Chemistry 114 Fourth Hour Exam Name:____________ Please show all work for partial credit
advertisement

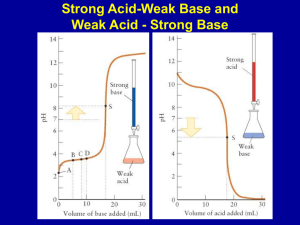
Chemistry 114 Fourth Hour Exam Name:____________ (4 points) Please show all work for partial credit 1. (12 points) Calculate the pH of the following solutions A. 1.45x10-5M HCl [H+]=1.45x10-5 pH=-log(1.45x10-5) =-(-4.84) =4.84 B. 1.45x10-5 M Fe(OH)3 1.45x10-5M Fe(OH)3 x (3 moles OH-/1 mole Fe(OH)3) =4.35x10-5 OHpOH = -log(4.35x10-5) = 4.36 pH + pOH =14; pH= 14-4.36 pH=9.64 C. 1.45x10-5M Nitrous Acid (KA = 5.6x10-4) Ka=[A-][H+]/[HA] 5.6x10-4 = X2/(1.45x10-5 -X) Assume ~ X2/1.45x10-5 X2 = 5.6x10-4 x 1.45x10-5 X = sqrt(8.12x10-9) X =9.01x10-5, pH =-log(9.01x10-5) = 4.05 D. For a bonus point, What is the formula of nitrous acid HNO2 2. (12 Points) Identify the following compounds as : SA - Strong Acid, WA- Weak Acid, NNeutral, WB - Weak Base, or SB - Strong base. HClO4 ___SA_______ NH3 ____WB______ NH4NO3 ___WA_______ SeO2 ___A (S or W?)_______ BaO __SB________ Mn(NO3)5__A(S or W?)________ 1 3A. (5 points) Sketch the titration curve for a weak acid being titrated with a strong base. On this curve identify the following features: X-Axis, Y- Axis, Buffer region, Stoichiometric point (or equivalence point), point where pH = pKa. Should look like figure 21.9 from your text (1 point) Is the pH at the equivalence point <,=,or > 7? B. (5 points)Sketch the titration curve for a weak base being titrated with a strong acid. On this curve identify the following features: X-Axis, Y- Axis, Buffer region, Stoichiometric point (or equivalence point), point where pH = pKa. Should look like figure 21.11 from your text (1 point) Is the pH at the equivalence point <, =, or > 7? 4.Define the following terms: Conjugate base What remains of an acid after it donates its proton. Second law of thermodynamics The entropy of the universe is always increasing. Thermal disorder Entropy derived from the distribution of energy states at a given temperature Entropy-favored reaction A reaction where ÄS is positiveÄ van’t Hoff Equation Hydrocarbon A compound that contains only hydrogen and carbon. 2 5. (12 points) Does S increase, decrease, or remain the same in the following reactions: H2O (l) 6H2O (s) ___decrease_______ 4Al(s) + 3O2(g) 6 2Al2O3 (s) __decrease________ 2C2H6(g) + 5O2(g)64CO2(g) + 6H2O(g)_increase_________ C2H6(g)6C2H4(g) + H2(g) __increase________ 2H2(g) +O2(g) 62H2O(g)__decrease________ Cu2+(aq) + 6NH3(aq) 6Cu(NH3)6(aq) _decrease_________ 6. (12 points) When will the following process be spontaneous? A. Br2(l) 6Br2 (g) (ÄH is positive) Never At low T At High T Always (Circle one) Why?ÄS+,ÄH+ Will be favorable at High T where favorable ÄS term is maximal B. Never CH4(g) + 2O2(g) 6CO2(g) + H2O(l) (ÄH is negative) At low T At High T Always (Circle one) Why?__ÄS-,ÄH- Will be favorable at Low where unfavorable S term is a minimum C. Never 3O2(g) 6 2O3 (g) (ÄH is positive) At low T At High T Always (Circle one) Why? Both ÄH and ÄS are unfavorable at all T D. Never NaOH(s) 6Na+(aq) + OH-(aq) (ÄH is positive) At low T At High T Always Both ÄH and ÄS are unfavorable at all T 3 (Circle one) 7A. (4 points) ÄGo for the reaction CH3COO-(aq) + H2O(l) 6 CH3COOH(aq) + OH-(aq) is 27.1 kJ/mol. What is the K for this reaction at 25oC ? ÄG0=-RTlnK 27100 J = -8.315 x 298 x ln(K) -27100/(8.314x298) = lnK -10.94=lnK K=e-10.94 = 1.77x10-5 B. (4 points) The reaction CH3COO-(aq) + H3O+ (aq) 6CH3COOH(aq) + H2O(l) has a K of 5700. What is the ÄGo for this reaction at 250C ? ÄG0=-RTlnK X = -8.315 x 298 x ln(5700) X=-8.314x298x8.65 = -21,400J or -21.4 kJ C. (4 points) The reaction A(aq) + B(aq) 6C(aq) has a ÄGo of +10 kJ/mol. What is the ÄG for this reaction when the concentrations of A, B, and C are all 5M and T = 25oC ? ÄGRXN = ÄG0 + RTlnQ =10,000 + 8.314(298)ln(5/5A5) =10,000 + 2478ln(.2) =10,000 + -3990 =6,010 J or 6.01 kJ 8. There are nine different structural isomers for Heptane (C7H16). You get 6 points for drawing 6 different structural isomers for this compound and 6 more points for naming them correctly. 4


![MA1124 Assignment3 [due Monday 2 February, 2015]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/010730345_1-77978f6f6a108f3caa941354ea8099bb-300x300.png)