Study Guide Chapter 16 The Citric Acid Cycle
advertisement

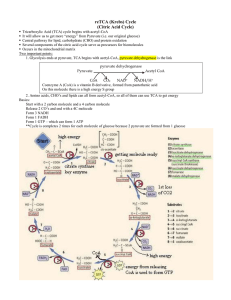
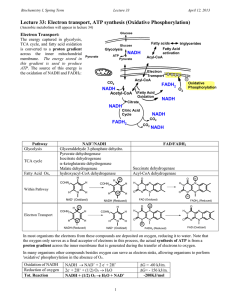
Study Guide Chapter 16 The Citric Acid Cycle 1. Trace out the citric acid cycle from pyruvate to acetyl CoA and through the complete cycle. In the cycle be able to name and give the structure of every intermediate, give the name of every enzyme, locate all steps where NADH, FADH2, or ATP are produced. Locate the reactions where you have the most favorable )G, and the reactions that are control points. 2. Discuss the mechanism of the Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. What enzymes are involved, what cofactors are involved, etc. 3. Give the structure for the active part of NAD+/NADH, and FAD/FADH@/FADH2 how are these coenzymes similar and different from each other. What are the vitamins from which we obtain these cofactors 4. Give the structure for the active part of CoASH/AcetylCoA, Lipopic acid, TPP, and biotin. Which of these are derived from vitamins, and what are the vitamins. What is the function of each cofactor. Give an example of an enzyme in which each is used. 5. How is the "ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex similar to and different from the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex? 6. Discuss the mechanism of the succinyl Ca-A synthase reaction. 7. Put the whole thing together. Go from Glucose to CO2, emphasizing just the steps where ATP NADH and FADH2 are formed. Can you account for all 32 of the ATP’s 8. What is anabolism, catabolism, an amphibolic pathway, an anaplerotic reaction? 9. You don’t need to know all the details, but on your diagram of the TCA cycle can you point out places where TCA intermediates are siphoned off to make other compounds? Where are places in the cycle where you can replenish TCA intermediates? 10. Where are the major control points for the TCA cycle, and what are some of the control mechanisms used at each point. 11. What parts of the TCA cycle are performed in the cytoplasm, in the mitochondiral matirx, in the mitochondiral membrane. What intermediates have to past into and out of the mitochondria? 12. The Glyoxylate cycle was not covered this year so there are no questions on this section.