) 4.570* (2.115) Staffing Ave. Hours worked All RNs Staffing Staffing Squared Staffing Categories OLS OLS β β (Robust Std Er) (Robust Std Er) Not sig Not enough people in the lower categories Note: age, age squared, ethnicity, marital status, children, other dependents, level of education, location of education, location of employment, position held, region of residence, staffing, other income, and wages were included in the equations. DV: Ave. Hours worked per week OLS β (Robust Std Er) OLS with Interactions β (Robust Std Er) All RNs Wage*2004 Wage*2006 Wage *2008 -0.194** (0.012) -0.139** (0.022) -0.104** (0.029) -0.039 (0.027) -0.054* (0.023) Acute care RNs Wage*2004 Wage*2006 Wage *2008 -0.206** (0.018) -0.144** (0.034) -0.100* (0.040) -0.054 (0.046) -0.064 (0.034)) -0.741* (0.361) 0.070 (0.230) 0.428 (0.257) 0.496 (0.285) -0.192** (0.019) -0.136** (0.031) -0.099* (0.044) -0.066 (0.045) -0.046 (0.524) -0.575* (0.260) 0.075 (0.188) 0.219 (0.206) 0.408 (0.210) Acute care + direct pt care Wage*2004 Wage*2006 Wage *2008 2SLS with Interactions and Ivs β (Robust Std Er) Not sig Tested for non-linear relationship DV: Hours worked All RNs 1997-2008 Wage Wage squared Wage Categories $25-$29.99 vs <$25 $30-$34.99 vs <$25 $35-$39.99 vs <$25 $40-$44.99 vs <$25 $45-$49.99 vs <$25 $50-$54.99 vs <$25 $55-$120. vs <$25 OLS Wage & Wage squared OLS Wage Categories -0108** (0.028) -0.0008** (0.0003) -0.683 (0.459) -1.975** (0.403) -1.933** (0.419) -3.106** (0.408) -3.898** (0.445) -5.424** (0.477) -8.190** (0.442) Note: age, age squared, ethnicity, marital status, children, other dependents, level of education, location of education, location of employment, position held, region of residence, staffing, other income, and wages were included in the equations. Wage effects by year of survey 2 0 $25-29.99 $30-34.99 $35-39.99 $40-44.99 $45-49.99 $50-54.99 Wage effects -2 -4 -$55 120.00 1997 2004 -6 2006 2008 -8 -10 -12 -14 Wage categoreis Year of survey DV: Ave. hours worked per week OLS All RNs 2004 2006 2008 -0.422 (0.424) 0.886 (0.468) 1.863** (0.505) Acute care 2004 2006 2008 -1.102 (0.551) 0.519 (0.626) 1.450* (0.650) Acute + direct pt care 2004 0.450 (0.559) 2006 1.55* (0.702) 2008 1.850* (0.685) Note: age, age squared, ethnicity, marital status, children, other dependents, level of education, location of education, location of employment, position held, region of residence, staffing, other income, and wages were included in the equations. Conclusion • • • • Satisfaction – already max out. Staffing – positive effect to staff nurses Wages – afford nurses to work fewer hours Ratios law – improve the workload and helped maintain the hours worked stable. Thank you!